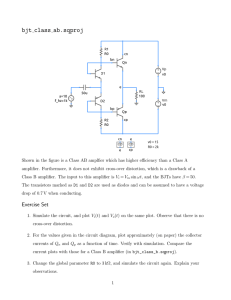
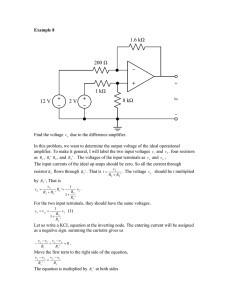
EC6304-Electronic Circuits-I - Valliammai Engineering College
advertisement

VALLIAMMAI ENGINEERING COLLEGE SRM Nagar, Kattankulathur – 603 203. DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONICS & COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK SUBJECT : EC6304/ ELECTRONIC CIRCUITS-1 SEM / YEAR: III/ II Year ECE UNIT I POWER SUPPLIES AND BIASING OF DISCRETE BJT AND MOSFET Rectifiers with filters- DC Load line, operating point, Various biasing methods for BJT-DesignStability-Bias compensation, Thermal stability, Design of biasing for JFET, Design of biasing for MOSFET PART A Q.No Questions BT Level Competence 1. What is need of Biasing? BTL 1 Remembering 2. Draw D.C load line. BTL 1 Remembering 3. Define stability factor. BTL 1 Remembering 4. Discuss about operating point. BTL 1 Remembering 5. BTL 1 Remembering 6. Show the equations for the stability factors S’ and S’’. How to find the expression for stability factor? BTL 1 Remembering 7. Summarize the requirements for biasing circuits? BTL 2 Understanding 8. Illustrate the main idea of compensation techniques? BTL 2 Understanding 9. When the thermal runway happens at the amplifier circuit? Give outline for compensation techniques? BTL 2 Understanding BTL 2 Understanding Identify the operating regions of N-channel MOSFET and how do you identify the operating region? Categorize the different methods of biasing a JFET? How would you apply various conditions for thermal stability and What are the conditions for thermal stability? BTL 3 Applying BTL 3 Applying BTL 3 Applying 10. 11. 12. 13. Prepared By :A.PandianA.SuganyaS.Abirami 14. Analyze the function of Q-point? How it varies the output? BTL 4 Analyzing 15. Examine why the operating point selected at the Centre of the active region? List out the advantages of using emitter resistance in the context of biasing? Assess the importance of selecting the proper operating point. How would you explain FET is known as voltage variable resistor? Build the fixed bias single stage transistor circuit. BTL 4 Analyzing BTL 4 Analyzing BTL 5 Evaluating BTL 5 Evaluating BTL 6 Creating How would you adapt a D.C load line in fixed bias amplifier circuit? PART-B What is D.C. load line? How will you select the operating point, explain it using common emitter amplifier characteristics as an example? (13) Demonstrate common source self bias and voltage divider bias for FET with neat diagrams? (13) Find voltage divider bias circuit for NMOS such that 𝐼𝐷𝑄 = 400µ𝐴, 𝑉𝐷𝐷 = 14𝑉, 𝑉𝐷𝑆 = 2.3𝑉, 𝑘𝑛 = BTL 6 Creating BTL 1 Remembering BTL 1 Remembering BTL 1 Remembering BTL 1 Remembering BTL 2 Understanding BTL 2 Understanding BTL 2 Understanding 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 1 2 3 𝑊 µ𝑛 𝐶𝑜𝑥 ( 𝐿 ) = 1𝑚𝐴 𝑝𝑒𝑟 𝑉 2 , 𝑉𝑡 = 1𝑉. Assume a current 4 5 6 of 1µA through R1 and R2, and 𝑉𝑠 = 1.2𝑉.(13) With neat diagrams, how would you show two bias compensation techniques and state its advantages and disadvantages. (13) Relate the various methods of biasing using BJT in terms of their stability factors. (13) (i) Illustrate stability and thermal stability. (7) (ii) Summarize the working of Full wave rectifier with CLC filter and derive for its ripple factor? (6) 7 Interpret the circuit as shown in below. β =100 for the si transistor. Calculate 𝑉𝐶𝐸 for a given circuit. (13) Prepared By :A.PandianA.SuganyaS.Abirami 8 For the circuit shown in fig.