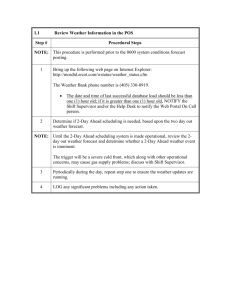
resource interconnection handbook
advertisement

RESOURCE INTERCONNECTION HANDBOOK Version 1.3 12/12/2014 This handbook is intended to provide a general description of ERCOT’s generator interconnection process for current and potential ERCOT Market Participants. This handbook is not a replacement for the ERCOT Protocols, Operating Guides, Planning Guide, or Other Binding Documents. In the event of any conflict, the ERCOT Protocols, Market Guides, and/or Other Binding Documents (OBDs) shall control. Version 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 Date 10/12/2012 10/24/2012 10/29/2012 11/1/2012 Author Al Garcia John Adams W. Rickerson John Adams 11/6/2012 Paul Tan 0.6 Description of Changes Original Document Draft Editing and reduction of scope Editing and Addition of Description of Changes/Table of Contents Replacing details of each process with checklist in appendix and other edits Editing, make Figure 2 and 3 consistent with Planning Guide, changes to Appendices G and H, updated TOC Editing for simplicity & clarity 11/13/2012 0.7 Incorporate comments Art Deller, Bill Blevins, 11/26/2012 0.8 Incorporate comments Patrick Coon, Ed Geer, Art Deller 11/30/2012 0.9 Editing and cleanup – initial draft 11/30/2012 1.0 Add planning model requirements, commercial operation requirements, corrections & Initial Issue Clarify SCADA Point plan, Generation checkout, and fate of projects if FIS scope not agreed to within 60 days. Incorporate recommendations of QMWG to clarify Update language to Incorporate ERCOT and Market Participant comments pertaining to the Resource Interconnection, Modeling, and Operations processes. 12/20/2012 Eric Adams/John Adams Art Deller, Bill Blevins, John Adams Ed Geer, Art Deller, Patrick Coon Woody Rickerson John Adams 12/28/2012 John Adams 3/29/2013 12/12/2014 John Adams Isabel Flores, Art Deller, Bill Blevins, Chad Thompson, Ed Geer, Ted Hailu, Patrick Coon 0.5 1.1 1.2 1.3 2 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS ...................................................................................................................... 3 ACRONYMS AND ABBREVIATIONS ................................................................................................. 4 DOCUMENT MAINTENANCE PROCESS ........................................................................................... 5 STAGE 1: HOW TO BEGIN: INTERCONNECTION STUDIES AND PROJECT DEVELOPMENT ......... 10 STEP 1: GINR AND SCREENING STUDY ............................................................................................................... 10 STEP 2: FULL INTERCONNECTION STUDY (FIS) ..................................................................................................... 11 STEP 3 – NEGOTIATION OF INTERCONNECTION AGREEMENT ................................................................................. 14 STEP 4 – SUBMITTING A RARF WITH RESOURCE DATA FOR PLANNING MODELS ....................................................... 14 STEP 5 – PROTOCOL COMPLIANCE REVIEW ......................................................................................................... 15 STAGE 2: REGISTRATION AND MODELING................................................................................... 16 STEP 1: REGISTRATION AS A RESOURCE ENTITY ................................................................................................... 16 STEP 2: MODELING, METERING, AND TELEMETRY ................................................................................................ 17 STAGE 3: ENERGIZATION, SYNCHRONIZATION AND COMMERCIAL OPERATIONS .................... 22 APPENDIX A: SUBCATEGORIES OF GENERATORS ........................................................................ 27 APPENDIX B: LIST OF ERCOT FORMS FOR INTERCONNECTION PROCESS ................................... 28 APPENDIX C: GUIDE TO PROTOCOL AND OTHER BINDING DOCUMENTS .................................. 29 APPENDIX D: SCREENING STUDY CHECKLIST ............................................................................... 30 APPENDIX E: GINR COORDINATOR CHECKLIST UPON RECEIPT OF FIS OR IA FROM TSP ........... 32 APPENDIX F: SSO STUDY – GRID SIDE SCREENING STUDY .......................................................... 35 APPENDIX G: FIS SCOPE MEETING CHECKLIST ............................................................................. 36 APPENDIX H: FIS MANAGEMENT PROCESS CHECKLIST ............................................................... 38 APPENDIX I: PROJECT PROTOCOL REVIEW CHECKLIST ................................................................ 41 APPENDIX J: ERCOT NOTICE FOR COMMISSIONING PLAN .......................................................... 42 APPENDIX K: MODELING REQUIREMENTS FOR SYNCHRONIZATION WITH THE GRID .............. 44 APPENDIX L: LETTER TEMPLATE SENT UPON EXECUTION OF IA ................................................ 46 3 ACRONYMS AND ABBREVIATIONS Acronym AVR ESI ID FIS GINR GINR Coordinator IE ME MRD NOIE NOMCR PFR POI PSS PUCT QSE RARF SCADA SCED SGIA TSP/TDSP Definition Automatic Voltage Regulator Electric Service Identifier Full Interconnection Study Generation Interconnection or Change Request The ERCOT Resource Adequacy analyst who owns the GINR database and coordinates engineering access Interconnecting Entity Meter Engineering Model Ready Date Non-Opt-In Entity Network Operations Model Change Request Primary Frequency Response Point of Interconnection Power System Stabilizer Public Utility Commission of Texas Qualified Scheduling Entity Resource Asset Registration Form Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition Security-Constrained Economic Dispatch Standard Generation Interconnection Agreement (commonly referred to as “IA”) Transmission and/or Distribution Service Provider 4 DOCUMENT MAINTENANCE PROCESS This document provides an overview of the process an Interconnecting Entity or a Resource Entity must follow as it progresses through the Generation Interconnection Process. While this document is primarily written for new Generation Resources interconnecting to the ERCOT grid at transmission voltages, it is expected to serve as a general guideline for other instances. Any revisions to this document will be made by ERCOT. When changes are made to this document, a market notice will be sent to Market Participants and the updated document will be posted to the ERCOT website. GENERATION INTERCONNECTION PROCESS The process of bringing a resource to commercial operation has been divided into three stages in this handbook for the purpose of defining the interactions between the developer of the resource and ERCOT. These stages are indicated below. . 1. Interconnection Studies and Project Development 2. Registration and Modeling 3. Energization, Synchronization and Commercial Operations Figure 1: Generation Resource Interconnection Process Flow In Stage 1, if the proposed resource adds 10 Megawatts or more of generation at the proposed Point Of Interconnection (POI), a Generation Interconnection or Change Request (GINR) application must be submitted to ERCOT along with applicable data and fees. Interconnecting Entities should review section 5.1.1 of the ERCOT Planning Guide for a more detailed description of the applicability of the GINR process for new Generation Resources as well as capacity upgrades, re-powering and changes to Points of Interconnection for existing Generation Resources. When ERCOT receives a GINR, ERCOT will notify the Interconnecting Entity of the receipt and completeness of the GINR, and conduct a series of screening studies to evaluate the proposed resource’s effect on the system. The completion of a screening study and a notice to proceed from the Interconnecting Entity sets into motion the Full Interconnection Study (FIS) process performed by the host Transmission and Distribution Service Provider (TDSP). Once all FIS studies are completed, a Standard Generation Interconnection Agreement (SGIA) may be executed with the host TDSP. Upon completion of the SGIA, Generation 5 Resource data sufficient to update the ERCOT planning cases shall be supplied by the Interconnecting Entity to ERCOT using the current version of the Resource Asset Registration Form (RARF). ERCOT then models the new Generation Resource in future planning base cases, which it then makes available to all registered Market Participants. Stage 1 requirements are documented in Section 5 of the ERCOT Planning Guides, available on the Planning Guide page of the ERCOT website. Registration of the Resource Entity and the associated new Generation Resource begins the transition to Stage 2. In Stage 2, the Interconnecting Entity becomes a Resource Entity, and registers as a Market Participant with ERCOT. Once registered, the Resource Entity is responsible for updating the RARF. ERCOT models the new Resource node by updating the Network Operations Model to reflect changes as a result of the addition of the new Generation Resource and related facilities. ERCOT reviews the proposed telemetry points list to establish real-time communication and control between ERCOT and the QSE. ERCOT also establishes ERCOT Polled Settlement (EPS) meter communication which allows gathering of 15-minute data for settlements. In Stage 3, ERCOT reviews the Generation Resource’s Commissioning Plan, and approves the following requests described in the New Generator Commissioning Checklist: a) Request to commission Point of Interconnection b) Request for Initial Synchronization c) Request to begin Commercial Operations In order for the Resource to be released for commercial operations, it must demonstrate that it can satisfy ERCOT’s requirements for Reactive Power (both leading and lagging), Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR), Primary Frequency Response (PFR), and Power System Stabilizer (PSS), as applicable to the Generation Resource type. Public Utility Commission of Texas (PUCT) Substantive Rules 25.198 governs the initiation of transmission service in Texas, and Substantive Rule §25.109 outlines the certification, licensing, and registration of generators. ERCOT Protocol Section 16.5 identifies additional requirements related to the registration of the Resource Entity as a Market Participant and the Generation Resources that it will represent in the ERCOT market. Refer to the following links for additional information. PUCT rules: http://www.puc.texas.gov/industry/electric/business/pgc/Pgc.aspx. ERCOT Protocols: http://www.ercot.com/mktrules/nprotocols/index.html ERCOT Planning Guides Section 5: http://www.ercot.com/mktrules/guides/planning/index Interconnecting Distributed Generation (less than 10 MW and at voltages below 60-kV) is described in PUCT substantive Rule 25.211, and is not discussed in this document. 