G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of
advertisement

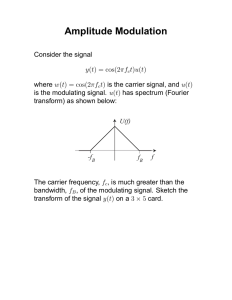
G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology ITDC Fifth Semester G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology List of Experiments 1. To construct the circuit of amplitude modulation on bread board and observe waveforms. 2. To construct the circuit of frequency modulation on bread board and observe waveforms. 3. To construct the circuit of amplitude demodulation on bread board & observe the waveform. 4. To construct the circuit of frequency demodulation on bread board & observe the waveform. 5. To construct the circuit of DSBSC on bread board and observe waveforms. 6.To construct the circuit of Phase Shift Keying on bread board & observe the waveform. 7.To construct the circuit of Frequency Shift Keying on bread board & observe the waveform. 8.To construct the circuit of Pulse Amplitude Modulation on bread board & observe the waveform. 9.To construct the circuit of Pulse Width Modulation on bread board & observe the waveform. 10. To construct the circuit of Pulse Position Modulation on bread board & observe the waveform. ITDC Fifth Semester G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology Experiment No.: - 01 Aim:- To construct the circuit of amplitude modulation on bread board and observe waveform. Equipments required:CRO, CRO probes, Function Generator (2 nos.), Power supply, Breadboard, connecting wires. Components:Transistor: - BC548/549 (1 nos.),Resistor: - 330Ω (2 nos.), Inductor: 1mH (1 nos.) Theory:In amplitude modulation, the amplitude of the carrier voltage varies in accordance with the instantaneous value of modulating voltage. Let the modulating voltage be given by expression, Vm = Vm cos wmt Where wm is angular frequency of the signal & Vm is the amplitude. Let the carrier voltage be given by expression, Vc = Vc coswct On Amplitude Modulation, The instantaneous value of modulated carrier voltage is given by, V = V(t) cos wct V(t)=Vc + ka Vm cos wmt V=Vc[1+ ma cos wm t] cos wct Where ma is modulation index and the modulation index is defined as the ratio of maximum amplitude of modulating signal to maximum amplitude of carrier signal. ITDC Fifth Semester G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology ma= K Vm / Vc % modulation is defined as, %ma=Vm/Vc Circuit Diagram: - Procedure: 1. Assemble components and make connections on the breadboard. 2. Adjust the function generator to obtain the sine wave of frequencies 2 KHz and 1 MHz respectively. 3. Apply the sine wave of modulating signal and carrier signal to the ckt. 4. Observe the resulting amplitude modulated signal on CRO. 5. Calculate Vmax and Vmin from the obtained AM wave and hence calculate modulation index. 6. Vary amplitude of modulating signal to get overmodulation, 100% modulation and undermodulation condition. 7. Draw the waveform for overmodulated, 100% modulated, and undermodulated ITDC Fifth Semester G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology AM wave on graph paper. . Observation Table: Table (1): Sr.No. Voltage signal Frequency Amplitude (Vs ) Modulating signal Carrier signal Table (2): Sr. No. Vmax Vmin Modulation index % of modulation index Result: When Vm = ……… ma =………. When Vm = ……… ma =………. When Vm = ……… ma =………. Conclusion: Thus the amplitude-modulated signal is generated and modulation index for different values of modulating amplitudes is calculated. Viva Questions: 1. What are the advantages of AM over FM? 2. What are the advantages of FM over AM? 3. What are the disadvantages of over modulation? ITDC Fifth Semester G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology Experiment No.2 Aim: - To construct the circuit of frequency modulation on bread board and observe waveform. Equipments Required:Breadboard ,CRO , function generator, power supply, CRO probes, connecting wires. Components:IC:-XR 3038, Resistors:-100K(2),5.6KΩ,Capacitors :-0.1µf(NO. 2) Circuit Diagram:- ITDC Fifth Semester G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology Theory:Frequency modulation consists in varying the frequency of the carrier voltage in accordance with the instantaneous value of the modulating voltage.Thus the amplitude of the carrier does not change due to frequency modulation. Let the modulating voltage be given by expression: Vm=Vm coswmt. Where wmis angular frequency of the signal & Vm is the amplitude. Let the carrier voltage be given by expression, Vc=Vcsin ( wct+θ θ) On frequency modulation, the instantaneous value of modulated carrier voltage is given by, Vc=Vcsinφ φ Where φ=wct+θ; ϕ=w θ1 ϕ ct+kfVm1/wmsinwmt+θ Hence the frequency modulated carrier voltage is given by, V=Vcsin[wct+kfVm/wm sinwmt] The modulation index is defined as the ratio of frequency deviation to frequency of modulating signal mf=d/fm where deviation f(fmax=fmin)/2. Procedure:1. Study the circuit diagram provided in the manual. 