Electricity and Magnetism Chapter 5
advertisement

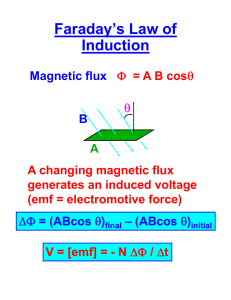
Electricity and Magnetism Chapter 5 Q.1 Define the following physical quantities and State their Units (wherever applicable) in SI. 1) Electromagnetic induction 2) Self inductance 3) Mutual inductance 4) Back emf 5) Motional emf 6) Transformer Turns Ratio 7) Efficiency of Transformer 8) Transformer emf 9) Flux Rule Q.2 Attempt the following Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) 1) The strength of an electromagnet in the form of a coil having n no. of turns, crosssectional area A, length l, carrying current I can be varied by varying a) no. of turns of coil b) cross-sectional area A of coil c) length l of coil d) current I in coil 2) In the phenomenon of mutual induction a) magnetic coupling takes place between two coils carrying a current. b) The unit of the coefficient of coupling k is henry. c) The coefficient of coupling k can have any value from 0 to ∞. d) Mutual inductance M is proportional to the sum of self-inductances of coils 3) A small bar magnet is falling freely through a vertically held, seamless metal tube. Its acceleration during the fall will be a) Equal to g b) Greater than g c) Less than g d) Zero 4) If the current in an inductor doubles, the energy stored in the inductor will (a) remain the same, (b) double, (c) quadruple, (d ) halve. 5) A current is induced in a conducting loop that lies in a horizontal plane and the induced current is clockwise when viewed from above. Which of the following statements could be true? (a) A constant magnetic field is directed vertically downward. (b) A constant magnetic field is directed vertically upward. (c) A magnetic field whose magnitude is increasing is directed vertically downward. (d ) A magnetic field whose magnitude is decreasing is directed vertically downward. 6) Motional emf is a) the emf generated due to the motion of a conductor in an electric field. b) generated due the motion of a conductor in time varying magnetic field. c) not governed by the Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction d) due to voltage induced in a moving rod which is equal to the work done per unit time 7) The statement of Lenz’s law is a) the induced emf is equal and opposite to the magnetic flux of applied field b) the polarity of induced current is such that its magnetic field opposes the applied magnetic field. c) induced magnetic field always acts to keep the magnetic flux in the loop constant d) a particular case of a very general principle in Physics-Le Chatelier’s Principle 8) Faraday’s law states the relation between induced electric field E & magnetic field B a) (the surface S enclosed by a contour C ) b) c) Induced emf d) It is not applicable to circuits moving in a magnetic field. Q.3 State whether the following statements are True (T) or False (F) 1) The induced emf in a circuit is equal to the negative of the magnetic flux through the circuit. 2) There can be a non-zero induced emf at an instant when the flux through the circuit is equal to zero. 3) The self inductance of a solenoid is proportional to the rate of change of the current in the solenoid. 4) The magnetic energy density at some point in space is proportional to the square of the magnitude of the magnetic field at that point. 5) Faraday’s law of electromagnetic induction is applicable in the case of transformer emf generated by an electric force due to a changing magnetic field, but not to motional emf generated by a magnetic force on a moving wire. 6) Transformers are useful to transmit all types of electricity over long distances without much loss of power. 7) The word "force" in "electromotive force" is a misnomer. Electromotive force is not really a force. 8) The induced electric field due to changing magnetic flux density is nonconservative. Q.4 Answer in brief 1) Write the statement of Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction in words & equation 2) Write the formula for the efficiency of a transformer 3) Write the relation between the primary and secondary voltages, currents and number of turns of a transformer 4) What different types of losses occur in the transformer? 5) Giving a labeled diagram explain the principle and working of a Transformer. 6) State in brief the technological applications of Electromagnetic induction 7) What is meant by Self inductance and Mutual inductance? 8) State the difference between transformer emf and motional emf 9) What are the two types of voltages? 10) State and explain in brief the Lenz’s law Q.5 Attempt the following Numerical Examples 1) Two flat circular coils no. 1 with radius 4 cm and 27 turns and no. 2 with radius 12 cm and 3 turns are situated in two uniform magnetic fields B1 and B2. B1 Field is varied from 0.55 Wb/m2 to 0.60 Wb/m2 in 0.5 sec. B2 Field is varied from 0.24 Wb/m2 to 0.30 Wb/m2 in 0.2 seconds. Calculate the ratio of emf induced in coil 1 to the emf induced in coil 2. 2) As shown in the figure given below, a bar magnet moved between the coils (1) and (2). Find giving reason, the directions of the induced currents through the resistors AB and CD when the magnet is moving (a) towards the right, and (b) towards the left. 3) The output voltage of an ideal transformer, connected to a 240V ac mains is 24V. When this transformer is used to light a bulb with rating 24V, 24W; calculate the current in the primary coil of the circuit. 5) Two solenoids have equal length and radius, and identical cylindrical cores of iron material However solenoid A has four times number of turns per unit length as solenoid B. a) Which solenoid has the larger self-inductance? (b) What is the ratio of the self-inductance of solenoid A to the self-inductance of solenoid B? 6) Compare the energy density stored in Earth’s electric field to that stored in Earth’s magnetic field near its surface. Take Earth’s magnetic field to be 0.3 G and its electric field to be 100 V/m near its surface 7) (a) Estimate the maximum possible motional emf between the wingtips of a typical commercial airoplane in flight. (b) Estimate the magnitude of the electric field between the wingtips. Assume that Earth’s magnetic field is 0.3 G, the speed of airoplane relative to Earth’s magnetic field is 220 m/s and a wingspan is 75 m.