6 Stage 3 Stage 2 Stage 1 What milestones do I need to keep track of? Figure 2: Major Milestones 7 How long does it take? Every project is different, and study lengths can vary. Interconnecting Entities may apply for interconnection year round, and add their Resource to the list of active projects by submitting a completed GINR application. Provided that all required information is received by ERCOT, interconnection studies are performed in the order in which they are received; however, ERCOT Planning Guides set some timeframes that both ERCOT and Interconnecting Entities must comply with during the interconnection process. Estimated Duration (days) (from completion of the prior Key Processes Generation Interconnection or Change Request (GINR) application process RARF provided to ERCOT ERCOT Screening Study Decision to proceed to Full Interconnection Study (FIS) FIS assigned to a TSP Negotiation of FIS study scope/pricing Complete RARF provided to ERCOT/TSP Full Interconnection Studies FIS Acceptance by ERCOT Decision to proceed with and execute Standard Generation Interconnection Agreement (SGIA) Submit executed SGIA to ERCOT Review and comment on project’s adherence to binding requirements Resource Registration and Modeling Resource Registration and Modeling Commissioning, Final Testing, Commercial Operations Responsible Party process - Some processes may run concurrently) Up to 25 Up to 10 Up to 90 Interconnecting Entity Interconnecting Entity ERCOT Up to 180 Interconnecting Entity Up to 5 ERCOT Up to 60 Interconnecting Entity and TSP GINR Cancellation ERCOT mediates discussions between IE and TSP Interconnecting Entity Up to 500 TSP Up to 15 ERCOT Up to 180 Interconnecting Entity Up to 10 GINR Cancellation TSP Up to 60 days ERCOT Up to 180 Resource Entity Up to 180 Resource Entity Up to 90 Resource Entity 8 Result if process requirements are not met The application does not proceed to the Screening Study phase until all documentation is provided. GINR deemed incomplete/rejected New Generator Commissioning Checklist requests are rejected Figure 3-Key Process Duration and Deadlines 9 STAGE 1: INTERCONNECTION STUDIES AND PROJECT DEVELOPMENT All transmission interconnected Generation Resources with a capacity equal to or greater than 10-MW, or an aggregate capacity equal or greater than 10-MW at the same point of transmission connection, must submit a Generation Interconnection Change Request (GINR). ERCOT may require Interconnecting Entities to follow the full process detailed in this guide for interconnection of Generation Resources with less than 10 MW of capacity interconnected at 60 kV or above. Interconnecting Entities should review section 5.1.1 of the ERCOT Planning Guide for a more detailed description of the applicability of the GINR process for new Generation Resources as well as capacity upgrades, re-powering and changes to Points of Interconnection for existing Generation Resources. Contact ERCOT Client Services if you have questions about the applicability of the interconnection process for a specific project. Stage 1 of the Generation Interconnection Process is described below in five steps: 1. GINR and Screening Study 2. Full Interconnection Study (FIS) 3. Negotiation of Interconnection Agreement 4. Submitting a RARF with Resource data for planning models 5. Protocol Compliance Review STEP 1: GINR AND SCREENING STUDY The first interaction with ERCOT comes through a GINR application. This application consists of three components: 1. Generation Entity Information Sheet 2. Resource Asset Registration Form RARF) 3. ERCOT Security Screening Study fee During this initial stage, the developer or group of developers is referred to as the Interconnecting Entity (IE) by ERCOT Protocols and other binding documents. An Interconnecting Entity should contact ERCOT at GINR@ERCOT.com to acquire an Interconnection Request (INR) number that should be referenced on all documents. The Generation Interconnection or Change Request process and related forms are available on the New Generation Resources page of the ERCOT website. Once completed, these forms may be submitted to ERCOT by email as distinct file attachments to GINR@ERCOT.com with e-mail subject containing the assigned INR number. The Interconnecting Entity is responsible for submitting the entire GINR application forms, including the RARF with the required Screening Study data using the applicable forms1. The Interconnecting Entity 1 The Resource Asset Registration Form (RARF) has entries describing the characteristics of the resource. Screening and Final interconnection studies may be completed with an abbreviated set of information. Instructions for what information must be filled out in each step are posted at http://www.ercot.com/mktrules/guides/resourcereg/library.html. Data required during the interconnection process are identified by column with “R” meaning “Required.” Data is to be entered on the currently posted version of the RARF and updated to new RARF versions if new versions are posted. No changes to the RARF form structure – worksheet names or order and column names or order are allowed. 10 will also declare its proposed Commercial Operation Date (COD) and the proposed Point of Interconnect (POI). In addition to submitting the GINR application forms, the Interconnecting Entity must pay an ERCOT Security Screening Study fee. The Screening Study fee will be determined by the capacity of the proposed resource. Please refer to the current ERCOT Fee Schedule posted on the ERCOT website for the ERCOT Security Screening Study fee.2 ERCOT may take up to 90 calendar days after submission of the GINR to complete the Screening Study. Details on fee submittal are found in the ERCOT Planning Guide Section 5.2.2. This study identifies steady state transmission constraints at the proposed Generation Resource’s Point of interconnection which will require transmission improvements to allow full output. Upon completion of the Screening Study, the Interconnecting Entity has 180-days to notify ERCOT in writing of its intention to pursue the project by proceeding to the Full Interconnection Study (FIS). If ERCOT does not receive the Interconnecting Entity’s notification that it intends to pursue the project within 180-days, the results of the Screening Study will expire, and the GINR will be cancelled. Any further action on the project will require a new GINR application, including the payment of a fee for a new study. A checklist describing the steps taken by ERCOT in the Screening Study is included in Appendix D. As a part of each Screening Study, the ERCOT engineer will review the point of interconnection for possible Sub-synchronous Oscillation (SSO) risk as follows. Screening Study: SSO Risk Grid Screen Sub-synchronous Oscillation screening is performed by ERCOT Staff if it is determined, through a visual evaluation of the proposed resource’s location, that any set of six Transmission Element outages can make the proposed generation interconnection connect in series to a series-compensated transmission line. Appendix F contains a checklist for performing this SSO screening study. 3 STEP 2: FULL INTERCONNECTION STUDY (FIS) The FIS is a set of 4 to 6 studies conducted by the TSP under an agreement with the Interconnecting Entity . These studies always include: 1. 2. 3. 4. Steady state and transfer analysis Short-circuit and breaker duty review Dynamic and transient stability analysis Facility study Two further studies may be required: 5. An SSO Study may be required based upon the results of the SSO screening analysis. 6. An Economic Study will be required if the estimated cost of transmission improvements exceeds 25 million dollars. FIS Scope Meeting 2 3 http://www.ercot.com/mktrules/nprotocols/current Contingencies may include transformer outages as well as transmission lines. 11 The Interconnecting Entity may request a Full Interconnection Study (FIS) scope meeting by submitting the items listed below via e-mail to the GINR coordinator at GINR@ercot.com: 1. 2. 3. 4. Written notice to “proceed with FIS” GINR application4 Payment of Full Interconnection Study fee Proof of Site Control This request may take place even before the Screening Study is completed if requested by the Interconnecting Entity, but ERCOT discourages this practice. When FIS studies are requested by the Interconnecting Entity, the ERCOT GINR coordinator notifies the engineer who performed the original Screening Study for this project, and enters the request date into the GINR database. The assigned engineer organizes the Full Interconnection Study (FIS) scope meeting with the TSP and Interconnecting Entity. A checklist for the FIS scope meeting is included in the Appendix G. The FIS scope meeting defines the scope of work for the Full Interconnection Studies. ERCOT will facilitate this interaction, and an ERCOT representative will either attend the initial meeting in person or participate via phone. It is the responsibility of the TSP and the Interconnecting Entity to reach an agreement on the scope of the studies within 60 days. If the TSP and the Interconnecting Entity cannot reach an agreement, the GINR will be terminated. Before this termination takes place, the ERCOT engineer will attempt to mediate an agreement. .Full Interconnection Study (FIS) The FIS proceeds as follows: 1. Once an FIS scope agreement has been reached between the Interconnecting Entity and the TSP, and the ERCOT engineer has approved the scope, the TSP proceeds with the studies. 