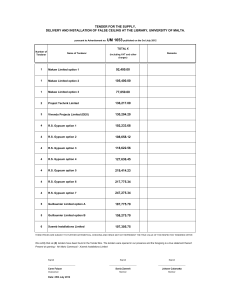
Abuse and Impact Resistant Gypsum
advertisement

2001 Rexford Road Charlotte, NC 28211 704-365-7300 ngcaia@nationalgypsum.com © Ron Blank & Associates, Inc. 2012 Abuse and Impact Resistant Gypsum: Stronger and Safer Walls Please note: you will need to complete the conclusion quiz online at RonBlank.com to receive credit Course #: NGC09K An AIA Continuing Education Program Credit for this course is 1 AIA HSW CE Hour An American Institute of Architects (AIA) Continuing Education Program Approved Promotional Statement: Ron Blank & Associates, Inc. is a registered provider with The American Institute of Architects Continuing Education System. Credit earned upon completion of this program will be reported to CES Records for AIA members. Certificates of Completion are available for all course participants upon completion of the course conclusion quiz with +80%. Please view the following slide for more information on Certificates of Completion through RBA This program is registered with the AIA/CES for continuing professional education. As such, it does not include content that may be deemed or construed to be an approval or endorsement by the AIA or Ron Blank & Associates, Inc. of any material of construction or any method or manner of handling, using, distributing, or dealing in any material or product. An American Institute of Architects (AIA) Continuing Education Program Course Format: This is a structured, web-based, self study course with a final exam. Course Credit: 1 AIA Health Safety & Welfare (HSW) CE Hour Completion Certificate: A confirmation is sent to you by email and you can print one upon successful completion of a course or from your RonBlank.com transcript. If you have any difficulties printing or receiving your Certificate please send requests to certificate@ronblank.com Design professionals, please remember to print or save your certificate of completion after successfully completing a course conclusion quiz. Email confirmations will be sent to the email address you have provided in your RonBlank.com account. Course Description Analyze the different types of gypsum technologies in terms of composition, characteristics, and testing. Discover the benefits of impact resistant gypsum in terms of performance, application, and cost. Learning Objectives Define key terms associated with gypsum and wall surfaces. Discuss ASTM C 1629 classification system for abuse resistant panels and ASTM test methods. Compare and contrast the performance of different gypsum board technologies. Discuss the installation process, performance features, various applications, and cost benefits of impact resistant gypsum. Definition and Product Types Win or Lose… Can the walls take the team? Introduction Abuse and Impact Resistant products were introduced in mid-90’s as a lower cost alternative to Cement Masonry Units (CMU). Enhancements such as mold and moisture resistance were added in 2004. In school districts across the country , these products have replaced CMU for most walls. Architects Still Ask What’s the difference between abuse and impact resistance? Definitions Abuse Resistance Designed for use in wall assembly areas where surface abrasion is a concern -Surface of the board Impact Resistance Designed for use where abuse and impact resistance is needed -Surface of the board -Intrusion into the wall cavity Types of Damage Surface damage: Abrasion or scuffing due to high traffic during standard use and indentation of the wall surface from low-energy or occasional impact Penetration: Damage due to high-energy or continual impact that breaks into the stud cavity Understand the Products Three different types of gypsum board discussed here: Impact Resistant Gypsum Abuse Resistant Gypsum Standard Gypsum Regular Gypsum Fiberboard 5/8 Type X (baseline) Enhanced Paper Enhanced Gypsum Core Gypsum Fiberboard with Fiberglass Mesh Enhanced Paper Enhanced Gypsum Core with Fiberglass Mesh Fiberglass faced – Enhanced Core Fiberglass faced – Enhanced Core Abuse Resistant (AR) Gypsum Used where surface damage is a concern Gypsum Fiberboard Enhanced with manufacturer’s proprietary slurry of gypsum particles and cellulose fibers Abuse Resistant Gypsum Abuse-resistant gypsum wallboard features an enhanced gypsum core wrapped with heavy abrasion resistant paper or abrasion resistant fiberglass facing Impact Resistant (IR) Gypsum Used where damage of the cavity is a concern Gypsum Fiberboard Enhanced with manufacturer’s proprietary slurry of gypsum particles and cellulose fibers and reinforced