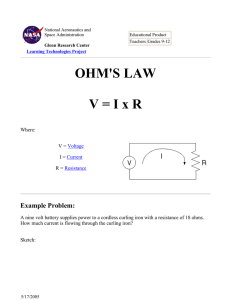
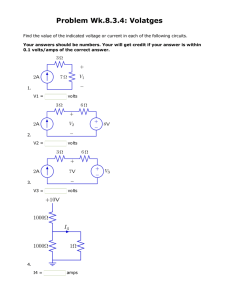
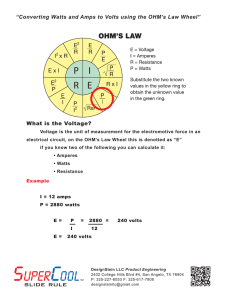
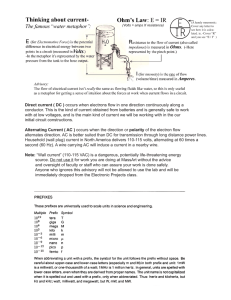
Common Electrical Formulas including Ohms Law
advertisement
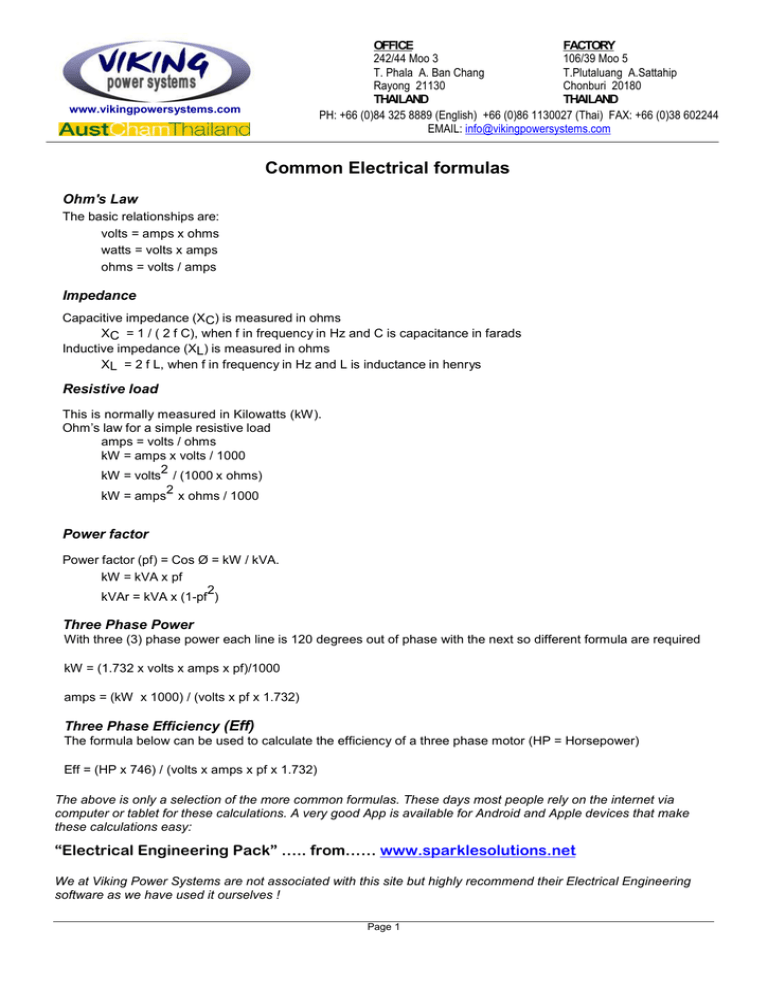
OFFICE FACTORY 242/44 Moo 3 106/39 Moo 5 T. Phala A. Ban Chang T.Plutaluang A.Sattahip Rayong 21130 Chonburi 20180 THAILAND THAILAND PH: +66 (0)84 325 8889 (English) +66 (0)86 1130027 (Thai) FAX: +66 (0)38 602244 EMAIL: info@vikingpowersystems.com www.vikingpowersystems.com Common Electrical formulas Ohm's Law The basic relationships are: volts = amps x ohms watts = volts x amps ohms = volts / amps Impedance Capacitive impedance (XC) is measured in ohms XC = 1 / ( 2 f C), when f in frequency in Hz and C is capacitance in farads Inductive impedance (XL) is measured in ohms XL = 2 f L, when f in frequency in Hz and L is inductance in henrys Resistive load This is normally measured in Kilowatts (kW). Ohm’s law for a simple resistive load amps = volts / ohms kW = amps x volts / 1000 2 kW = volts / (1000 x ohms) 2 kW = amps x ohms / 1000 Power factor Power factor (pf) = Cos Ø = kW / kVA. kW = kVA x pf 2 kVAr = kVA x (1-pf ) Three Phase Power With three (3) phase power each line is 120 degrees out of phase with the next so different formula are required kW = (1.732 x volts x amps x pf)/1000 amps = (kW x 1000) / (volts x pf x 1.732) Three Phase Efficiency (Eff) The formula below can be used to calculate the efficiency of a three phase motor (HP = Horsepower) Eff = (HP x 746) / (volts x amps x pf x 1.732) The above is only a selection of the more common formulas. These days most people rely on the internet via computer or tablet for these calculations. A very good App is available for Android and Apple devices that make these calculations easy: “Electrical Engineering Pack” ….. from…… www.sparklesolutions.net We at Viking Power Systems are not associated with this site but highly recommend their Electrical Engineering software as we have used it ourselves ! Page 1