2. After FIS scope agreement has been reached, ERCOT will publish the information listed below about the interconnection project as part of its next planning report to the Reliability & Operations Subcommittee as per ERCOT Protocols section 1.3.1.2. a. Project INR Number b. Facility nameplate capacity c. Facility fuel type d. County where facility is located 3. ERCOT verifies that it has received RARF data needed for the FIS per the Resource Registration Glossary and forwarded to the TSP performing the FIS studies, if necessary. All data sent to the TSP should also be sent to ERCOT as there is no requirement for the TSP to share this data with ERCOT. FIS Study descriptions 1. Steady State Analysis- This analysis is created from the most recently approved Steady State Working Group power flow base case for the interconnection year. It will identify transmission facilities which may have a limiting impact on resource output. The TSP shall perform contingency analysis sufficient to demonstrate that existing or planned 4 http://www.ercot.com/services/rq/re/newgen‐steps.html 12 transmission capacity in the area meets ERCOT Planning and Operating Guides and NERC transmission criteria following installation of the proposed resource. The TSP performs contingency analysis and documents any constraints in existing transmission facilities that are likely to limit generation output from the Resource. If such constraints are identified, the analysis will propose facility improvements which can accommodate the proposal without limitation. 2. Short Circuit Study - The FIS agreement shall specify locations where available shortcircuit fault duty will be identified, calculated, and documented. If any of the required transmission system improvements associated with the GINR result in violations of the TSP short circuit criteria, the TSP shall plan and identify facilities to address those violations. The initial short-circuit base case transmission configuration shall be the System Protection Working Group base case for the resource’s first planned year of commercial operation. 3. Dynamic and Transient Stability Analysis- The interconnecting TSP shall perform these studies examining the proposed Generation Resource’s response to transient events on the ERCOT transmission grid including local transmission faults and the expected normal and delayed clearing of faults. All existing or publicly committed resources in the area shall be modeled at full net output. The initial stability study base case transmission configuration shall be one of the latest approved Dynamic Working Group flat start cases adjusted to be consistent with the steady state base case in the region near the interconnection for the interconnection year. Transient Stability Studies will analyze the performance of the proposed Generation Resource and the ERCOT system. Studies must meet NERC requirements. 4. Facilities Study- This study provides details and estimated cost of the facility requirements for the direct interconnection of the proposed Generation Resource project to the TSP. The Facilities Study includes conceptual design descriptions, construction milestones, and detailed cost estimates for all direct interconnection-related transmission and substation facilities proposed to be installed in accordance with the findings and recommendations of other FIS studies. 5. SSO study - If the ERCOT Screening Study determines that a detailed SSO study is required; this study shall also be included in the scope of the FIS. 6. Economic Study - This study is required only if the ERCOT screening study or Full Interconnection Studies (typically steady state analysis) identify transmission upgrades expected to cost more than $25 million. If facilities cost is estimated as exceeding the $25 million threshold, notification from the TSP to ERCOT that an Economic Study will be required (email to GINR@ercot.com) must take place within ten days of estimating the facilities cost. This notification shall contain a description of the proposed interconnection facilities; information necessary to modify a power flow case to include these facilities, and any other information available to the TSP required to model the proposed generation resource and estimate cost/benefit of the proposed facilities. This study is performed by 13 ERCOT and does not require a financial contribution from the Interconnecting Entity. The study report will be available within 30 days of request after the analysis is completed. The TSP issuing the final FIS element report shall indicate that the report is the final report required by the FIS. At the end of the ten Business Day review period following the issuance of the final FIS element report, the FIS will be deemed complete and the Interconnecting Entity and TSP may execute an SGIA. If an economic study of the direct interconnection facilities is required, pursuant to Section 5.4.7, Economic Study, and has not yet been completed, the Interconnecting Entity and TSP may agree that the completion of the economic study is not required before the FIS is deemed complete. . ERCOT is not a party to the FIS contract. The cost and responsibility for completing each internal phase of the FIS lies with the Interconnecting Entity and the TSP. Currently, there is no specific time limit for completion of the FIS. However, the Interconnecting Entity is required to update ERCOT by updating the Pre-RARF any time there are changes to the proposed system design during the FIS process, and the Interconnecting Entity must provide an affidavit every March and September that the RARF is correct. The Interconnecting Entity is required to conduct new studies if the capacity increases by more than 20%, or if the proposed resource specifications are revised making the existing studies invalid. Note that planning guide 5.3.2 requires all Interconnecting Entities that have submitted an FIS request to submit to ERCOT, twice each year, for each proposed facility, an electronic copy of a notarized attestation that, to the best of the attesting party’s knowledge, the Resource registration form data are correct. The attestation shall be sent by email to GINR@ercot.com. This obligation to update continues even after any interconnection agreement is signed. Interconnecting Entities must immediately notify ERCOT and the relevant TSP(s) of any change in ownership and shall provide conclusive documentary evidence of the ownership change (such as a purchase/sale agreement). A checklist for ERCOT actions in coordinating the FIS studies is included in Appendix H. STEP 3 – NEGOTIATION OF INTERCONNECTION AGREEMENT The Standard Generation Interconnection Agreement (SGIA) is negotiated between the host TSP and the Interconnecting Entity. ERCOT is not a party to these negotiations or this agreement but should be provided an update of the status for the SGIA. The SGIA template is posted on the ERCOT website at the following link: www.ercot.com/content/services/rq/re/SGIA.DOC. The IA is filed with the Public Utility Commission of Texas (PUCT), and the TSP is required to send a copy of the signed IA to ERCOT within 10 days of execution. STEP 4 – SUBMITTING A RARF WITH RESOURCE DATA FOR PLANNING MODELS In accordance with the ERCOT Planning Guide Section 6.9 after the IA has been signed and all other Planning Guide Section 6.9 requirements are met, the Interconnecting Entity must provide ERCOT an updated RARF with all necessary data to model the Generation Resource in the Steady-State Working Group (SSWG), System Protection Working Group (SPWG), and Dynamics Working Group (DWG) 14 planning models. Glossary. The information necessary for submittal is detailed in the Resource Registration STEP 5 – PROTOCOL COMPLIANCE REVIEW After an interconnection agreement (IA) is signed by the TSP and the Interconnecting Entity; ERCOT is obligated by Protocol section 16.5 (3) to review and assess whether or not the Resource, as proposed in the RARF, would violate any operational standards established in the Protocols, Market Guides and Other Binding Documents. ERCOT has 60-days to review the document and provide a written determination of whether or not the proposed system design as provided in the RARF complies with protocols and other binding documents. A review must also take place if an IA is amended by one or both parties. In either case, the TSP informs the Public Utilities Commission and ERCOT of the new or revised IA. The TSP notifies ERCOT through GINR@ercot.com of the new or revised IA. ERCOT sends a form letter to the Interconnecting Entity with a list of information required to assess compliance with ERCOT Protocol and Planning Guides including data items needed to model the proposed resource in the Steady-State Working Group (SSWG), System Protection Working Group (SPWG), and Dynamics Working Group (DWG) planning models. Based on information from the FIS, IA and the RARF, ERCOT will evaluate whether or not the proposed resource meets all binding requirements for interconnection. If, based on the information contained in the FIS, IA, RARF and other submitted data, ERCOT determines that the resource does not meet binding requirements, or if ERCOT cannot determine whether the resource will meet the requirements, the engineer in charge of the project will provide a written document to the Interconnecting Entity explaining this determination. Additional data may be requested at this time. Additional data is provided to ERCOT by updating the RARF with any other required studies or documents. The Interconnecting Entity is required to submit to ERCOT a reactive study that provides an engineering analysis of the reactive capability of the proposed interconnected generation facilities. This study shall include the list of equipment and systems that are to be installed to meet ERCOT reactive support requirements. It is recommended that the Interconnecting Entity incorporate in their project plan at least one month for ERCOT to review and approve the study with consideration for lead-time necessary for procurement of associated equipment. New generation facilities adding reactive equipment, in addition to the generation’s reactive capability specified in the ERCOT approved reactive study, shall have the reactive equipment installed in the field and ready to be placed in service at the time of initial synchronization. All Generation Resources connecting over 20 MVA of gross capacity or those units connected at the same POI aggregating to greater than 20 MVA of gross capacity, shall provide VSS and AVR according to Protocol Section 3.15 Voltage Support. 