2. Study the pin configuration of IC-XR8038. 3. Adjust the function generator to obtain the sine wave of frequency 1KHZ. 4. Apply the sine wave modulating signal to the circuit. 5. Adjust the amplitude & frequency of modulating signal to get the frequency modulated output. 6. From the carrier sidebands chart find the highest order sideband corresponding to obtained modulation index. 7. Change the amplitude of modulating signal & repeat step 5 & 6. 8. Draw the waveform on graph paper. ITDC Fifth Semester G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology IC 8038 Observation:Table1:Sr no. Signal 1 2 Modulating Signal Carrier Signal ITDC Amplitude Frequency Fifth Semester G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology Result:when Vm=…. then B.W.= Conclusion:Thus by changing the amplitude of modulating signal the amount of deviation willchange, but it remains constant for any change in modulating signal frequency. Any slight change in deviation for change in modulating frequency was due to the change in amplitude of generator output. Viva Questions:1)What is frequency deviation in FM? 2)What are the advantages of FM over AM? ITDC Fifth Semester G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology Experiment No: - 3 Aim: - To construct the circuit of amplitude demodulation on bread board & observe the waveform. Equipment Required: CRO, Probes, Connecting wires. Components: Diode OA79 (1 no.), Resistor 10 K (1 no.), capacitor 0.1 µF (1 no.) Theory: Envelope detector is also called as linear diode detector. The envelope detector operates over linear region of the dynamic current voltage characteristic of the diode. Envelope detector utilizes the rectification characteristics of a diode. The modulated carrier voltage is applied to the series combination of diode and the load impendence consisting of resistor R in shunt with capacitor C. During the positive half cycle the diode conducts thereby charging the capacitor C to the peak value of the carrier voltage. During the negative half cycle the diode does not conduct and hence discharges the capacitor through R. Thus the output voltage is spiky in nature but it almost traces the envelope of the modulated carrier voltage and hence it is nothing but original modulating voltage. The departure of this output voltage from the envelope may be reduced by proper choice of R and C depending upon the modulation frequency and depth of modulation. Circuit Diagram: - ITDC Fifth Semester G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology Procedure: (1) Assemble the components on the breadboard as shown in the circuit diagram. (2) Apply the amplitude modulated signal to the input side. (3) Observe the output on CRO. (4) Draw the Amplitude modulated signal and demodulated on graph paper. Observations: AM signal: Carrier frequency= Vmax= Vmin= Demodulated Signal: Frequency= Amplitude= Result: The demodulated signal at the output of envelope detector was found to be equal to the modulating signal. Viva Questions: (1) Why envelope detector is also called as linear diode detector? (2) How by proper choice of R and C the performance of the envelope detector can be improved? ITDC Fifth Semester G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology Experiment No.4 Aim: - To construct the circuit of frequency demodulation on bread board & observe the waveform. Equipment required:IC 565, Function generation ,CRO. Component required:R1=560_NO.),R2=10K_,C1=470Pf,C2=0.001µf,C3=0.1µf,C4 =0.01µf. Theory:The process of FM Demodulation is to exact the original modulating voltage from the frequency modulated voltage. This detection should be done efficiently and linearly. Further it is desirable that the detector circuit should be in sensitive to amplitude changes and should not be too critical in its adjustment and operation. The FM demodulator performs the detection process in two steps:-1)it converts the frequency modulated voltage into corresponding amplitude modulated voltage using one or more tuned circuits .2)it rectifies this amplitude modulated voltage in linear diode demodulator to extract the original modulation frequency voltage. The FM demodulator may be of the following types: i) The slope demodulator. ii) The balanced slope demodulator. iii) Phase difference discriminator iv) Ratio detector v) Foster seeley discriminator vi) PLL. PLL -Phase-locked loop principal has been used in application such as FM modulation ,FM demodulator FSK. The PLL IC 565 is used as FM Demodulator IC and it performs its demodulation operation. ITDC Fifth Semester G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology Circuit diagram:- Procedure:1) The output of FM is forward to the input of demodulator. 