𝐼𝐶 =2mA, β =100 , Calculate 𝑅𝐸 ,𝑉𝐸𝐶 and stability factor. BTL 3 Applying BTL 3 Applying BTL 4 Analyzing BTL 4 Analyzing BTL 4 Analyzing (13) 9 10 11 12 The amplifier shown in Fig. an n-channel FET for which, ID=0.8mA, VP=-20V and IDSS=1.6mA. Assume that rd>Rd. Calculate the following parameters. (1) VGS (2) gm (3) Rs. (13) Analyze various techniques of stabilization of Q-point in a transistor. (13) Explain in detail about various methods of biasing MOSFET. (13) (i) The parameters for each transistor in the circuit in figure are ℎ𝑓𝑒 = 100, 𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑉𝐵𝐸(𝑂𝑁) = 0.7𝑉. Examine the Q-point values of base, collector and emitter currents in Q1 and Q2. Prepared By :A.PandianA.SuganyaS.Abirami (7) (ii) Examine the change in collector current produced in each bias referred to in figure 1 and 2, when the circuit temperature raised from 25°C to 105°C and 𝐼𝐶𝐵𝑂 = 15𝑛𝐴@25°𝐶. (6) 13 (i) Assess the importance of emitter stabilized biasing with necessary circuit diagram? BTL 5 Evaluating BTL 6 Creating (7) (ii) Determine IB, IC, VCE, VC, VB, VE and VBC For the emitter bias network shown below, (6) 14 (i)Design a Emitter bias circuit for BJT with Vcc = 18V, VCE = 10V, IC = 2mA, β = 150. (7) (ii) Invent the stability factor of self bias circuit of BJT with neat diagram. (6) PART-C Prepared By :A.PandianA.SuganyaS.Abirami 1 Explain in detailwith neat circuits the various methods used for stabilizing the Q point against the change in device parameters. BTL5 Evaluating (15) 2 Elaboratethe various techniques that use temperature sensitive devices to maintain constant operating point and explain in detail.(15) BTL 6 Creating UNIT II BJT AMPLIFIERS Small signal Analysis of Common Emitter-AC Load line, Voltage swing limitations, Common collector and common base amplifiers – Differential amplifiers- CMRR- Darlington Amplifier- Bootstrap technique - Cascaded stages - Cascode Amplifier-Large signal Amplifiers – Class A , Class B and Class C Power Amplifiers . PART A Q.No 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Questions List out the needs of AC load line? BT Level BTL 1 Remembering How would you show Miller effect input capacitance. BTL 1 Remembering Define CMRR of BJT differential amplifier. How to improve it. BTL 1 Remembering State miller’s theorem. BTL 1 Remembering What is an amplifier? BTL 1 Remembering Can you recall trans conductance. BTL 1 Remembering Compare cascade and cascode amplifier. BTL 2 Understanding Find CMRR of differential amplifier with differential gain 300 and common mode gain of 0.2. BTL 2 Understanding Summarize the bootstrapping technique. BTL 2 Understanding Draw the low frequency equivalent circuit of FET. BTL 2 Understanding Identify 𝑉0 (𝑡) for small signal source 𝑉𝑖 (𝑡) = 20𝑐𝑜𝑠20𝑡 + 30𝑠𝑖𝑛106 𝑡 is applied to a transistor amplifier as shown in BTL 3 Applying Prepared By :A.PandianA.SuganyaS.Abirami Competence figure. The transistor hasℎ𝑓𝑒 = 150,𝑟0 = ∞ and𝑟𝜋 = 3𝐾Ω. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. Construct a CE amplifier and analyze ac parameters of its hybrid equivalent circuit. Why you choose emitter bypass capacitor CE in CE amplifier circuit. Categorize the different coupling schemes used in multistage amplifiers. Analyze the need of differential amplifier? BTL 3 Applying BTL 3 Applying BTL 4 Analyzing BTL 4 Analyzing List the various methods of improving CMRR. BTL 4 Analyzing What is the importance of Darlington circuit? BTL 5 Evaluating Assess why 𝑅𝐸 is replaced by a constant current bias in a differential amplifier. Design a cascade amplifier and its ac equivalent circuit. BTL 5 Evaluating BTL 6 Creating Design the AC equivalent circuit for the given figure. BTL 6 Creating BTL 1 Remembering BTL 1 Remembering 20. 1. 2. PART B (16 Marks) What is CMRR? Derive CMRR of differential amplifier with its equivalent circuit. (13) Define the following parameters and the Drive from small signal transistor CE amplifier in terms of the h-parameters, a) Current gain b) Voltage gain c) Input impedance d) Output admittance (13) Prepared By :A.PandianA.SuganyaS.Abirami 3. 