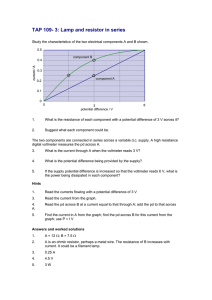
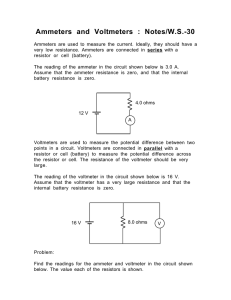
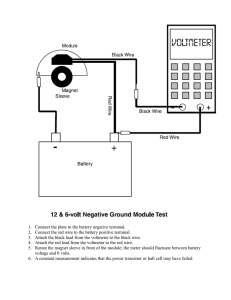
Capacitor discharge
advertisement

16:220 - Internal Resistance 1 Laboratory 6 INTERNAL RESISTANCE Objective: Measure the internal resistance of a battery and a voltmeter and determine when the effect of the internal resistance is significant. Introduction: Ideal components (batteries, voltmeters, etc.) have no internal resistance; however, real components have an internal resistance that affects its performance in some (but not all) applications. Apparatus: Battery, resistors, 0-10 K variable resistor, microvoltmeter, digital voltmeter (DVM) A. Internal Resistance of a Voltmeter Introduction: An ideal voltmeter draws no current; however, when a real voltmeter makes a measurement, it draws a current because it has an internal resistance in parallel with an ideal voltmeter. Procedure: Measure V1, the potential of the battery. Place a 10 M! resistor in series with the standard voltmeter. Measure V2, the new potential. Prove that V2/V1 = r/(r + 10 M!) Calculate r, the internal resistance of the voltmeter.