Conductors, Insulators and Semiconductors What are insulators
advertisement

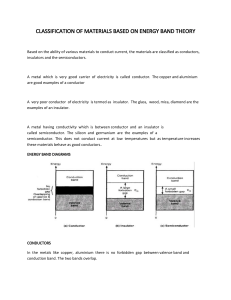
Conductors, Insulators and Semiconductors What are insulators? Insulators • Materials that do not conduct electrical current • Mostly compounds rather than single element materials • Very high resistivity • Valence electrons are tightly bound to the atom • Examples: rubber, plastic, glass, quartz, What are conductors? What are conductors? • Materials that easily conduct electrical current • Mostly single element materials like metals • Characterized by one valence electron loosely b bound to the atom d h • Examples: copper, silver, gold aluminum What are semiconductors? Semiconductors • Materials that are between conductors and insulators in its ability to conduct electrical current • Neither a good conductor nor a good insulator Neither a good conductor nor a good insulator in its intrinsic (pure) state • Characterized by four valence electrons • Examples: antimony, arsenic, astatine, boron, polonium, tellurium, silicon, germanium What is a band gap? Band Gap • difference in energy between the valence band and the conduction band of an atom What is a crystal? What is a Electron Current? Electron Current • movement of free electrons in a semiconductive material What is a Hole Current? Doping • Increasing conductivity by controlled addition of impurities to the intrinsic material What is doping? N Type Semiconductors What are N Type Semiconductors? • Produced by adding pentavalent impurity atoms to increase the number of conduction‐ band electrons in intrinsic silicon P Type Semiconductors What are P Type Semiconductors? What is a PN Junction? • Produced by adding trivalent impurity atoms to increase the number of holes in intrinsic silicon