4. How to make the Emitter Coupled Differential Amplifier circuit and also explain that operation. (13) State and prove the Miller’s theorem, and also give examples. BTL 1 Remembering BTL 1 Remembering BTL 2 Understanding (13) 5. (i) (ii) Illustrate bootstrapped Darlington circuit with neat sketch. (7) Outline the common emitter amplifier. (6) 6. Summarize the gain, input impedance and output impedance of single stage BJT amplifier using mid band analysis. (13) BTL 2 Understanding 7. Demonstrate the transfer characteristic of differential amplifier? Derive it. (13) Construct the basic circuit of Darlington pair and explain with mathematical substantiation. (13) Identify the changes in the AC characteristics of a common emitter amplifier when an emitter resistor and an emitter bypass capacitor are incorporated in the design? Explain with necessary equations. (13) (i) Analyze the circuit shown in figure with the parameters are ℎ𝑓𝑒 = 120 𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑉𝐴 = ∞. Inspect the following parameters. (1) The current gain, voltage gain, input impedance and output impedance. (2) The maximum undistorted output voltage swing. BTL 2 Understanding BTL 3 Applying BTL 3 Applying BTL 4 Analyzing 8. 9. 10. (10) (ii) The parameters for each transistor in the circuit in given figure are ℎ𝑓𝑒 = 100, 𝑉𝐴 = ∞ and Prepared By :A.PandianA.SuganyaS.Abirami 𝑉𝐵𝐸(𝑂𝑁) = 0.7𝑉. Determine the input and output impedance. (3) 11. 12. 13. Contrast the operation of cascade amplifier and derive gain, input and output impedance. (13) Examine the circuit diagram for a differential amplifier using BJT’s. Describe common mode and differential modes of working. (13) BTL 4 Analyzing BTL 4 Analyzing (i) For the circuit shown in figure, the transistor parameters are ℎ𝑓𝑒 = 125, 𝑉𝐴 = ∞, 𝑉𝐶𝐶 = 18𝑉, 𝑅𝐿 = 4𝑘Ω, 𝑅𝐿 = 3𝑘Ω, 𝑅𝐶 = 4𝑘Ω, 𝑅1 = 25.6𝑘Ω𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑅2 10.4𝑘Ω. the input signal is a current Source. Measure its small signal voltage gain, current gain, maximum voltage gain and input impedance BTL 5 Evaluating BTL 6 Creating (8) (ii) Assess the circuit diagram of bootstrapped emitter follower with its equivalent circuit, derive for its input and output impedance. (5) 14. (i) Design the small signal voltage gain of an emitter follower circuit. Given 𝛽 = 100, 𝑉𝐵𝐸(𝑜𝑛) = 0.7𝑉, 𝑉𝐴 = 80𝑉, 𝐼𝐶𝑄 = 0.793𝑚𝐴, 𝑉𝐶𝐸𝑄 = 3.4𝑉. (7) (ii) Discuss in detail about the operation of Darlington amplifier. (6) Prepared By :A.PandianA.SuganyaS.Abirami PART-C 1 Elaborate the small signal equivalent circuit and derive the transistor parameters of widely used amplifier whose current and voltage gain are greater than unity. (15) BTL 5 Evaluating 2 Explain the bootstrapping technique of improving input resistance in common collector circuit. (15) BTL 6 Creating UNIT III JFET AND MOSFET AMPLIFIERS Small signal analysis of JFET amplifiers- Small signal Analysis of MOSFET and JFET, Common source amplifier, Voltage swing limitations, Small signal analysis of MOSFET and JFET Source follower and Common Gate amplifiers, - BiMOSCascode amplifier PART – A Q.No. Question Competence Level 1 2 List the advantages of common drain amplifier. What are the features of BIMOS cascode amplifier? Remembering Remembering BTL1 BTL1 3 Can you recall voltage swing limitation in JFET? Remembering BTL1 4 How a MOSFET can be used to amplify a time varying voltage? Remembering BTL1 5 Define Bandwidth. Remembering BTL1 6 Relate pinch off voltage and drain resistance. Remembering BTL1 7 Define rise time and give the relation between bandwidth and rise time. Understanding BTL2 Prepared By :A.PandianA.SuganyaS.Abirami 8 Discuss the effect of bypass capacitor on bandwidth of the amplifier. Two amplifiers having gain of 20 dB and 40 dB are cascaded. Estimate the overall gain in dB. Distinguish between JFET and MOSFET amplifiers. If the midband gain of an