29 Kirchhoff`s Rules
advertisement

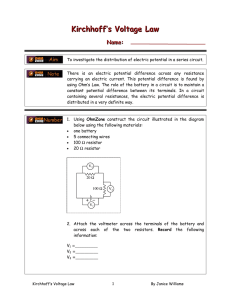
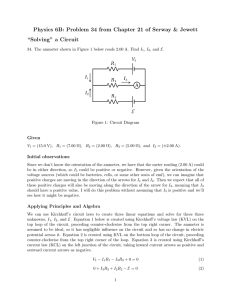
KIRCHHOFF’S RULES Kirchhoff’s Rules 1. The sum of the currents entering any junction in an electric circuit must equal the sum of the currents leaving that junction: 2. The sum of the potential differences across all elements around any circuit loop must be zero: Serway 28.19, p. 897 Determine the current in each branch of the circuit shown in the figure. Serway 28.24, p. 897 In the circuit of the figure, determine the current in each resistor and the voltage across the 200-Ω resistor. SEATWORK Serway 28.18, p. 897 The ammeter shown in the figure reads 2.00 A. Find I1, I2, and ε. Answers: I1 = 0.714 A, I2 = 1.29 A, ε = 12.6 V SEATWORK Serway 28.21, p. 897 The circuit considered in Problem 19 and shown in the figure is connected for 2.00 min. (a) Find the energy supplied by each battery. (b) Find the energy delivered to each resistor. (c) Find the total amount of energy converted from chemical energy in the battery to internal energy in the circuit resistance. SEATWORK Serway 28.22, p. 897 (a) Using Kirchhoff ’s rules, find the current in each resistor shown in the figure and (b) find the potential difference between points c and f. Which point is at the higher potential? Answers: I1 = 0.385 mA, I2 = 3.08 mA, I3 = 2.69 mA ∆Vcf = –69.2 V, point c is at higher potential SEATWORK Serway 28.23, p. 897 If R = 1.00 kΩ and ε = 250 V in the figure, determine the direction and magnitude of the current in the horizontal wire between a and e. SEATWORK Serway 28.25, p. 897 A dead battery is charged by connecting it to the live battery of another car with jumper cables. Determine the current in the starter and in the dead battery.