Basic Electron Theory
advertisement

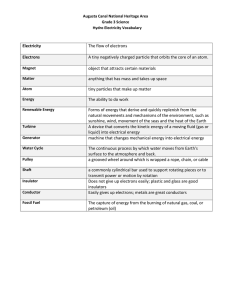
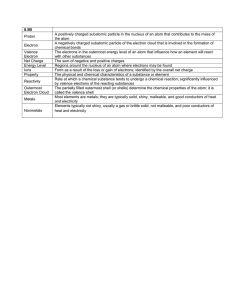
Basic Electron Theory Digital Electronics Basic Electron Theory This presentation will • Review the basic structure of the atom. • Define conductor, insulator, and semiconductor. 2 Structure of an Atom Example – Carbon Atom Nucleus • 6 Protons • 6 Neutrons - Electrons - - + + - Orbits - - The distribution of electrons in the orbital rings around an atom’s nucleus determines the element’s electrical properties. 3 Conductor/Insulator/Semiconductor • The stability of the electrons in the outer ring determines whether a material made from this element is a conductor, insulator, or semiconductor. • Elements whose electrons are unstable and can easily move from one atom to another make good conductors. 4 Conductor/Insulator/Semiconductor • Elements whose electrons are stable and cannot easily move from one atom to another make good insulators. • Any elements that are not considered conductors or insulators are categorized as semiconductors. 5 Conductors • When an element’s outer electron ring is incomplete or not full, its electrons can move more freely from one atom to another atom. • Elements whose electrons can move more freely make good conductors. 6 Conductors • In general, most metals make good conductors because they only have one or two electrons in their outer band. • Silver and gold are the best conductors. Copper is the second best conductor. Most wiring uses copper wire because it is a good conductor and is less expensive than the other metals. 7 Conductors: Example Ag & Cu Silver (Ag) 2 8 18 18 1 Because the outer-most band is incomplete, the single electron is unstable and loosely bonded to the atom. Hence, it can easily move to the outer band of another adjacent atom. Copper (Cu) 1 18 8 2 This free flow of electrons is what makes silver and copper good conductors. Nucleus Number of Electrons in Orbit 8 Insulator • When an element’s outer ring is complete, or full, its electrons cannot easily move from one atom to another atom. • Elements whose electrons can not move freely make good insulators. • Examples of good insulators are glass, plastic, rubber, paper, or air. Most wiring uses plastic as an insulator. 9 Insulator • Plastics are polymers or long chains of atoms bonded to one another. • Neon and argon, both gases, are good insulators and are often used in light bulbs. 10 Insulator: Example Ne & Ar Neon (Ne) 2 8 The outer-most orbits of neon and argon can each contain a maximum of eight (8) electrons. This is exactly how many they have. This makes the electron in the outer-most bands stable. This stable electron structure is what makes neon and argon good insulators. Argon (Ar) 8 8 2 11 Semiconductor • When an element’s outer ring is neither complete nor incomplete, the element is considered to be a semiconductor. • Examples of good semiconductor materials: Carbon (used to make resistors). Silicon (used to make transistors) 12 Semiconductors: Example C & Si Carbon (C) 2 4 The outer-most orbits of carbon and silicon can each contain a maximum of eight (8) electrons. Because they both contain four (4), these electrons are neither stable nor unstable. This electron structure is what makes carbon and silicon good semiconductors. Silicon (Si) 4 8 2 13