15 STAGE 2: REGISTRATION AND MODELING ERCOT and Transmission Service Providers are responsible for the physical operation of the ERCOT electric grid and the coordination of the ERCOT power market. These complex tasks are made possible by a set of internal software systems that track, model, control, and manage data about the ERCOT grid. Connecting a new generation resource to the grid requires that these systems be updated with accurate engineering models of the new resource and associated equipment. Through this process, the new generation resource will become part of the ERCOT Network Operations Model. Addition of information to the ERCOT Network Operations Model is controlled by strict procedures. This model underlies all of ERCOT’s commercial and operational systems. The registration and modeling process ensures this data is accurate and that communication between ERCOT systems and the new resource’s systems by way of the QSE are in place before the resource is commissioned. All entities that either own or control an All-Inclusive Resource connected to the ERCOT System must register as a Resource Entity (RE). The RE must register each All-Inclusive Resource through ERCOT registration by completing a current version of the Resource Asset Registration Form (RARF). The Resource registration process incorporates electronic and manual processes to submit, validate, approve, and authorize ERCOT to apply Resource Asset data in studies, planning, market and operation systems per Protocol and Planning Guide Section 6.8. For the remainder of the interconnection process, ERCOT’s Client Services department is the primary contact for the newly registered Resource Entity. The ERCOT Client Services department is responsible for tracking each Generation Resource through the remaining steps of the interconnection process and facilitating interactions between ERCOT, the Resource Entity and QSE as well as resolution of any issues that may arise. Each Resource Entity is assigned an account manager upon registration who serves as the primary contact for all of its interactions with ERCOT. The assigned account manager is responsible for guiding each Resource Entity through the end of the interconnection process and beyond as the Resource starts commercial operation in the ERCOT market. STEP 1: REGISTRATION AS A RESOURCE ENTITY With the completion of a signed SGIA, the Interconnecting Entity or resource owner registers as a Resource Entity (RE) in the ERCOT market. Power Generation Companies operating within Texas are also required to register with the Public Utility Commission of Texas in accordance with PUCT Substantive rules which may be found at http://www.puc.texas.gov/agency/rulesnlaws/Default.aspx.5 Registering the Resource Entity is necessary for completing a Resource Asset Registration Form that is used for modeling the resource in the Network Operations Model. ERCOT recommends that the Resource Entity register as a Market Participant at least 140 days prior to the date that the new resource is to be added to the Network Operations Model. The Resource Entity needs to complete the RARF with all data for the new resource at least 130 days prior to the desired date that the new resource and associated equipment is to be added to the Network Operations Model on the Model Ready Date (MRD). Selecting the desired MRD, needs to be based on the desired initial energization date and initial synchronization date. The MRD needs to precede the desired initial proposed energization date by at least 15 - 30 days to allow time to resolve issues with telemetry or other operational issues. An overall 5 When this document was written, PUCT requirements for registration were contained in rule 25.109 “Registration of Power Generation Companies and Self‐Generators” 16 schedule of the milestones in Stage 2 is contained in the New Generation Coordination Log that is sent to the Resource Entity by the assigned ERCOT account manager. Registration as a Resource Entity usually takes 10 to 15 days and is composed of the following key components: 1. Submission of Resource Entity (RE) Application for Registration 2. Execution of a Standard Form Market Participant Agreement The Resource Entity Application for Registration form has 3 critical subcomponents: 1. Basic Entity Information - Each registering Resource Entity needs to provide basic company information that allows ERCOT to enter the entity into the Registration systems and populate ERCOT systems with necessary information. This information includes legal company name, Dun & Bradstreet DUNS number, address and company officers. 2. Designation of a Qualified Scheduling Entity (QSE) - Each new Resource Entity must designate a QSE to be associated with the new generation resource. This QSE will work with the RE during the commissioning and final steps of the interconnection process. The QSE will be responsible for scheduling and directing ERCOT dispatches to the generation resource. For an overview and more information on QSEs and QSE qualification, see the QSE Qualification Guide. 3. Designation of contacts for communication with ERCOT: Every Resource Entity must identify key personnel, which will serve as primary contacts for a variety of ERCOT activities related to market operations and system operations. The contacts listed below are crucial towards completing the remaining steps of the Generation Interconnection Process: o Authorized Representative – Responsible for authorizing all registration information required by ERCOT Protocols and ERCOT business processes o User Security Administrator (USA) – Responsible for managing the Resource Entity ’s access to all of ERCOT’s computer systems including the Market Information System (MIS) through digital certificates o Resource Outage Submittal Contact (ROSC) – Responsible for coordinating and submitting Resource outages to ERCOT o Outage of transmission facilities owned by the Resource Entity - All Resource Entities must notify ERCOT whether the host TSP or ERCOT will submit outage requests for transmission facilities owned by the Resource Entity in the Outage Scheduler. Complementary to the Resource Entity Application for Registration is the Managed Capacity Declaration Form. This form identifies for ERCOT the Decision Making Entity (DME) whether itself or another legal entity with authority over the generation resource, including the authority to offer the resource into the market. STEP 2: MODELING, METERING, AND TELEMETRY The final technical phase of the interconnection process begins once the Resource Entity completes registration as a market participant and registration of the resource via the Resource Entity registration process. In this step, the logical and system structure for dispatching, metering, and communicating with the new generator will be established and verified prior to modeling the Resource in the ERCOT Network 17 Operations Model. This model is updated on a scheduled basis, with a set model load date calendar6. On the Model Ready Date (MRD), ERCOT systems will link together the following key components: 1. Metering and Meter Data Acquisition System (MDAS) 2. ERCOT market settlement information and pricing location 3. Supervisory Control And Data Acquisition (SCADA) and Inter-Control Center Communication Protocol (ICCP) communication points 4. QSE and Resource Entity relationship and contact information Establishing these links requires coordination between all involved Market Participants and internal ERCOT departments. ERCOT Client Services maintains a New Generation Coordination Log as a reference for this process. Appendix B also provides a list of forms and links to the ERCOT website where Resource Entities can find the forms and additional information on how to submit modeling data to ERCOT. The MRD for loading the new resource and associated equipment into the Network Operations Model is expected to precede the desired Planned Energization Date of the Point of Interconnection by at least 15- 30 days. The responsibility for these submissions is shared between the TSP, Resource Entity, and QSE. TSP must submit: 1. Model data through the Network Operations Model Change Request (NOMCR) process The TSP is responsible for submitting network modeling information to ERCOT for equipment it owns through the NOMCR process. More details about this process are available in the Network Operations Modeling and Expectations Guide 2. Metering plan – EPS Design Proposal The design of EPS equipment and a one-line diagram of the TSP’s interconnection and the generator site topology. This plan is reviewed and approved by ERCOT’s Meter Engineering group. The Meter Engineering group will also conduct a site certification review after energization. For more details about metering and technical requirements refer to the Settlement Metering Operating Guide 3. Meter Data Acquisition Form Verification of meter communication with ERCOT meter polling systems. 4. EPS Cutover Form Submitted 15 days before meters are officially cut-over to ERCOT’s systems, this will occur at the same day as the model load date. QSE must submit: 1. Outage Schedule 6 The model load calendar is located on the ERCOT website at: http://www.ercot.com/gridinfo/transmission/opsys‐change‐schedule.html 18 In the final stage of the interconnection process before energization, on the MRD the new resource will become live in ERCOT systems. To ensure that the generator is not dispatched by ERCOT, the QSE must submit an outage through the Outage Scheduler. This outage status will be updated throughout the final verification and testing phases. 2. ICCP Points List The ICCP Points List contains the needed resource and interconnection telemetry points that the QSE plans on providing, subject to the intended network model topology indicated in the RARF. This ICCP Points List is built in collaboration with the QSE and ERCOT’s Energy and Market Management Systems (EMMS) Production Support organization. The QSE will provide ERCOT a points list of proposed SCADA points and their definition for ERCOT to review and begin implementing. The list of required telemetry points is indicated in the Nodal ICCP Communication Handbook.7 The Resource Entity and QSE should use the list below for typical telemetry requirements in creating and submitting an ICCP QSE Points list for a new generation Resource site. All telemetry should be provided as required in the ERCOT Nodal ICCP Communications Handbook and should include the following for all modeled equipment as specified in the RARF: 1. For each modeled generation Resource o o o o Gross and Net MW Gross and Net MVAr, PSS status (Note: can be set to 'Off' for wind or solar Resources) AVR status 2. For each modeled generator auxiliary load and/or station service load ( if on the high-side) o o MW MVAr 3. For each modeled Reactor / Capacitor bank including dynamic reactive devices (SVC, STATCOM, etc.) o MVAr (Note: can be provided from each modeled control breaker) 4. For each modeled Breaker and Disconnect o Breaker/disconnect statuses (low-side and high-side, where the high slide is not owned by the TSP) 5. For each modeled Generator Step-Up Transformer on the high-side o o o MW flows MVAr flows Voltages (KV) 6. For each modeled Generator Step-Up Transformer on the low-side 7 The Nodal ICCP Communication Handbook is an Other Binding Document, posted on the ERCOT website at: http://www.ercot.com/services/mdt/userguides/index 19 o Voltages (KV) 7. For each modeled Transmission line to the Point of Interconnection (POI) if the POI is not at the same substation as the Generation Resource site o o o MW flows MVAr flows Note: the RE and QSE should confirm that the TSP will submit Transmission line MW and MVAr flows for the POI at the TSP station. 