with fiberglass mesh Fiberglass Mesh Impact Resistant Gypsum Impact-resistant gypsum wallboard features an enhanced gypsum core wrapped with heavy abrasion resistant paper or abrasion resistant fiberglass facing and reinforced with fiberglass mesh Fiberglass Mesh ASTM C 1629 Standard Classification for Abuse-Resistant Non-decorated Interior Gypsum Panel Products and Fiber-Reinforced Cement Panels Issued in January 2006 ASTM C 1629 This standard consists of four testing methods ASTM D 4977 Surface Abrasion ASTM E 695 Soft Body Impact Test ASTM D 5420 Gardner Impact Surface Indentation Resistance Applicable only on Impact Resistant products Annex A1 Hard Body Impact Test ASTM C 1629 - Classifications and Performance Requirements ASTM D 4977 ASTM D 5420 ASTM E 695 Annex A1 Surface Abrasion Surface Indentation Resistance Soft Body Impact Hard Body Impact Classification Level Abraded Depth Maximum Indentation Maximum Impact Minimum Impact Minimum 1 0.126" 0.150" 90 ft-lbs 50 ft-lbs 2 0.059" 0.100" 195 ft-lbs 100 ft-lbs 3 0.010" 0.050" 300 ft-lbs 150 ft-lbs See next slide for description ASTM C 1629 - Classifications and Performance Requirements Each classification level is based on specific minimum or maximum results depending on the test. A product may meet Level 1 on one type of test and Level 3 on another test. Each performance characteristic should be specified based upon the desired classification level. Note: The minimum level for the Hard Body Test is not a lot better than standard gypsum (35 lbs). A Level 1 result on the Hard Body Test is not a very impact resistant product. ASTM C 1629 - Classification Levels Each abuse/impact property of abuse resistant wall panels is divided into three classification levels. Level 1: Minimum performance that meets the standard Level 2: Mid-range performance Level 3: Highest performance The test methods specified are utilized to establish the abuse-resistance classification of an abuse resistant wall panel. Each classification level requires a minimum overall specified performance. Any classified abuse resistant wall panel can be used at a classification level which is rated lower than the highest level qualified. “This standard will enable manufacturers to quantify their products' performance.” -Robert Wessel ASTM C11 member and assistant executive director, Gypsum Association ASTM C 1629 Test Methods and Performance Comparisons Surface Abrasion - ASTM D 4977 Purpose: Measure the ability of a wall system to withstand scuffs and abrasions ASTM D 4977 Surface Abrasion Results 5/8” (15.9mm) Type X Gypsum Board Surface Abrasion - ASTM D 4977 0.126” 0.576” 0.126” - Classification Level 1 maximum 0.576” - Type X gypsum board Over 1/2” is worn away on a 5/8” thick board Third Party Testing by H.P. White Laboratory 5/8” Abraded Depth ASTM D 4977 Surface Abrasion Results Abuse Resistant Products Type X Gypsum Board Fiberglass Faced –Enhanced Gypsum Core Gypsum Fiberboard Enhanced Paper – Enhanced Gypsum Core Result 0.576 0.009 0.284 0.009 Classification NA 3 NA 3 Level 1 maximum abraded depth = 0.126” Third Party Testing by H.P. White Laboratory and Timber Products Inspection Note that the Gypsum Fiberboard does perform much better than Type X, it does not meet the minimum for Level 1. ASTM D 4977 Surface Abrasion Results Impact Resistant Products Surface Indentation Resistance - ASTM D 5420 Gardner Impact Purpose: Measure gypsum board’s resistance to dents ASTM D 5420 Surface Indentation Results Abuse Resistant Products Type X Gypsum Board Fiberglass Faced –Enhanced Gypsum Core Gypsum Fiberboard Enhanced Paper – Enhanced Gypsum Core Result 0.230 0.132 0.11 0.132 Classification NA 1 1 1 Note: Level 1 maximum indentation = 0.150” Third Party Testing by H.P. White Laboratory and Timber Products Inspection ASTM D 5420 Surface Indentation Results Impact Resistant Products Type X Gypsum Board Fiberglass Faced – Enhanced Gypsum Core with Fiberglass Mesh Gypsum Fiberboard with Fiberglass Mesh Enhanced Paper – Enhanced Gypsum Core with Fiberglass Mesh Result 0.230 0.129 0.11 0.129 Classification NA 1 1 1 Note: Level 1 maximum indentation = 0.150” Third Party Testing by H.P. White Laboratory and Timber Products Inspection Soft Body Impact Test - ASTM E 695 Purpose: Measure the ability of a wall system to withstand single impact force from a small object ASTM E 695 Soft Body Impact Results Abuse Resistant Products Type X Gypsum Board Fiberglass Faced –Enhanced Gypsum Core Gypsum Fiberboard Enhanced Paper – Enhanced Gypsum Core Result 120 ft - lbs 270 ft - lbs 180 ft - lbs 210 ft - lbs Classification 1 2 1 2 Level 1 Soft Body Minimum = 90 ft-lbs Third Party Testing by H.P. White Laboratory and Timber Products Inspection ASTM E 695 Soft Body Impact Results Impact Resistant Products Type X Gypsum Board Fiberglass Faced – Enhanced Gypsum Core with Fiberglass Mesh Enhanced Paper – Gypsum Enhanced Fiberboard with Gypsum Core Fiberglass Mesh Result 120 ft - lbs >540ft - lbs 210 ft - lbs >540 ft - lbs Classification 1 3 2 3 with Fiberglass Mesh Level 1 Soft Body Minimum = 90 ft-lbs Third Party Testing by H.P. White Laboratory and Timber Products Inspection Hard Body Impact Test - Annex A1 Purpose: Measure resistance to penetration by a hard object, such as a baseball bat or a boot heel Hard Body Impact -Annex 1 Results Abuse Resistant Products Type X Gypsum Board Fiberglas Faced –Enhanced Gypsum Core Gypsum Fiberboard Enhanced Paper – Enhanced Gypsum Core Result NA NA NA NA Classification NA NA NA NA Hard Body Impact Test - Not applicable to Abuse Resistant products. Some manufacturer’s will test and publish a result for abuse resistant products. This is not part the test standard. Hard Body Impact -Annex 1 Results Impact Resistant Products Type X Gypsum Board Fiberglass Faced – Enhanced Gypsum Core with Fiberglass Mesh Gypsum Fiberboard with Fiberglass Mesh Enhanced Paper – Enhanced Gypsum Core with Fiberglass Mesh Result 35 ft - lbs 115 ft - lbs 175 ft - lbs 175 ft - lbs Classification NA 2 3 3 Level 1 Hard Body Minimum = 50 ft-lbs Third Party Testing by H.P. White Laboratory and Timber Products Inspection Fiberglass mesh increases performance on this test. Abuse Resistant Comparison ASTM D 4977 ASTM D 5420 ASTM E 695 Annex A1 Surface Abrasion Surface Indentation Resistance Soft Body Impact Test Hard Body Impact Test Abraded Depth Maximum Indentation Maximum Impact Minimum Impact Minimum 5/8" Type X Gypsum Board N/A N/A 1 N/A Gypsum Fiberboard N/A 1 1 N/A Enhanced Gypsum Core 3 1 2 N/A Classification Level Impact Resistant Comparison ASTM D 4977 ASTM D 5420 ASTM E 695 Annex A1 Surface Abrasion Surface Indentation Resistance Soft Body Impact Test Hard Body Impact Test Abraded Depth Maximum Indentation Maximum Impact Minimum Impact Minimum 5/8" Type X Gypsum Board N/A N/A 1 N/A Gypsum Fiberboard w/ Fiberglass Mesh N/A 1 3 3 Enhanced Gypsum Core w/ Fiberglass Mesh 3 1 2-3 3 Classification Level Frequently Asked Questions Frequently Asked Questions Why specify abuse and impact resistant products? How does it install? What other properties are important? Where do I specify these products? How do I specify these products? How much does it cost? Why Specify? Lower cost alternative to CMU and OSB Speed of construction Lighter weight construction More decorative finish options Use conventional building materials Ease of maintenance Installation and Finishing Guidelines Gypsum Fiberboard Enhanced Core Products Control joints required when adjacent to regular gypsum board No control joints needed when adjacent to regular gypsum board Setting type joint compounds required Drying type joint compound can be used Skim coat required /suggested Finishes like regular gypsum board Skim coat required/suggested for fiberglass faced products Paper or Fiberglass Faced? Paper Faced Not warranted for pre-rock installations No exposure warranty Skim coat not required Fiberglass Faced Warranted for pre-rock installations 12 month exposure warranty Skim coat required/ suggested Pre-rock is a term contractors use when interior gypsum products are installed prior to the building being dried in. High Performance Features Many abuse and impact resistant products offer additional features. Fire Rated Assemblies Indoor Air Quality Mold Resistance per ASTM D 3273 Paper Tape (without any enhanced mold resistance) can be used in conjunction with a mold resistant gypsum board and a mold resistant joint compound to achieve a mold resistant system. Check with the manufacturer as to whether a tested system is available. Abuse Resistant Applications Areas prone to surface abrasion and indentation Residential: Institutional: Commercial: Stairwells Garages Hospital observation rooms Operating rooms Cafeterias Dormitories Day care centers Corridors Public areas Lobbies Entries Impact Resistant Applications Areas prone to stud cavity penetration Residential: Institutional: Commercial: Multi-family housing Classrooms Stairwells Correctional Facilities Corridors Gymnasiums Psychiatric wards Workshops Mailrooms Loading areas Heavily trafficked corridors Public areas Impact Resistant Shaft Wall On August 26, 2006, the City of New