Carbon Utility
advertisement
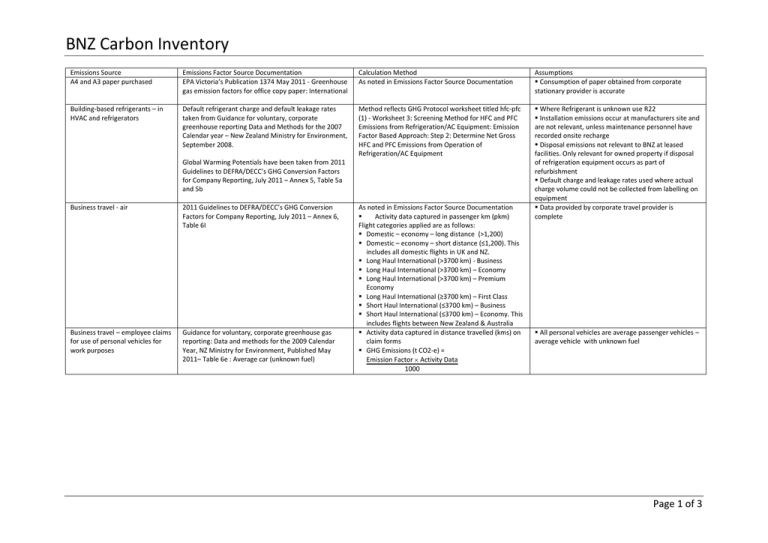
BNZ Carbon Inventory Emissions Source A4 and A3 paper purchased Emissions Factor Source Documentation EPA Victoria’s Publication 1374 May 2011 - Greenhouse gas emission factors for office copy paper: International Calculation Method As noted in Emissions Factor Source Documentation Assumptions Consumption of paper obtained from corporate stationary provider is accurate Building-based refrigerants – in HVAC and refrigerators Default refrigerant charge and default leakage rates taken from Guidance for voluntary, corporate greenhouse reporting Data and Methods for the 2007 Calendar year – New Zealand Ministry for Environment, September 2008. Method reflects GHG Protocol worksheet titled hfc-pfc (1) - Worksheet 3: Screening Method for HFC and PFC Emissions from Refrigeration/AC Equipment: Emission Factor Based Approach: Step 2: Determine Net Gross HFC and PFC Emissions from Operation of Refrigeration/AC Equipment Where Refrigerant is unknown use R22 Installation emissions occur at manufacturers site and are not relevant, unless maintenance personnel have recorded onsite recharge Disposal emissions not relevant to BNZ at leased facilities. Only relevant for owned property if disposal of refrigeration equipment occurs as part of refurbishment Default charge and leakage rates used where actual charge volume could not be collected from labelling on equipment Data provided by corporate travel provider is complete Global Warming Potentials have been taken from 2011 Guidelines to DEFRA/DECC’s GHG Conversion Factors for Company Reporting, July 2011 – Annex 5, Table 5a and 5b Business travel - air 2011 Guidelines to DEFRA/DECC’s GHG Conversion Factors for Company Reporting, July 2011 – Annex 6, Table 6I Business travel – employee claims for use of personal vehicles for work purposes Guidance for voluntary, corporate greenhouse gas reporting: Data and methods for the 2009 Calendar Year, NZ Ministry for Environment, Published May 2011– Table 6e : Average car (unknown fuel) As noted in Emissions Factor Source Documentation Activity data captured in passenger km (pkm) Flight categories applied are as follows: Domestic – economy – long distance (>1,200) Domestic – economy – short distance (≤1,200). This includes all domestic flights in UK and NZ. Long Haul International (>3700 km) - Business Long Haul International (>3700 km) – Economy Long Haul International (>3700 km) – Premium Economy Long Haul International (≥3700 km) – First Class Short Haul International (≤3700 km) – Business Short Haul International (≤3700 km) – Economy. This includes flights between New Zealand & Australia Activity data captured in distance travelled (kms) on claim forms GHG Emissions (t CO2-e) = Emission Factor Activity Data 1000 All personal vehicles are average passenger vehicles – average vehicle with unknown fuel Page 1 of 3 BNZ Carbon Inventory Emissions Source Business travel – hotel stays Emissions Factor Source Documentation Stationary electricity and associated transmission loss factors taken from: - 2011 Guidelines to DEFRA/DECC’s GHG Conversion Factors for Company Reporting, July 2011 – Annex 10, Table 10a/b: United States, New Zealand, Australia, Hong Kong, and United Kingdom - IEA CO2 Emissions from fuelled combustion Highlights (2010 Edition) – Section 6: Rest of World Calculation Method Activity data captured in nights stays (nights) Hotel Emission Factor = [Emission Factor Average hotel room activity] GHG Emissions (t CO2-e) = Hotel Emission Factor Activity Data (nights) 1000 Assumptions No Emissions from food consumption included in Hotel Emissions Data provided by corporate travel provider is complete Activity data captured in distance travelled (km) Passenger Transport Conversion tabes used. Data provided by service providers is complete Data provided by facilities manager and utilities is complete Natural gas and associated transmission loss factors taken from: - IEA CO2 Emissions from fuelled combustion Highlights (2010 Edition)Summary Tables - CO2 emissions per kWh from electricity and heat generation - Average 06-08: Rest of World, United States, New Zealand, Hong Kong, and United Kingdom - National Greenhouse and Energy Reporting (Measurement) Determination, Compilation 27 June 2009: Australia (Average of all states taken for transmission loss) Business travel – rental cars Stationary energy - diesel, gas and electricity Transmission losses – Stationary energy – gas and electricity Average hotel room activity data (per night) for electricity and natural gas taken from Emissions factors from CIBSE Guide F - Energy Efficiency in building – Section 20 Guidance for voluntary, corporate greenhouse gas reporting: Data and methods for the 2009 Calendar Year, NZ Ministry for Environment, Published May 2011– Table 7: Rental car - Small (<1600cc), Rental car Medium (1600-<2500cc) and