8. For each modeled Wind Generation Resource o Met data - as measured at the site 9. Other Resource site telemetry, as requested by ERCOT The ICCP Points List is provided as a final update of the communication and telemetry points agreed upon between ERCOT and the QSE in compliance with the Nodal ICCP Communication Handbook. Typically development of the ICCP Point List is an iterative process between the QSE and ERCOT, whose purpose is to ensure that ERCOT will have all the necessary telemetry to monitor the ERCOT grid prior to station energization and synchronizing the generator to the grid. Upon submittal of the ICCP QSE Points list, ERCOT will review and provide preliminary feedback regarding the ICCP Points List to the QSE and Resource Entity. 3. Verifiable Costs Verifiable Cost encompasses data that represents the actual start-up and minimum energy at Low Sustainable Limit (LSL) applied in economic commitment and deployment in accordance with ERCOT Protocol Section 5.6.1, Verifiable Cost. Resource Entity must submit: 1. Model data through the ERCOT-prescribed process applicable to Resource Entities o The Resource Entity is responsible for submitting the RARF with network modeling information to ERCOT for equipment it owns through the ERCOT-prescribed process applicable to Resource Entities. 2. Generation Node and Meter Mapping package (GENMAP) verification The Generation Node and Meter Mapping (GENMAP) package is compiled by ERCOT and provided to the Resource Entity. The GENMAP package provides documentation on the detailed modeled configuration of how the resource node and metering will be mapped in the Network Operations Model on the Model Ready Date. The Resource Entity will review and provide confirmation to ERCOT that the Generation Node and Meter Mapping is accurate by submitting the Resource Node & EPS Meter Mapping Verification document included in the Generation Node and Meter Mapping package. 3. Updated RARF data 20 If at any point the parameters of the All-Inclusive Generation Resource that are documented on the RARF are changed, the Resource Entity must submit updated RARF data in accordance with the ERCOT Planning Guide Section 6.8.2. All RARF data submissions and verifications are designed to take effect on the MRD. On this day, with submission of the EPS Cutover form, all telemetry and metering with ERCOT will be fully functional and the resource will appear in the ERCOT Network Operations Model. At this point, the All-Inclusive Generation Resource is modeled such that it later can be dispatched, scheduled, and settled in ERCOT market systems. 21 STAGE 3: ENERGIZATION, SYNCHRONIZATION AND COMMERCIAL OPERATIONS Background Stage 3 is governed by the ERCOT New Generator Commissioning Checklist (Checklist). This Checklist is intended to coordinate the energization and synchronization of a new All-Inclusive Generation Resource, as well as provide the Resource Entity approval to declare commercial operation of said new All-Inclusive Generation Resource, once all qualification measures have been met to the satisfaction of ERCOT. Approximately 30 - 55 days prior to the MRD, the QSE shall submit the ICCP Point List to ERCOT. It is expected that the ICCP Points List includes parameters of the new Generation Resource and associated equipment, including the interconnecting transmission substation equipment. If insufficient information is provided during the modeling process, there is a high risk of delay in the synchronization, commissioning, and commercial operation of the new resource. At least 30 days before the Resource Entity plans to submit Checklist PART 1, the Resource Entity is to submit a commissioning plan detailing how the facility will be operated during Stage 3, including testing of generation and systems while supporting grid security in accordance with ERCOT Protocols, including, but not limited to Section 3.15, Voltage Support. Resource Entities adding capacity to existing Generation Resources, re-powering previously commissioned Generation Resources or changing / adding Points of Interconnection may use the commissioning plan to communicate their plans to ERCOT and determine what parts of the commissioning process are applicable to their specific project. ERCOT shall review the commissioning plan and provide feedback with regards to compliance with operational standards and identify possible operational limitations during the commissioning process within 15 days of receipt. The commissioning plan must include the planned dates for all ERCOT required testing and Checklist submissions. A template commissioning plan is posted on the ERCOT website along with the Checklist. The Checklists verify critical communication points and generation security measures before allowing the Resource Entity to energize the point of interconnection, synchronize generation, and prepare for commercial operations. This Checklist process is coordinated by ERCOT Client Services, and Checklist approvals are made by ERCOT Operations Support. Checklist submittals and approval: Separate Checklists must be submitted for each new Generation Resource associated with the same Point of Interconnection. Submit all Checklists to ERCOT’s Client Services Department. Prior to submitting Part-1 (energization of Point of Interconnection) of the Checklist, the QSE, Resource Entity, and interconnecting Transmission Service Provider shall ensure that the transmission switchyard facilities have been modeled in ERCOT’s Network Operations Model, constructed, energized and operational. ERCOT recommends that Part-1 of the Checklist be submitted at least 7 Business Days in advance of the planned date for energization of Point of Interconnection ERCOT shall provide a response to a submitted Checklist part within 3 Business Days of receipt. This is to allow ERCOT to incorporate the new Generation Resource into operational studies and troubleshoot any identified issues. ERCOT recommends that Checklist PART 2 and PART 3 be submitted after satisfactory completion of testing and approval of the previous Checklist part by ERCOT 22 ERCOT recommends that the planned date for Part-2 (synchronization) and Part-3 (commercial operations) of the Checklist be at least 7 Business Days from the date ERCOT approves the previous Checklist part. Any Checklist PART submitted prior to receiving approval of the previous Checklist PART will be considered as being submitted on the next business day after the approval of the previous Checklist part by ERCOT 23 Checklist Submissions for Existing Generation Resources Seeking to Increase Output Existing Generation Resources who submit plans to increase their capability still follow the standard interconnection process. Upon reaching Stage 3 of the interconnection process, these Generation Resources are still required to submit the Checklist. ERCOT understands that PART 1 and PART 2 are somewhat redundant as the Generation Resource is already connected to the ERCOT grid and providing commercial power. ERCOT still requires PART 3 of the Checklist to be submitted to ensure that the Generation Resource is able to pass all required testing up to the increased capability. This check helps ensure that any Generation Resource previously exempt from PSS requirements as indicated in Section 2.2.6 of the ERCOT Nodal Operating Guides that have done work on their excitation systems have installed a PSS and are operating with it in service. A few final notes on Checklist submissions: ERCOT typically approves Checklist PART submissions for execution on Business Days only, during the hours of 8 AM to 5 PM Central Prevailing Time. Due to ERCOT system operations personnel shift schedule rotations and technical support limitations, ERCOT requests that Resource Entities submit Checklist approvals for target dates on Tuesday through Saturday excluding ERCOT holidays. Checklist submissions received by ERCOT after 4 PM Central Prevailing Time will be considered as received by ERCOT on the following Business Day. ERCOT’s approval of Part-1 and Part-2 of the checklist, energization of the Generation Resource Point of Interconnection and synchronization of the Generation Resource to the grid, is given for a specific target day requested by the Resource Entity and is subject to real-time grid operating conditions. Accordingly, the Resource Entity’s QSE must contact the ERCOT control room as per ERCOT’s Operating Procedures and receive permission to proceed prior to station energization or synchronization of the Generation Resource. In the event that system conditions are such that energizing the Generation Resource station facilities or allowing the Generation Resource to synchronize to the grid will place unnecessary risk to the ERCOT Interconnection, ERCOT System Operators have the authority to cancel or otherwise prohibit these actions.” All generation resources connecting over 20 MVA of gross capacity or those units connected at the same Point of Interconnection aggregating to greater than 20 MVA of gross capacity shall provide VSS and AVR according to Protocol Section 3.15 Voltage Support. This means that for Generation Resources, such as wind or solar plants, who plan on energizing their facility as new equipment is installed, shall have the ability to provide VSS as required in the Protocols once the gross connected capacity of the Generation Resource exceeds 20 MVA. If unable to provide VSS until the Generation Resource is fully constructed, the Resource Entity may continue commissioning the new equipment so long as the Resource Entity self-limits connected capacity and output from the Generation Resource to 20 MVA.8 Once a Generation Resource has enough generation capacity available for AVR and VSS control, the Resource Entity is to request approval from ERCOT to generate above 20 MVA and up to the capability in which the Generation Resource can provide voltage control. The manner in which a Generation Resource can operate above 20 MVA shall be documented in the Commissioning Plan. Process 8 For Intermittent Renewable Resources planning on providing VSS through the use of capacitor and reactive banks, it is encouraged that those reactive devices be installed at the beginning of Stage 3 (prior to Checklist PART 1 approval) to maximize output from the Generation Resource during the Commissioning process. 