2) Set deviation control R1fully clockwise for maximum deviation .Also set the generation frequency control to be 200HZ. 3) Connect your oscilloscope to pin 7 of the 565 phase locked loop .set the time/cm control to 2ms/cm and the vertical input to 0.5v/cm.At this point ,you may or may not have an audio output signal displayed on the oscilloscope. You must adjust the 565 PLL to the correct operating frequency .To do this adjust R2 until you obtain a sine wave output on the oscilloscope. 4) Using the generation frequency control and R the deviation control, verify that the output of the phase locked loop is directly proportional to the modulating signal. Result:The demodulated signal was found equal to the modulating signal. Viva Question: 1. What is Frequency Discriminator? 2. What is the advantage of using PPL for FM Demodulation? ITDC Fifth Semester G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology Experiment No.:- 5 Aim: - To construct the circuit of DSBSC on bread board and observe waveform. Equipment Required:Function Generator, CRO, Connecting wires. Components: IC 1496 (1 nos.), Resistors: 1KΩ (3 nos.), 100Ω (2 nos.) Theory: The amplitude-modulated signal is simple to produce but has two practical drawbacks in application to many real communications systems: the bandwidth of the AM signal is twice that of the modulating signal and most of the power is transmitted in the carrier, not in the information bearing sidebands. To overcome these problems with AM, versions on AM have been developed. These other versions of the AM are used in applications were bandwidth must be conserved or power used more effectively. If the carrier could somehow be removed or reduced, the transmitted signal would consist of two information-bearing sidebands, and the total transmitted power would be information. When the carrier is reduced, this is called as double sideband suppressed carrier AM or DSB-SC. Instead of two third of the power in the carrier, nearly all being the available power is used in sidebands. ITDC Fifth Semester G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology Procedure: -1. Assemble components and make connections of the breadboard .2. Adjust the function generator to obtain the sine wave of frequencies 2 KHz and 1 MHz respectively. 3. Apply the sine wave of modulating signal and carrier signal to the ckt. 4. Observe the resulting DSB-SC signal on CRO. 5. Draw the time domain and frequency domain representation of DSB-SC on graph paper. Observation Table : - Sr. No. Signals Frequency Amplitude in Vs Modulating signal Carrier signal Result & Conclusion: The Balanced modulator IC 1496 can be used for the generation of DSB-SC signal. The frequency domain representation of DSB-SC signal shows that DSB-SC signal do not contain the carrier component and it consists of two symmetrically placed sidebands. Viva Questions: 1. What is the bandwidth of the DSB-SC signal? 2. How SSB signal could be generated from DSB-SC signal? 3. What is ring modulator? 4. what is use of DSB-SC ? ITDC Fifth Semester G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology Experiment No.:-6 Aim: - To construct the circuit of Phase Shift Keying on bread board & observe the waveform. Equipment Required: PSK kit, Function generator dual channel, CRO, Digital multimeter, IC1496. Theory: The original source of information, text, speech, the most commonly used coding scheme is binary sequence such as 0011101011. For transmission purpose this has to be converted to a continuous electrical waveform, conversion process is referred to as the modulation .The o/p of the PCM system is also a binary data. If they are to be transmitted over copper wires, they can be Directly Transmitted as two voltage levels +v and –v. But if they are to be transmitted through space using antenna, Phase Modulation is used. As the modulating signal consists of only two levels the modulation technique is known as Phase Shift Keying. Phase Shift Keying is a modulation in which the phase of the carrier signal changes with respect to the digital signal. The binary signal to be transmitted changes the phase of the sine wave carrier depending upon whether 0 or 1 is transmitted. It is also called as Binary Phase Shift Keying (BPSK). The BPSK can be implemented by using a Balanced Modulator. IC1496 is used as a Balanced Modulator for implementing BPSK. The circuit diagram is shown in the manual. The carrier is applied to pin no.8 and Modulating Binary signal is applied to pin no.1 The BPSK O/P is taken from pin no. 12.IC 1496 internally consists of differential amplifier configuration .its carrier suppression is rated at a minimum of –5db with a typical value of –65db at ITDC Fifth Semester G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology 500khz. Procedure: 1) Study the circuit provided on the front panel of kit. 2) Apply the sine wave of 400Hz to pin no. 8. 