amplifier is 100 and half power frequencies are fL =40Hz and fH=16kHz. Calculate the amplifier gain at 20Hz and 20kHz frequency. Understanding BTL2 Understanding BTL2 Understanding Applying BTL2 BTL3 12 13 14 Illustrate about JFET common source amplifier. Construct a small signal model of JFET. The parameters for the transistor below are Kn= 0.5mA/V2, VTN = 1.2V , and λ = 0. Simplify VDSandVGS for IQ=50 µA. Applying Applying Analyzing BTL3 BTL3 BTL4 15 Analyze the output impedance for the MOSFET amplifier given below. Provided: Kn= 1mA/V, VTN = 1.2V,λ = 0.01V−1, Av= 0.855 and IDQ= 1mA. Compare the three FET configurations (CS,CD and CG). The small signal parameters of the MOSFET below are gm = 5mA/V , and the output resistance ro= 100K. Measure the voltage gain. Analyzing BTL4 Analyzing Evaluating BTL4 BTL5 18 Why N channel FET’s are preferred over P channel FET’s? Evaluating BTL5 19 Develop the output impedance of a JFET amplifier shown in the figure. Let gm=2mA/v and λ=0. Creating BTL6 Creating BTL6 9 10 11 16 17 20 Create the small signal equivalent circuit for common source NMOS. PART-B Prepared By :A.PandianA.SuganyaS.Abirami Q.No. 1 2 Question Competence (i)How would you describe the expression for the voltage gain of JFET common source amplifier with bypassed RS? (7) (ii) Can you recall the expression for the voltage gain of JFET common source amplifier? (6) Examine the expression for common gate circuit of JFET. Level Remembering BTL1 Remembering BTL1 Remembering BTL1 (13) 3 What is JFET amplifier? Derive gain, input and output impedance of common source JFET amplifier with neat circuit diagram and equivalent circuit. (13) 4 Define common source amplifier. Derive the expression for common source amplifier with unbypassedRS. (13) Remembering BTL1 5 (i)Explain the voltage gain of BIMOS cascode amplifier shown in the figure. (8) (ii)Illustrate a discrete common gate JFET amplifier and derive voltage gain Av,input impedance Rin,and output impedance Rout with small signal equivalent circuit. Understanding BTL2 Understanding BTL2 Understanding BTL2 Applying BTL3 (5) 6 7 8 Demonstrate gain, input and ouput impedance of MOSFET source follower with neat circuit diagram and equivalent circuit.(13) Illustrate the biasing of the BiMOScascode circuit to meet the specific requirements. For the circuit shown in figure 38 the transistor parameters are: VTN 1 = VTN 2 = 1.2V, Kn1 = Kn2 = 0.8mA/V 2, and λ1 = λ2 = 0. Let R1 + R2 + R3 = 300KΩ and RS = 10KΩ. Design the circuit such that IDQ = 0.4mA and VDSQ1 = VDSQ2 = 2.5V. (13) (i) Construct how JFET can be used as an amplifier. (7) (ii)Develop and explain a small signal low frequency model of JFET. (6) Prepared By :A.PandianA.SuganyaS.Abirami 9 10 11 12 13 14 In a common gate configuration of MOSFET, (i) Illustrate small signal voltage and current gain. (7) (ii) Examine input and output impedance. (6) Analyze a simple JFET source-follower amplifier circuit and discuss the general AC circuit characteristics. (13) (i)Explain on voltage swing limitations, general conditions under which a source follower amplifier would be used. (10) (ii) Examine and describe the characteristics of BiCMOS circuits. (3) (i) Pointout the small signal parameters of MOSFET.(7) (ii) Select and configure a common-source amplifier with source resistor. (6) (i)Consider the PMOS amplifier. The transistor parameters are Vtp=-1v,βp=(µpCox(W/L)=1mA/v2 and λ=0. 