24 Upon submittal of PART 1 of the Checklist, ERCOT shall review it for accuracy and completeness. ERCOT shall then perform a verification of the network model and SCADA telemetry, and perform system studies as appropriate to ensure that no reliability risks exist with providing energization approval. ERCOT shall provide a response within 3 Business Days of receipt. If any problems are encountered with the network model or SCADA telemetry that cannot be readily resolved, ERCOT shall reject PART 1 of the Checklist, and request the QSE, Resource Entity or Transmission Service Provider, where appropriate, to review and correct any outstanding issues as required, and then resubmit Checklist PART 1. PART 1 of the Checklist shall not be resubmitted until all identified problems have been resolved to the satisfaction of ERCOT. As indicated above, PART 1 of the Checklist should not be submitted before the interconnecting transmission switchyard facilities have been modeled with ERCOT, are constructed, energized and operational. The same process for Checklist PART 1 applies with Checklist PART 2. ERCOT shall review the model and telemetry, and perform system studies as appropriate, rejecting PART 2 of the Checklist if any problems are encountered that cannot be readily resolved. Use of On‐Test Status during the Commissioning Process During the commissioning process for a new resource, the QSE will submit a resource status in accordance with Protocol section 3.9.1 Current Operating Plan (COP) Criteria. The status of “ONTEST” should be used during the actual testing of the resource. ERCOT System Operations may require that a QSE provide a MW schedule for the Generation Resource’s output for the duration of the planned test. At the point when the resource is not testing and is on control and capable of following SCED Base Points and curtailment flags, the resource would begin using an “ON” status in the COP and telemetry. Resources using an “ON” status are subject to Base Point Deviation charges and GREDP monitoring. Checklist PART 3 approval requires verification of several generator parameters such as reactive capability, primary frequency response, and voltage control. Obtaining approval of Checklist PART 3 is dependent on the time necessary for the Resource Entity and QSE to perform all required performance testing. Once all testing has been performed and Checklist PART 3 is submitted to ERCOT, ERCOT shall review all test results and approve Checklist PART 3 as appropriate. If any issues are identified with regards to performance testing that cannot be readily resolved, ERCOT shall reject the PART 3 submittal, and request the QSE, Resource Entity or Transmission Service Provider, where appropriate, to review and correct any outstanding issues as required, and then resubmit Checklist PART 3. PART 3 of the Checklist shall not be resubmitted until all identified problems have been resolved to the satisfaction of ERCOT. Once Checklist Part 3 approval has been given, ERCOT allows the Resource Entity to declare its Resource available for commercial operations. Final review by ERCOT Operations and initial qualification testing has been completed. 25 The Reactive Capability, AVR, PSS and Governor Performance tests The Reactive Power Capability, AVR, PSS and Governor Performance tests are the final step before approval to be released for commercial operations. These tests are described in the ERCOT Operating Guides sections 2.2.5 (AVR), 2.2.6 Power System Stabilizers, 2.2.7 (Turbine governors), and 3.3.2.2 – 3.3.2.3(Reactive testing). All ERCOT required testing must be completed and submitted to ERCOT within 90 days of receiving ERCOT approval of PART 2 of the Checklist. If all ERCOT required testing has not been completed within 90 days of receiving ERCOT approval of PART 2 of the Checklist, ERCOT may direct the Generation Resource to isolate from the grid until the required testing has been completed or mitigation plans have been established to address operational risks until the testing can be completed. Typically, coordinated Reactive Power Capability tests are performed in coordination with ERCOT and the TSP as described in section 3.3.2.3 Coordinated Reactive Testing of the ERCOT Operating Guides to allow for assistance of other reactive resources needed to exercise the full reactive capability of the new resource. Although ERCOT operating guides recommend maximum leading reactive tests be performed in low load months, and maximum lagging reactive tests be performed in high load months, this is often not possible for initial operation. Coordinated Reactive testing is generally required for PART 3 approval. If issues arise in completing a non‐coordinated reactive test, then a coordinated reactive test will be required. No extensions to complete reactive testing for PART 3 approval are provided. If either leading or lagging reactive test cannot be completed due to RE plant limitations, the issues must be resolved and a new reactive test conducted. If either leading or lagging coordinated reactive test cannot be completed due to limitations on the TSP/ERCOT system (not due to limitations inside the RE plant) then approval of the reactive test may be granted if all submitted information and test results meet ERCOT requirements. Otherwise, additional reactive testing will be required. 26 APPENDIX A: SUBCATEGORIES OF GENERATORS Combined Cycle Train Combined Cycle Generation Resource Intermittent Renewable Resource (IRR) Quick Start Generation Resource (QSGR) Split Generation Resource Switchable Generation Resource Wind-powered Generation Resource (WGR) The combinations of gas turbines and steam turbines in an electric generation plant that employs more than one thermodynamic cycle. For example, a Combined Cycle Train refers to the combination of gas turbine generators (operating on the Brayton Cycle) with turbine exhaust waste heat boilers and steam turbine generators (operating on the Rankin Cycle) for the production of electric power. In the ERCOT market, Combined Cycle Trains are each registered as a plant that can operate as a Generation Resource in one or more Combined Cycle Generation Resource configurations. A specified configuration of physical Generation Resources (gas and steam turbines), with a distinct set of operating parameters and physical constraints, in a Combined Cycle Train registered with ERCOT. A Generation Resource that can only produce energy from variable, uncontrollable Resources, such as wind, solar, or run-of-the-river hydroelectricity. A Generation Resource that in its cold-temperature state can come On-Line within ten minutes of receiving ERCOT notice and has passed an ERCOT QSGR test that establishes an amount of capacity that can be deployed within a ten-minute period. Where a Generation Resource has been split to function as two or more independent Generation Resources in accordance with Section 10.3.2.1, Generation Resource Meter Splitting, and Section 3.10.7.2, Modeling of Resources and Transmission Loads, each such functionality independent Generation Resource is a Split Generation Resource. A Generation Resource that can be connected to either the ERCOT Transmission Grid or a non-ERCOT Control Area. A Generation Resource that is powered by wind. Wind turbines may be aggregated together to form a WGR if each turbine is the same model and size and located behind the same GSU transformer. 27 APPENDIX B: LIST OF ERCOT FORMS FOR INTERCONNECTION PROCESS Process/Form Entity Location Submission Generation Interconnection or Change Request (GINR) Screening Study Data submission SGIA IE GINR@ercot.com IE Resource Registration RE New GINR Page (TBD) New GINR Page (TBD) New GINR Page (TBD) RE Registration Standard Market Participant Agreement Managed Capacity Declaration Form Resource Asset Registration Form (RARF) Resource Registration Glossary RE SFMA ERCOT Account Manager or clientservices@ercot.com ERCOT Legal via fax or mail RE RE Managed Capacity Form RARF Forms ERCOT Account Manager or clientservices@ercot.com MIS System IE/RE Res Reg Glossary RARF submission requirements EPS Design Proposal TSP/RE EPS Design Form MDAS Form TSP/RE MDAS Form epsmetering@ercot.com, ERCOT Account Manager mreads@ercot.com EPS Cutover Form TSP/RE EPS Cutover Form Outage Schedule QSE MIS System epsmetering@ercot.com, 1ERCOTEAADataAggregation@ercot.com Through MIS outage scheduler QSE ICCP Points List QSE MIS System Through MIS service request New Generation Checklist, Part 1 Request for Unit Testing RE New Gen Checklist QSE Operating Procedures ERCOT Account Manager or clientservices@ercot.com Sent to the ERCOT Shift Supervisor: shiftsupv@ercot.com. New Generation Checklist, Part 2 Net Dependable Capability and Reactive Capability (NDCRC New Generation Checklist, Part 3 QSE New Gen Checklist QSE MIS System RE/QSE New Gen Checklist IE 28 GINR@ercot.com GINR@ercot.com ECS representative or clientservices@ercot.com Through MIS dashboard ERCOT Account Manager or clientservices@ercot.com APPENDIX C: GUIDE TO PROTOCOL AND OTHER BINDING DOCUMENTS Key Processes References Feasibility studies and project development Planning Guide Section 5 Generation Interconnection or Change Request (GINR) application process Decision to proceed ERCOT Screening Study Full Interconnection Study (FIS) FIS acceptance Decision to proceed with Standard Generation Interconnection Agreement (SGIA) SGIA signed