3) Apply the square wave i.e. non linear binary data minimum 200Hz pin no.1 4) Connect CRO at the o/p i.e. pin no. 12. 5) Switch ON the power supply. 6) Observe the PSK O/P on the CRO. 7) Draw the observed waveform on the graph paper. ITDC Fifth Semester G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology Observation Table: - Result: The carrier signal changes phase as Binary signal changes its state from logic 0 to logic 1. Viva Questions:1. What is the advantage of PSK over FSK? 2. What is the difference between PSK, FSK and ASK? ITDC Fifth Semester G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology Experiment No.:-7 Aim:- To construct the circuit of Frequency Shift Keying on bread board & observe the waveform. Requirements:Breadboard , CRO dual channel, function generator, power supply, CRO probes, connecting wires. Components:IC:-XR2206, Resistors:-22K,1K(2),100K(2),220ΩCapacitors-1µf,10µf Theory:Frequency shift keying is the digital system of frequency modulation .Digital signal generated in system like telegraphy is not transmitted as it is instead they are transmitted using keying techniques .In FSK the nominal unmodulated carrier frequency .Corresponding to mark condition and space condition is transmitted for logic level 1 and logic level 0 respectively. Procedure:ITDC Fifth Semester G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology 1. Assemble components and make connection on breadboard as shown in fig. 2. Get it checked before turn on the power supply . 3. Apply square wave input. 4. Observe the waveform on CRO & note down mark & space frequencies. Observation:The standard mark frequency f(mark)= 1/R1C3 Space frequency f(space)= 1/R2C3 Observe I/P square wave Frequency= Amplitude = Observe O/P sine wave Mark frequency= Space frequency= Result:Mark frequency is ……. And Space frequency is …… Conclusion: Mark frequency is greater than space frequency. FSK system is used for digital data transmission. Viva question:1) What is FSK? 2) What are mark and space frequencies? 3) Which component in the circuit governs the mark and space frequencies? ITDC Fifth Semester G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology Experiment No.8 Aim: - To construct the circuit of Pulse Amplitude Modulation on bread board & observe the waveform. Equipment required:PAM kit, dual channel CRO, signal generator. Component required:R1=39K, R2=18K, R3=R4=10K,R5=10K pot C1=0.01µf,C2=0.01µf,C3=1µf,IC1=555,IC2=4016 CMOS switch. Theory:In pulse modulation some characteristics of pulse (carrier) is change in accordance with the sample of the modulating signal .Such type of modulation is called as Pulse Modulation. It is applied in many types .But some of common types are Pulse Amplitude modulation (PAM) ,Pulse width modulation (PWM),and Pulse position modulation (PPM).If the characteristics of pulse such as amplitude ,duration(width), position is change in accordance with the modulating signal than it is called as PAM,PDM or PWM and PPM respectively. Pulse Amplitude Modulation the amplitude of the pulse is varied in accordance with the modulating signal then it is called as pulse Amplitude modulation .Its waveform is shown in fig 1.PAM gives dual polarity (AC type) PAM output called as natural PAM sampling .But If DC level is introduced to the modulating signal then it results single polarity PAM. ITDC Fifth Semester G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology Procedure:1. Assemble components and make connection on breadboard as shown in fig. 2. Switch on the power supply and note the amplitude and frequency of sample pulse internally generated by IC555 connect the same at pin 13 of CMOS IC by using patch cord. 3. Apply a sine wave modulating signal of around 5-VPp, 70 Hz at the point marked as I/P 4.Connect dual Channel CRO for at i/p and o/p side. 4. Adjust the amplitude and frequency of modulating i/p to get Dual polarity PAM output. 5. Note DC voltage V2 given potential divider R3 and R4 now introduced DC voltage V2 by shorting points A and B by patching repeat. In the above step keep CRO in DC mode. 6. Vary the input frequency and amplitude of the modulating signal and observe the corresponding change in PAM output. ITDC Fifth Semester G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology Conclusion:As the amplitude of sampling pulse is changed in accordance with the modulating signal so it is called as pulse amplitude modulation (PAM). By introducing DC voltage it gives single polarity PAM output. Viva Questions:1. What is the difference between single polarity and dual polarity PAM signal? 