3. 1 Introduction - Nodal analysis : based on a systematic application
advertisement

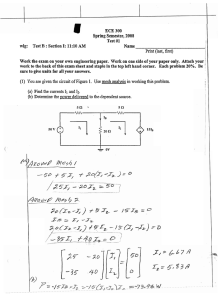
Chungbuk National University Electric Engineering – Circuit Theory I The first semester, 2010 Chapter 3- Methods of Analysis Written by Ohmin Kwon 3. 1 Introduction - Nodal analysis : based on a systematic application of KCL - Mesh analysis : based on a systematic application of KVL 3.2 Nodal Analysis - Nodal analysis : a general procedure for analyzing circuits using node voltages as the circuit variables. Steps to Determine Node Voltages 1. Select a node as the reference node. Assign voltages v1 , v2 ,..., vn −1 to the remaining n-1 nodes. The voltages are referenced with respect to the reference node. 2. Apply KCL to each of the n-1 nonreference nodes. Use Ohm’s law to express the branch currents in terms of node voltages. 3. Solve the resulting simultaneous equations to obtain the unknown node voltages. <Fig. 3.1> Common symbols for indicating a reference node, (a) common ground, (b) ground, (c) chassis ground. Current flows from a higher potential to a lower potential in a resistor. i= vhigher − vlower R Example 3.2 Calculate the node voltages Chungbuk National University Electric Engineering – Circuit Theory I The first semester, 2010 Chapter 3- Methods of Analysis Written by Ohmin Kwon 3.3 Nodes Analysis with Voltage Sources <Fig. 3.7> A circuit with a supernode Example 3.4 Find the node voltages Chungbuk National University Electric Engineering – Circuit Theory I The first semester, 2010 Chapter 3- Methods of Analysis Written by Ohmin Kwon 3.4. Mesh Analysis - General procedure for analyzing circuits using mesh currents as the circuit variables - Only applicable to a circuit that is planar(No branch crossing) <Fig.3.15> Planar circuit <Fig.3.16> A nonplanar circuit Chungbuk National University Electric Engineering – Circuit Theory I The first semester, 2010 Chapter 3- Methods of Analysis Written by Ohmin Kwon Steps to Determine Mesh Currents: 1. Assign mesh currents i1 , i2 ,..., in to the n meshes. 2. Apply KVL to each of the n meshes. Use Ohm’s law to express the voltages in terms of the mesh currents 3. Solve the resulting n simultaneous equations to get the mesh currents <Fig.3.17> A circuit with two meshes. Example 3.6 Find I o by using mesh analysis Chungbuk National University Electric Engineering – Circuit Theory I The first semester, 2010 Chapter 3- Methods of Analysis Written by Ohmin Kwon 3.5 Mesh Analysis with Current Sources <Fig.3.23> Two meshes having a current source in common, (b) a supermesh, created by exclusing the current source. Example 3.7 Find i1 and i4 Chungbuk National University Electric Engineering – Circuit Theory I The first semester, 2010 Chapter 3- Methods of Analysis Written by Ohmin Kwon 3.6 Nodal and Mesh Analyses by Inspection ⎡G1 + G2 ⎢ −G 2 ⎣ ⎡ R1 + R3 ⎢ −R 3 ⎣ −G2 ⎤ ⎡ v1 ⎤ ⎡ I1 − I 2 ⎤ = G2 + G3 ⎥⎦ ⎢⎣v2 ⎥⎦ ⎢⎣ I 2 ⎥⎦ − R3 ⎤ ⎡ i1 ⎤ ⎡ v1 ⎤ = R2 + R3 ⎥⎦ ⎢⎣i2 ⎥⎦ ⎢⎣ −v2 ⎥⎦ See Example 3.8 and 3.9 3.7 Nodal Versus Mesh Analysis - Mesh analysis : series-connected elements, voltage sources, or supermehes(Only method in analyzing transistor circuits) - Nodal analysis : parallel-connected elements, current sources, or supernodes(Only method in analyzing OP amp)