and approved by ERCOT Resource registration and modeling Planning Guide Section 5.2 RE Registration RARF Completion Metering Certification, final testing, commercial operations Communications Outage Scheduling Decommissioning and RMR Contracts Planning Guide Section 5.3 Planning Guide Section 5.4.1 Planning Guide Section 5.4.2 Planning Guide Section 5.4.8 Planning Guide Section 5.5 Planning Guide Section 5.5 Protocol Sections 2, 3, 16 Nodal Operating Guides Sections 2, 3, 5, 7 Protocol Section 16.5.2 Other Binding Documents Protocol Section 10 Settlement Metering Operations Guide Nodal Operating Guide Sections 2, 3, 7 Nodal Operating Guide Sections 7 Nodal ICCP Communication Handbook Protocols Section 3.1 Protocols Section 3.14 Protocols Section 22 Attachment 29 APPENDIX D: SCREENING STUDY CHECKLIST □ □ □ (1) Assigned ERCOT Engineer check for GINR, project name, and intended year of interconnection in the generation interconnect folder and determine if enough data is available and notifies the Interconnecting Entity if anything more is needed within 5-days of the project receipt. (2) When all information is available to complete the screening study, the engineer sends an email to the Interconnecting Entity notifying it that the application is now complete. (3) The assigned ERCOT Engineer selects a Steady State Working Group summer peak base case from data set B, and performs the following modifications: □ Add projects in the vicinity with a recently signed IA which were not included in the base case □ Add approved TPIT transmission projects that are in the vicinity, and according to the engineer’s judgment, are likely to affect the study results. □ Increase nearby dispatchable thermal generation to 100% output and nearby wind to 80% output if in the West and 95% output if in the Coast. “Dispatchable” excludes Mothball, Private Use Network, Hydro, Nuclear, Equivalent, and Blackstart, as these are not normally available for dispatch. Engineer inspects the NON_MB_GENS subsystem list and removes any Resources which are nearby the interconnection study area. The increase in nearby generation is counter-balanced by scaling down generators in subsystem NON_MB_GENS. □ If the slack bus is in the study vicinity, the Engineer changes it to a distant generator. □ All changes are noted in the report. □ (4) If the project is in the South or West zone, the project may be affected by nearby wind patterns. The engineer will thus create a second case for study, a high wind case, □ (5) Engineer lists the identified equipment overloaded in study case(s). □ (6) Engineer adds the proposed generator to the study case with capacity indicated by the Interconnection Request and engineer sets the Qmin and Qmax reactive power limits to fixed quantities corresponding to a 0.95 power factor capability. (7) Using AC Transfer Limit Analysis, ERCOT engineer examines base case and N-1 contingency limitations for the proposed generators. Engineer identifies Max transfer limit and limiting contingency and element for each scenario. Engineer documents these results in the report using the report template. (8) If flows on transmission equipment are >100% of the equipment rating with the study generator injecting at 120% of capability, the ERCOT engineer identifies and models appropriate transmission upgrades or additions as necessary to allow injection without limit violations. Equipment rating upgrades will be applied using industry standard available conductor and facility ratings. The ERCOT engineer reruns the study to confirm the overloads are resolved. (9) The engineer notes the list of applied upgrades or reconfigurations in the report. (10) Reviewing a map, ERCOT engineer determines the number of outages that can make the proposed generator interconnection connect in a series to a series-compensated transmission line. If so, engineer performs a Subsynchronous grid side screening study. (11) If additional Point of Interconnection will be studied, repeat all steps for additional POI. □ □ □ □ □ 30 □ □ (12) Engineer emails report to the IE noting that IE has 180 days to request a Full Interconnection Study. Engineer calls the IE to confirm study was received. (13) Engineer updates the GINR database with completion date 31 APPENDIX E: GINR COORDINATOR CHECKLIST UPON RECEIPT OF FIS OR IA FROM TSP Upon being notified of a completed FIS or new IA, the GINR coordinator enters into the GINR database the signature date and ERCOT receipt date, and notifies the Resource Integration Manager. The ERCOT receipt date is important because it starts the 60 day review period which ERCOT must meet. The GINR coordinator sends a form letter to TSP with a list of requirements to meet ERCOT Protocol and Planning Guides. The GINR coordinator notifies via email and hard copy the Manager of Resource Integration and the engineer assigned to the project that the IA has been received. Resource Integration Engineer checklist upon notification that IA received The Resource Integration engineer assigned to the project reviews the project design utilizing the following checklist. □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ Confirm design will be able to meet all reactive power requirements. □ Produce ±0.95 Power factor reactive at all MW levels between LSL and HSL Protocol section 8.1.1.2.1.4. □ At the Point of Interconnection (high side of main transformer). Protocol section (3.15 [3]) □ Dynamically provide voltage regulation (or has documented permission from ERCOT to use switchable shunts). Protocol section 3.15 □ Able to respond to changes in the voltage profile. Protocol section 3.15 □ For Generation Resources under test phase, a reactive requirement proportional to the test output would have to be met. The full 0.95 lead/lag capability of the name plate would have to be fulfilled at the time of energization. This requires the Generation Resource to maintain ±0.95 power factor or less to support the reactive requirements at the Point of Interconnection (POI). This needs to be maintained at various levels of varying output from the plant. The generation resource shall provide ERCOT documentation which shows a reactive support study in compliance with protocols. ERCOT shall review these study reports and documents and ensure the reactive requirements have been met. Confirm a Power System Stabilizer or equivalent is included in the design if the generator is a synchronous machine: Protocol section 3.15.3[4] All QSEs providing VSS must have a PSS for the generation resource and need to provide telemetry to ERCOT. The design shall include the PSS specifics and needs to be notified to ERCOT while the FIS study scope is being decided. Confirm the Generation Resource will provide frequency response: Protocol section 8.5.1.1 and 8.5.1.3 Generation Resources that have capacity available to either increase output or decrease output in Real-Time must provide Primary Frequency Response, which may make use of that available capacity. Only Generation Resources providing Regulation Up (Reg-Up), Regulation Down (RegDown), Responsive Reserve (RRS), or Non-Spinning Reserve (Non-Spin) from On-Line Resources, as specified in Section 8.1.1, QSE Ancillary Service Performance Standards, shall be required to reserve capacity that may also be used to provide Primary Frequency Response. Confirm the Generation Resource will dynamically provide voltage regulation: Protocol section 3.15 Confirm breaker interruption capability of main high-side breaker is suitable to fault duty 32 □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ Confirm transient voltage ride through per Protocols and operating guides: Operating Guide section 2.9 All generation resources shall meet the operating guide section 2.9 requirements with wind powered resources or Intermittent Renewable resources meeting the 9 cycle voltage ride through requirements as shown in the figure below: VRT requirements may be met by the performance of the generators; by installing additional reactive equipment behind the POI; or by a combination of generator performance and additional equipment behind the POI. VRT requirements may be met by equipment outside the POI if documented in the SGIA. Confirm AVR is included in the design, and it will be operated in voltage control mode. Protocol section (3.15.3 & 3.15 [5]) Confirm the Generation Resource can respond to changes in the voltage profile. Protocol Section 3.15 Confirm reactive capability is based upon the ability to deliver to the HIGH side of the step-up transformer. Protocol section (3.15 [3]) The ERCOT Engineer evaluates the information provided by IE, cites evidence sources that back up the decision, formulates a protocol compliance review letter to the Interconnecting Entity, and scans a copy of results to the project folder. Resource Integration Engineer then sends letter to Legal Department for review. Upon authorization from Legal Department, the engineer sends the letter to the interconnecting TSP and IE. Engineer copies Model Administration and ERCOT Client Services (Account Rep, if designated already) on the email. Engineer also notifies RI Manager of checklist completion and of the results. If the ERCOT engineer’s decision was negative, or “not enough information”, TSP is directed to send information necessary to the same engineer. In case of “not enough information” ERCOT engineer must specify which changes need to be made. Engineer updates the GINR database the day the letter is sent to the TSP and IE, entering the date in the appropriate field, and saves a copy of the IA review letter in the project folder. The Resource Integration Engineer, in consultation with Model Administration, evaluates whether the RARF information needed to include the proposed resource in the SSWG, SPWG, and DWG planning models and identified in the Resource Registration Glossary has been provided. If the engineer’s decision was “Insufficient information at this time” or “Not meeting standards”, engineer repeats steps 7 through 11 as needed until all requirements are met, at which time; engineer updates the GINR database with the date of IA approval. 33 ERCOT engineer informs GINR coordinator via email that Protocol section 16.5 requirements have been met. The GINR coordinator acknowledges via email. The project is now ready to move to the Modeling and Registration stage of the interconnection process, and to be included in Resource Adequacy’s future capacity projections. 