1. Determine RD and RS, such that IDQ =0.75mA and VSDQ=6V. 2. Determine input impedance Ri and output impedance Ro. 3. Voltage gain, Current gain and maximum output voltage swing. (10) (ii)Determine the current gain of JFET source follower amplifier. (3) Applying BTL3 (8) Analyzing BTL4 Analyzing BTL4 Analyzing BTL4 Evaluating BTL5 Design a small signal voltage gain of an NMOS amplifier with enhancement load, and establish the Q-point in the middle of the saturation region. Consider the transistor parameters VTND = VTNL = 1V, K′n = 30µA/V 2, (W/L)L = 1. The circuit parameter is VDD = 5V. Design the circuit such that the voltage gain is |Av | =10. (13) Creating BTL6 Prepared By :A.PandianA.SuganyaS.Abirami PART-C 1 Explain Voltage swing limitations and general conditions under which a source amplifier would be used and explain common source amplifier with source resistor and source bypass capacitor. (15) BTL5 Evaluating 2 Elaborate the characteristics of BiCMOScascode amplifier, and explain graphically the amplification process in a simple MOSFET amplifier circuit. (15) BTL6 Creating UNIT IV FREQUENCY ANALYSIS OF BJT AND MOSFET AMPLIFIERS Low frequency and Miller effect, High frequency analysis of CE and MOSFET CS amplifier, Short circuit current gain, cut off frequency – fα and fβ unity gain and Determination of bandwidth of single stage and multistage amplifiers PART – A Q.No. Question Competence Level Remembering BTL1 2 What is the effect of miller’s capacitance on the frequency response of an amplifier? Define beta cutoff frequency. Remembering BTL1 3 List out the advantages of h parameter. Remembering BTL1 4 Can you recall the need of cascading multistage amplifiers? Relate the term bandwidth and gain bandwidth product. Remembering BTL1 Remembering BTL1 If the rise time of a BJT is 35 nano seconds. Identify the bandwidth that can be obtained using this BJT ? Differentiate small signal equivalent & hybrid π equivalent circuit. Express the equation of overall lower and upper cutoff frequency of multistage amplifier. Give the main reason for the drop in gain at the low frequency region & high frequency region. Discuss the limitations of multistage amplifiers. Remembering BTL1 Understanding BTL2 Understanding BTL2 Understanding BTL2 Understanding BTL2 The AC schematic of an NMOS common source stage is shown in the figure, where part of the biasing circuit has Applying BTL3 1 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Prepared By :A.PandianA.SuganyaS.Abirami been omitted for simplicity. For the N-channel MOSFET M1,thetransconductance, gm=1mA/v and body effect and channel length modulation effect are to be neglected. Identify the lower cutoff frequency. 12 Develop and explain about Miller Impedance. Applying BTL3 13 Solve the unity gain bandwidth of MOSFET whose gm = 6m A/V, Cgs = 8pF, Cgd= 4 pF, and Cds = 1 pF. Compare BJT and MOSFET Amplifiers. Short circuit CE current gain of transistor is 25 at a frequency of 2 MHz if fᵦ = 200 KHz Examine i) = 200 KHz ii) hfe iii) find |Ai| at frequency of 10 MHz and 100 MHz. Simplify the cut-off frequency due to the bypass capacitor in the figure. Applying BTL3 Analyzing Analyzing BTL4 BTL4 Analyzing BTL4 17 Common base amplifier is preferred for high frequency signal when compared to CE amplifier. Justify. Evaluating BTL5 18 A multistage amplifier employs five stages each of which has a power gain of 30. (i)Determine the total gain of the amplifier in db? (ii) If a negative feedback of 10 dB is employed, evaluate the resultant gain. Create the hybrid π equivalent circuit of common gate amplifier. Develop the high frequency equivalent circuit model for MOSFET. Evaluating BTL5 Creating BTL6 Creating BTL6 14 15 16 19 20 Prepared By :A.PandianA.SuganyaS.Abirami PART-B Q.No. Question Competence Level 1 Describe in detail with neat diagram frequency response of BJT amplifier. Discuss the significance of cut off frequencies and bandwidth of the amplifier. (13) Remembering BTL1 2 Examine the upper and lower cut off frequencies of multistage amplifier with expressions. (13) How would you describe the relation between rise time, upper cut off frequency and bandwidth? (13) Can you recall the operation of high frequency common source FET amplifier with neat diagram? Derive the expression for i) Voltage gain ii) Input admittance iii) input capacitance iv) Output admittance. (13) Remembering BTL1 Remembering BTL1 Remembering BTL1 5 For the circuit shown in the fig. Illustrate cut-off frequencies due to C1,C2,Cs due to interelectrode capacitors Cgs and Cgd, gm=0.49mA/v,Cgd=9.38pF,Cgs=1.8pF,rd=40 KΩ. (13) Understanding BTL2 6 (i)Discuss in detail about the bandwidth of single stage amplifiers.