2. How single polarity PAM signal is generated from dual polarity PAM? ITDC Fifth Semester G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology Experiment No.:-9 Aim: - To construct the circuit of Pulse Width Modulation on bread board & observe the waveform. Equipment Required: Pulse width modulator, pulse width demodulator, CRO, Patch cords. Components: R1=560_, R2=1K, R3=100_, R4=1K+1M pot, R5=2.7K, R6=10K, Q1=Q2=BC 148, C1=C2=0.1µF, C3=C4=0.22µF. Theory: In PWM, the width of the pulses of the carrier pulse train is varied in accordance with the modulating signal. The pulse width demodulator circuit can be formed by using transistorized circuit with OP-AMP low pass filter. A PWM i/p signal is applied to the base of Q1 and demodulated o/p is obtained from OP-AMP o/p. The transistor Q1 works as a inverter. Hence during the time interval when the PWM is high, the input to the transistor Q2 is low. Therefore, during this time interval the transistor Q2 is cut-off and the capacitor C1 gets charged through resistor R4. During the time interval when the PWM i/p is low the input to the transistor Q2 is high and it gets saturated. The capacitor C1then discharges very rapidly through Q2. The collector voltage of Q2 during this interval is then low. Thus the waveform at the collector of Q2 is more or less a sawtooth waveform whose envelope is same as the modulating signal. This signal is then passes through OP-AMP low pass filter to smooth the shape of envelope and finally it gives o/p whose envelope is nearly equals to the modulating i/p signal. ITDC Fifth Semester G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology Procedure: 1. Study the circuit provided in the manual switch on the power supply. 2. Apply a PWM i/p to the base of the transistor Q1. 3. Connect one channel of CRO to observe modulating signal and other to demodulated o/p. 4. First verify and note the PWM i/p signal. 5. Adjust the amplitude and frequency to obtain the demodulated o/p whose envelope is nearly equals to the modulating signal. 6. Vary the amplitude and frequency of modulating i/p and observe the corresponding change in demodulated o/p. Result: The envelope of the sawtooth waveform can be set equals to the modulating signal hence through OP-AMP IC 741 low pass filter we obtained demodulated o/p equals the modulating signal the circuit can be used for pulse width demodulator. Viva Questions:1) What is PWM ? 2) What is function of summing amplifier ? ITDC Fifth Semester G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology Experiment No.10 Aim: - To construct the circuit of Pulse Position Modulation on bread board & observe the waveform. Equipment Required: Breadboard, CRO, Signal generator, CRO probes, connecting wires. Components: IC 555 (1 no.), Resistors:- 18K (2 no), 10k (1 no), 1K (2 no.), Capacitors- 0.1µF (2 no.), 10 µF (1 no.). Theory:Pulse Position Modulation (PPM) is the type of pulse modulation in which the amplitude and width of the pulse is kept constant but the position of each pulse in relation to the position of a recurrent reference pulse is varied by each instantaneous sampled value of the modulating wave. PPM has the advantage over PWM of requiring constant transmitter power output but has the disadvantage of dependence on transmitter receiver synchronization. PPM may be obtained from PWM. In PWM each pulse has a leading edge and a trailing edge but the location of the leading edges are fixed whereas those of trailing edges are not but are dependent on the pulse width, which in turn is dependent on the signal value at that instant. Thus, we may state that the trailing edges of PWM pulses are position modulated. Thus PPM may be obtained from PWM by simply getting ride of the leading edges and flat tops of PWM pulses. Circuit Diagram: - ITDC Fifth Semester G.H. Raisoni College of Engineering, Nagpur. Department of Information Technology Procedure: 1. Study the circuit diagram and the pin configuration of IC 555. 2. Assemble the components on the breadboard to build the circuit of PPM as given in circuit diagram. 3. Apply sine wave modulating signal to pin number 5 of IC 555 and observe the same signal on CRO and note down its amplitude and frequency. 4. Observe the PPM signal on CRO. 5. Simulate the circuit to generate PPM in microcap. 6. Draw the modulating signal and PPM signal on graph paper. Observation Table: Sr.No. Signal Amplitude Frequency Result:PPM signal is generated using IC 555 and observed on CRO. The same circuit is simulated in microcap. Both PPM waveforms were compared and were found same. Conclusion:PPM signal can be generated by first generating PWM by using differentiator and diode clipper. Viva Questions: 1) What is the advantage of PPM over PWM? 2) What is the difference between pulse modulation and CW modulation? ITDC Fifth Semester