Rental car - Large (≥2500cc) Guidance for voluntary, corporate greenhouse gas reporting: Data and methods for the 2009 Calendar Year, NZ Ministry for Environment, Published May 2011– Table 1: Distributed Natural Gas – Commercial, Diesel Combustion – Commercial, Table 4 Purchased electricity Guidance for voluntary, corporate greenhouse gas reporting: Data and methods for the 2009 Calendar Year, NZ Ministry for Environment, Published May 2011– Table 5: Transmission and distribution line losses for purchased electricity, Table 6: Transmission and distribution losses for distributed natural gas Activity data for electricity is in KWh Activity data for diesel is in Litres Activity data for gas is in GJ GHG Emissions (t CO2-e) = Emission Factor Activity Data 1000 Activity data for electricity is in KWh Activity data for diesel is in Litres Activity data for gas is in GJ GHG Emissions (t CO2-e) = Emission Factor Activity Data 1000 Data provided by facilities manager and utilities is complete Page 2 of 3 BNZ Carbon Inventory Emissions Source Base building energy - diesel, gas and electricity Transmission losses – base building energy – gas and electricity Business travel – taxi use Business travel – work use vehicle fleet (diesel and petrol) Waste to Landfill Work use vehicle fleet – air conditioning refrigerant Emissions Factor Source Documentation Guidance for voluntary, corporate greenhouse gas reporting: Data and methods for the 2009 Calendar Year, NZ Ministry for Environment, Published May 2011– Table 1: Distributed Natural Gas – Commercial, Diesel Combustion – Commercial, Table 4 Purchased electricity Guidance for voluntary, corporate greenhouse gas reporting: Data and methods for the 2009 Calendar Year, NZ Ministry for Environment, Published May 2011– Table 5: Transmission and distribution line losses for purchased electricity, Table 6: Transmission and distribution losses for distributed natural gas Guidance for voluntary, corporate greenhouse gas reporting: Data and methods for the 2009 Calendar Year, NZ Ministry for Environment, Published May 2011– Table 7: Taxi travel – Dollars spent (GST inclusive) Guidance for voluntary, corporate greenhouse gas reporting: Data and methods for the 2009 Calendar Year, NZ Ministry for Environment, Published May 2011– Table 2: Regular Petrol and Diesel Guidance for voluntary, corporate greenhouse gas reporting: Data and methods for the 2009 Calendar Year, NZ Ministry for Environment, Published May 2011– Table 9: Office Waste – no landfill gas recovery (New Zealand) and Office Waste – landfill gas recovery (New Zealand) Default refrigerant charge and default leakage rates taken from Guidance for voluntary, corporate greenhouse reporting Data and Methods for the 2007 Calendar year – New Zealand Ministry for Environment, September 2008. Global Warming Potentials have been taken from 2011 Guidelines to DEFRA/DECC’s GHG Conversion Factors for Company Reporting, July 2011 – Annex 5, Table 5a and 5b Calculation Method Activity data for electricity is in KWh Activity data for diesel is in Litres Activity data for gas is in GJ GHG Emissions (t CO2-e) = Emission Factor Activity Data 1000 Activity data for electricity is in KWh Activity data for diesel is in Litres Activity data for gas is in GJ GHG Emissions (t CO2-e) = Emission Factor Activity Data 1000 Activity data captured in $NZ spent on taxi travel GHG Emissions (t CO2-e) = Emission Factor Activity Data 1000 Activity data captured in litres of fuel GHG Emissions (t CO2-e) = Emission Factor Activity Data 1000 As noted in Source Documentation GHG Emissions (t CO2-e) = Emission Factor Activity Data 1000 Method reflects GHG Protocol worksheet titled hfc-pfc (1) - Worksheet 3: Screening Method for HFC and PFC Emissions from Refrigeration/AC Equipment: Emission Factor Based Approach: Step 2: Determine Net Gross HFC and PFC Emissions from Operation of Refrigeration/AC Equipment Assumptions Data provided by facilities manager and utilities is complete Data provided by facilities manager and utilities is complete All taxi expense is captured in relevant general ledger account(s) Expenditure is inclusive of GST Based on national average flagfall of $2.50 per kilometre travelled All fuel is purchased with fuel card provided For sites where waste data is not available, extrapolation of waste to landfill in tonnes has been made using waste tonnage per property area (m2) for the same class/type of property Average quantity of refrigerant charge for year estimated based on inventories recorded at the end of H1 (Jul-Dec) and H2 (Jan-Jun) Where Refrigerant is unknown have assumed refrigerant is R134A Installation emissions occur at manufacturers site and are not relevant for BNZ vehicle fleet Disposal emissions not relevant to BNZ vehicle fleet which are leased for a three year term of an agreed km distance and then returned to the fleet manager Page 3 of 3