(7) (ii) Describe in detail about gain bandwidth product for voltage and current of BJT. (6) (i)Estimate the bandwidth of CE amplifier with the following specifications. R1=100kΩ, R2=10kΩ, RC=9kΩ, RE=2kΩ, C1= C2=25μF, CE=50μF, rbb’=100Ω, rb’e=1.1KΩ, hfe=225, Cb’e=3pF and Cb’c=100pF. (7) (ii) Summarize the expression for Low Frequency Analysis of BJT. (6) (i)Write a brief outline about multistage amplifiers.(8) (ii)Examine the advantages and applications of single stage and multistage amplifiers. (5) Understanding BTL2 Understanding BTL2 Applying BTL3 3 4 7 8 Prepared By :A.PandianA.SuganyaS.Abirami 9 Demonstrate the low frequency response of the amplifier shown in fig. (13) Applying BTL3 10 (i)Analyze the bandwidth of the amplifier shown. Analyzing BTL4 (10) rb=100Ω ,Rπ= 1.1 K ,Cπ= 3 pF ,Cµ= 100 pF ,hfe = 225 (ii) Simplify the cut-off frequency due to C1 and C2 in the circuit shown in the fig. (3) Prepared By :A.PandianA.SuganyaS.Abirami 11 12 Point out the function of transistor and derive the expression Analyzing for input conductance (gbe) and output resistance (gce) for hybrid – π common emitter transistor model. (13) (i)Analyze the relation between sag and lower cut off Analyzing frequency. (7) (ii) For the circuit shown in figure, Analyze the percentage tilt. Assume approximate h – parameter circuit for the transistor. (6) BTL4 BTL4 13 (i)Summarize alpha cut-off frequency, beta cut-off frequency and transition frequency. (8) (ii) For the circuit of the fig . We have R=100 KΩ, Rin=420KΩ,Cgs=Cgd=1pF,gm=4m/A,R1=3.33 KΩ. Evaluate the midband gain and upper 3 dB frequency,fH. (5) Evaluating BTL5 14 Develop the high frequency analysis of JFET circuit with necessary circuit diagram & gain bandwidth product. (13) Creating BTL6 PART-C 1 Explain low frequency response and high frequency response of an amplifier, derive its cutoff frequency &discuss the terms rise time and sag. (15) BTL 5 Evaluating 2 Elaborate the high frequency analysis of JFET with necessary circuit diagram& gain bandwidth product and explain the frequency response of MOSFET CS amplifier. (15) BTL 6 Creating Prepared By :A.PandianA.SuganyaS.Abirami UNIT- IC MOSFET AMPLIFIERS IC Amplifiers- IC biasing Current steering circuit using MOSFET- MOSFET current sources- PMOS and NMOS current sources. Amplifier with active loads - enhancement load, Depletion load and PMOS and NMOS current sources loadCMOS common source and source follower- CMOS differential amplifier- CMRR. PART- A Q.No Questions BT Level Competence 1. What is the common mode rejection ratio? BTL 1 Remembering 2. Define MOSFET load devices amplifiers? BTL 1 Remembering 3. Name two type of transistor current source? BTL 1 Remembering 4. How would you explain the saturation and non- saturation bias regions?. BTL 1 Remembering 5. Can you recall the advantage of Wilson current mirror circuit? BTL 1 Remembering 6. Summarize the advantages of an active load. BTL 1 Remembering 7. Outline about thecascode current mirror. BTL 2 Understand 8. Illustrate the various types of active loads. BTL 2 Understand 9. Demonstrate the MOSFET is biased in the saturation region. BTL 2 Understand 10. Contrast Wilson current source. BTL 2 Understand 11. Identify the limitation of the NMOS amplifier with depletion load? BTL 3 Apply 12. Develop the NMOS depletion load amplifier parameter. BTL 