Basic Unit Conversions - UOIT.CA: Faculty Web Server
advertisement
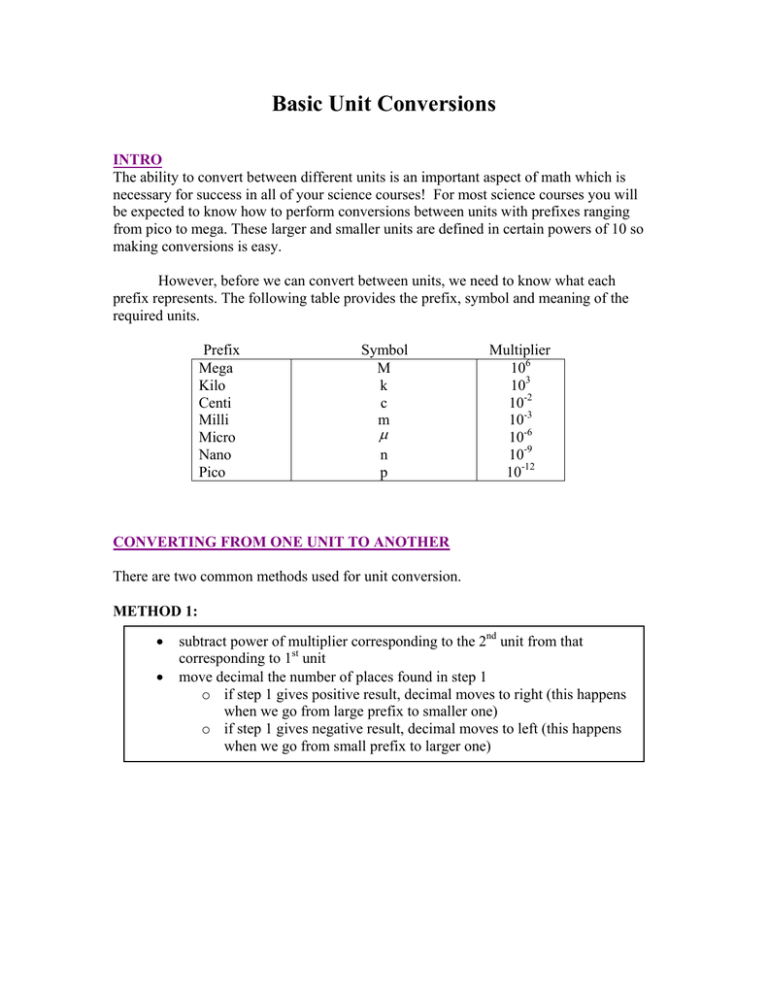
Basic Unit Conversions INTRO The ability to convert between different units is an important aspect of math which is necessary for success in all of your science courses! For most science courses you will be expected to know how to perform conversions between units with prefixes ranging from pico to mega. These larger and smaller units are defined in certain powers of 10 so making conversions is easy. However, before we can convert between units, we need to know what each prefix represents. The following table provides the prefix, symbol and meaning of the required units. Prefix Mega Kilo Centi Milli Micro Nano Pico Symbol M k c m μ n p Multiplier 106 103 10-2 10-3 10-6 10-9 10-12 CONVERTING FROM ONE UNIT TO ANOTHER There are two common methods used for unit conversion. METHOD 1: • • subtract power of multiplier corresponding to the 2nd unit from that corresponding to 1st unit move decimal the number of places found in step 1 o if step 1 gives positive result, decimal moves to right (this happens when we go from large prefix to smaller one) o if step 1 gives negative result, decimal moves to left (this happens when we go from small prefix to larger one) _______________________________________________________________________ Example: Convert 28 kg to mg. Solution: In order to convert 28 kg into mg, we would subtract the power of the multiplier for the 2nd unit (-3, since milligrams means we have 10-3 grams) from the first (3, since kilograms means we have 103 grams) 3 − (−3) = 6 Therefore, the decimal is moved 6 places to the right. Answer: 28 000 000 mg, which can be rewritten as 2.8 × 10 7 mg in scientific notation. _______________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Example: Convert 127 nm to μ m Solution: In order to convert 127 nm to μ m we would subtract power of the multiplier for the 2nd unit (-6, since micrometres means we have 10-6 metres) from the first (-9, since nanometers means we have 10-9 metres) − 9 − (−6) = −3 Therefore, the decimal is moved 3 places to the left. Answer: 0.127 μ m which can be rewritten as 1.27 × 10 −1 μ m in scientific notation. _______________________________________________________________________ METHOD 2: The second method is fairly similar to the first method. The number being converted is multiplied by a power of 10 which is determined by subtracting the power of the multiplier of the second unit from that of the first unit. The difference determines the power by which the value will be multiplied. _______________________________________________________________________ Example: Convert 326 μ g to kg Solution: Subtract the second multiplier’s power from that of the first: (3, since kilograms means we have 103 grams, is subtracted from -6, since micrograms means we have 10-6 grams) (−6) − 3 = −9 So, to perform the unit conversion, we multiply by 10-9. Answer: 326 ×10 −9 kg which can be written as 3.26 ×10 −7 kg in scientific notation. _______________________________________________________________________ CONVERTING MORE THAN ONE SET OF UNITS More advanced conversions often require two different units to be converted. The best method is to convert one unit at a time. _______________________________________________________________________ Example: Convert 18 km/hr into m/s. Solution: 18 km 1000m 1 hr 1 min × × × = 5 m/s 60 min 60 sec hr km Answer: Therefore 18 km/hr = 5 m/s _______________________________________________________________________ For a detailed explanation of some more difficult examples, check out the mini-clips!