York amended Section 1 of the building code. The new section amended title 1 of the Rules of the City of New York, section 32-05 Impact Resistant Stair and Elevator Enclosures. This new section was a direct result of the lessons learned after the World Trade Center disaster. The New York City Department of Buildings developed the requirement, and in 2009 the International Building Code (IBC) adopted a similar requirement, Section 403.2.3 Structural Integrity of exit enclosures and elevator hoist way enclosures. For more detailed design and code information, please refer to the appropriate sections of the IBC Code or the building code that governs your project. The code requirement pertains to specific building types and sets forth minimum design criteria for shaftwall impact-resistance. This is based on performance testing per ASTM C 1629 and C 1629M – Standard Classification for Abuse Resistant Non-Decorated Interior Gypsum Panel Products and Fiber Reinforced Cement Panels. In 2006, the gypsum industry adopted ASTM C 1629 as the testing standard for measuring the performance of all abuse and impact panels. Impact Resistant Shaft Wall 4” 20 Gauge J-Track 4” 20 Gauge C-T Stud 1” Type X Shaftliner Base Layer 5/8” Type X Impact Resistant Gypsum Board 1” Screws spaced 14” o.c. Face Layer 5/8” Type X Gypsum Board 1 5/8” Screws spaced 12” o.c. How to Specify Specs should include separate sections Abuse Resistant Gypsum Impact Resistant Gypsum Specify Classification Level for each ASTM test Abuse Resistant section should not include Hard Body Impact test May include other performance characteristics, such as mold resistance or GREENGUARD certification Specify by ASTM C 1629 Classification Level TEST DESCRIPTION ABUSE IMPACT ASTM D 4977 Surface Abrasion 1–3 1–3 ASTM D 5420 Surface Indentation 1 1 ASTM E695 Soft Body Impact 1–2 2–3 ASTM C 1629 Hard Body Impact NA 2–3 Products are classified on each test result and may have varying levels of performance Selector Guide Activity Level Type of Damage Suggested Product Moderate Duty Incidental surface and indentation damage. Standard Type X Abuse Resistant Medium Duty Resistance to surface damage from people and objects. Usually unintentional. Abuse Resistant – Impact Resistant Heavy Duty Resistance to heavy surface, indentation and penetration damage form people and objects. Usually intentional. Impact Resistant Extreme Duty Extreme levels of surface and impact damage. Usually intentional. Double Layer Impact Resistant Extreme Duty Hard Body Impact Test Level 3 = 150 ft. lbs Double Layer >260 ft. lbs. Steel Studs Type S Screws Impact Resistant Gypsum Board Impact Resistant Gypsum Board Cost Comparison $10.00 $9.00 $8.00 $0.00 8” CMU 6” CMU $1.00 Type X & ½” Plywood $2.00 IR Fiberglass Type X $3.00 AR Type X $4.00 5/8” Type X $5.00 IR Type X $6.00 AR Fiberglass Type X $7.00 Gypsum walls based on 3 5/8” 20 gauge – Level 4 Finish CMU ( hollow core) wall, tooled joints, not reinforced Level 5 finish recommended for optimal appearance on fiberglass faced products Source: RS Means 2011 Cost Data and manufacturer’s average sales price for various gypsum products Abuse Resistant Options Indentation Gypsum Fiberboard Abuse-Resistant Gypsum Surface Abrasion Abuse-Resistant Gypsum Impact Resistant Options Resist Stud Cavity Penetration Gypsum Fiberboard with Fiberglass Mesh Abuse and Impact Resistant Gypsum Wallboard with Fiberglass Mesh Fiberglass Mesh Reinforcement Surface Abrasion Abuse and Impact Resistant Gypsum Wallboard with Fiberglass Mesh Heavy Abrasion Mold and Moisture Resistant Face Paper Enhanced Mold and Moisture Resistant Type X Core Heavy Mold and Moisture Resistant Back Paper Note: For metal studs, specify a minimum of 20 gauge spaced a maximum of 16" on center. Test results based on vertical installation. Fiberglass Mesh Reinforcement Course Summary Define key terms associated with gypsum and wall surfaces. Discuss ASTM C 1629 classification system for abuse resistant panels and ASTM test methods. Compare and contrast the performance of different gypsum board technologies. Discuss the installation process, performance features, various applications, and cost benefits of impact resistant gypsum. 2001 Rexford Road Charlotte, NC 28211 704-365-7300 ngcaia@nationalgypsum.com © Ron Blank & Associates, Inc. 2012 Abuse and Impact Resistant Gypsum: Stronger and Safer Walls Please note: you will need to complete the conclusion quiz online at RonBlank.com to receive credit Course #: NGC09K An AIA Continuing Education Program Credit for this course is 1 AIA HSW CE Hour