3 Apply 13. Model the gm of CMOS differential amplifier in large signal equivalent circuit? BTL 3 Apply 14. Analyze the matched transistors load in CMOS amplifier.. BTL 4 Analyze 15. Categorize need for MOSFET differential amplifier with cascode active load. BTL 4 Analyze 16. BTL 4 Analyze 17. Contrast the operation of transistor in voltage transfer characteristics of CMOS common source amplifier. Assess opinion of active load MOSFET. BTL 5 Evaluate 18. Evaluate the output current in current steering circuit. BTL 5 Evaluate 19. Discuss the enhancement and depletion mode of MOSFET. BTL 6 Create Prepared By :A.PandianA.SuganyaS.Abirami 20. Elaborate on MOSFET cascode current source circuit. BTL 6 Create BTL 1 Remembering BTL 1 Remembering BTL 1 Remembering BTL 1 Remembering PART –B 1. (i)Define current source and explain basic MOSFET current source with suitable diagrams? (10) (ii)Label the effect of Vo and Io. (3) 2. How to made DC bias current in MOSFET current Steering circuit and explain withsuitable diagram. (13) 3. Define current mirror circuit and explain following (i) Cascode current mirror (7) (ii) Wilson current mirror. (6) 4. Why current steering circuit required in MOSFET Amplifier and Explain the operation with a circuit diagram? (13) 5. (i) Outline the voltage transfer characteristics MOSFET amplifier with gate and BTL drain shorted load. (7) 2 (ii) Summarize the voltage transfer characteristics NMOS amplifier with enhancement load. (6) 6. (i)Illustrate the NMOS inverter with depletion load amplifier. (10) BTL (ii) Contrast the PMOS with enhancement load. (3) 2 Understand 7. (i) summarize the NMOS CS amplifier?and Explain the operation with a circuit diagram. (10) (ii)State the advantages of CMOS common-source amplifier. (3) Understand 8. (i)Develop current mirror circuit in CMOS differential amplifier BTL 2 (8) (i) Model the equivalent circuit and drive expression for Ad, Acm and CMMR for CMOS differential amplifier. (5) 9. Examine the MOSFET cascade current source, all transistor are identical and transistor circuit parameters are as follows: Vt=1V,Kn=40uA/v2, λ=0.02v-1,iref=10uA and VDD=10V.find:a)VGS of each MOSFET. (5) b)The lowest possible voltage value VD4,the output resistance Ro. . (8) 10. Inspect the parameter in MOSFET current source amplifier for the following BTL Understand Apply 3 BTL 4 Analyze BTL 4 Analyze BTL 4 Analyze specifications: VDD = +5V, Kn’ = 40 µA/V2, VT = 1V, λ = 0, IREF = 0.2mA, I0 = 0.1mA and VDS2(sat) = 0.8V. (13) 11. Simplify the parameter in NMOS amplifier with depletion load, VTN1 = 0.8V, VTN2 = - 1.0V, Kn1 = 2mA/V2, Kn2 = 0.2mA/V2, IDQ = 0.2mA, λ1= λ2 = 0.01V-1. Calculate the small signal voltage gain. (13) 12. (i)Builda CMOS common source amplifier and explain the with the help of various characteristics.(10) (ii)Model the CMOS common-source amplifier,Kn”=80uA/v2.kp=20uA/V2,Vtn=0.8V, Vtp=-1V,(W/L)n=10,(W/L)P=20,Ibias=0.2mA and λ1=λ2=0.0101V-1,find the small- Prepared By :A.PandianA.SuganyaS.Abirami BTL 3 Apply signal voltage gain.(3) 13. (i) Explain the CMOS differential amplifier with Enhancement active load.(10) (ii) Assess the advantages of CMOS differential amplifier with current mirror load. (3) 14. Design a NMOS amplifier with depletion load ,Vtn1=.8v, Vtn2=-1V,Kn1=2mA/V2,Kn2=0.2mA/v2,IDq=0.2mA and λ1=λ2=0.01V-1,calculate the small-signal voltage gain.(13) BTL 5 Evaluate BTL 6 Create BTL 5 Evaluating BTL 6 Creating PART-C 1 2 Conclude the Input and Output Currents, Input and Output Impedances and Frequency Response, Advantages, Limitation of current mirror and Wilson current mirror circuit . (15) Construct a MOSFET current source amplifier for the following specifications: VDD = +5V, Kn’ = 40 µA/V2, VT = 1V, λ = 0, IREF = 0.2mA, I0 = 0.1mA and VDS2(sat) = 0.8V. Prepared By :A.PandianA.SuganyaS.Abirami (15)