34 APPENDIX F: SSO STUDY – GRID SIDE SCREENING STUDY PSCAD will be used to perform the necessary screening for the relevant case related to each interconnection request. The study shall be performed in the following phases: Phase 1- Base Case Preparation □ □ □ □ □ Select the base case created in the screening study for the year of interconnection. Perform Contingency analysis using TARA to confirm case is stable under contingency conditions. Define the area to be modeled in PSS/E using the area command and equivalence the rest of the model. Include in the conversion at least 5 buses in every direction from the POI to capture appropriate detail. If necessary include lower or higher kV levels Enter Step up transformer parameters for the POI in PSSE case before it is converted. Create a .raw file as input to ETran. Phase 2- Conversion using ETran □ □ Setup ETran parameters for a hybrid Pi model. Use the .etr file for Etran settings. Convert the base case selected will be converted into .psc format using ETran software Phase 3 – PSCAD run □ □ □ □ □ □ Read the ETran converted electromagnetic model of the area into PSCAD. Create the frequency injection model from the point of turbine connection, and the Graph model in PSCAD. Run a simulation of current injections at different frequencies, and model the frequency/impudence characteristic of the grid for base case conditions. Create scenarios based on the credible planning contingencies as per NERC standard TPL-005 contingencies. Plot Resistance(R) and Reactance(X) are plotted under these conditions. (To prepare for the next contingency, system adjustments may be made, including changes to generation, uses of the transmission system if necessary to make a credible case under contingencies) Once all possible ERCOT credible contingencies have been studied, create a scenario in which the connection of the POI is radial with that of series compensation. To prepare for the next contingency, system adjustments may be made, including changes to generation, uses of the transmission system if necessary to make a credible case under contingencies Prepare a report, in which R and X of the system are observed over the range of frequencies and observed for zero crossings of R and/or dips in X at certain frequencies is graphed. The general selection of applicable contingencies for studies is outlined in the ERCOT Planning Guides section 4. Contingencies and performance are identified in the ERCOT ISO System Planning methodology, ESP-METHOD-03 System Planning Contingency Identification. 35 APPENDIX G: FIS SCOPE MEETING CHECKLIST The Interconnecting Entity initiates the Full Interconnection Study (FIS) scope meeting process by submitting to the GINR coordinator, through GINR@ercot.com the following: o o o o o Written notice to “proceed with FIS” Resource Integration form Stability Modeling fee Proof of Site Control RARF data requirements per the Screening Study/Full Interconnection Study Guides for information needed for FIS. This can happen even before the Screening Study is completed. GINR coordinator notifies, via email, the ERCOT engineer who performed the original Screening Study for this project. □ □ □ □ □ □ The ERCOT engineer enters the request date into the GINR database. If the original Engineer (performed the screening study) is not available, GINR coordinator informs RI Manager so he can assign the FIS Scoping meeting duties to another ERCOT engineer. ERCOT engineer notifies IE whether it has provided all necessary information as part of the SGIA application. o If information is not sufficient, ERCOT engineer instructs IE to provide it promptly. o IF the information is not forthcoming after ten days, ERCOT engineer must contact IE via email and phone to request missing information. o If sufficient information not provided within 20-days the ERCOT engineer turns problem over to Manager. Once the information is provided, the ERCOT engineer determines if ERCOT has already completed a Screening Study for the project. o If it has not, then Engineer notifies IE that a Screening Study must be performed concurrently, and that the IE must request a screening study and pay screening study fees. Information provided by Interconnecting Entity will be used for the screening and FIS studies. o ERCOT engineer allows 10-days for a screening study to be requested. If a screening study is not requested the engineer notifies the Interconnecting Entity via email that the FIS request will be cancelled if a request for a screening study is not received within 30days with payment of screening study fees. o If a screening study request is not received within 35-days, a study cancelation notice is sent by the ERCOT engineer and the project canceled. The ERCOT engineer selects the lead Transmission Service Provider (TSP) to deal with the Interconnecting Entity (IE), within five days of getting the notice from the IE to proceed with a Full Interconnection Study (FIS), as indicated in Planning Guide 5.4.2.1 (1). This selection is based on the analysis of the most likely point of interconnection. ERCOT engineer contacts the TSP, and all other TSPs through the Transmission Owners Generation Interconnection list, to schedule a FIS scope meeting with IE. If ERCOT has already conducted a Screening Study, ERCOT engineer checks GINR database to determine if the Screening Study is over 180-days old. If it is, ERCOT engineer notifies IE that the FIS cannot be conducted because the deadline has passed, and that IE needs to apply for new GINR. 36 ERCOT engineer sends a copy of this letter to ERCOT Legal department. To increase the likelihood of projects getting past this stage, the new GINR database will send out a reminder email 90-days after Screening Study completion. If Screening Study has been conducted within the last 180-days, ERCOT proceeds with the FIS scope meeting. The ERCOT engineer determines if he/she has dealt with TSP(s) and/or IE previously. If they are new, then ERCOT engineer will attend the FIS Scope meeting in person. If the ERCOT engineer has met with them during last twelve months, then ERCOT engineer can participate in the meeting via telephone. At the scoping meeting, the IE presents the proposed GINR and ERCOT reviews the results of the Screening Study with the transmission provider. If during the Screening Study it was determined that a Sub Synchronous resonance study was needed, the results of the study are added to this FIS scope. If parties to not agree on the scope of work, including additions by ERCOT or TSP, (final cost, etc.) the ERCOT engineer will attempt to mediate for a period of 60-days. o If no agreement is reached during this 60 day period, ERCOT must then determine whether to terminate the GINR (Planning Guide 5.4.2.1 (8). ERCOT will send out an automated email (using new GINR database’s SharePoint/email functionality) after 30days have passed since the scoping meeting if no notification of agreement has been received. Another one, with more urgent wording, will be sent out after 45-days. If parties agree on the FIS scope at the meeting, IE has 10-days to make any changes or comments. o □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ Once the FIS scope agreement has been reached, ERCOT engineer reviews the scope within ten days of receipt. o check the assignment list for Protocol and Planning Guide information needed ERCOT engineer enters into the GINR database the FIS scope agreement date 37 APPENDIX H: FIS MANAGEMENT PROCESS CHECKLIST The FIS process described here can take place even before the Screening Study is completed. The FIS is conducted by the TSP, but the TSP is mandated to keep ERCOT updated of progress. Future Protocol or Planning Guide revisions will be aimed at making this part of the interconnection process more transparent to ERCOT in order to avoid surprises (equipment changes, capacity changes, etc.) □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ The ERCOT engineer will receive the Steady State study report when submitted to the Transmission Owners Generation Interconnection list The ERCOT engineer reviews the Steady State study report to determine/confirm what transmission improvements will be required to integrate the Resource. If the ERCOT engineer or other TSPs desire clarification or additional information on the Steady State study report, they send an email requesting clarification to the TSP producing the study within 10-days. If no comments are received or all comments are addressed, the TSP producing the report submits the accepted copy to the Transmission Owners Generation Interconnection list. The ERCOT engineer will save the study report in the study folder on System Planning/GenInterconnect. The ERCOT engineer enters the date the Steady State study report was accepted into the Steady State Study field of the GINR database. The ERCOT engineer will receive the Short Circuit study report when submitted to the Transmission Owners Generation interconnection list. The ERCOT engineer reviews the Short Circuit study report and confirms that local breakers have sufficient fault duty to clear a local fault. For areas in ERCOT with low short circuit ratio/grid strength, the ERCOT engineer reviews the Short Circuit study report and examines if the installed generator will have sufficient short circuit current to meet the generator vendor recommendations (normally an issue for induction machines to remain stable). If the ERCOT engineer or other TSPs desire clarification or additional information on the Short Circuit study report, they send an email requesting clarification to the TSP producing the study within 10-days. If no comments are received or all comments are addressed, the TSP producing the report submits the accepted copy to the Transmission Owners Generation Interconnection list. The ERCOT engineer will save the study report in the study folder on Gen Interconnects If no revisions are necessary, the ERCOT engineer sends an email to the TSP and IE notifying them that the Short Circuit study report is accepted by ERCOT The ERCOT engineer records the date the Short Circuit study report was accepted into the GINR database into field Short Circuit Study. The ERCOT engineer will receive the Dynamic & Transient Stability Analysis report when submitted to the Transmission Owners Generation interconnection list. The ERCOT engineer reviews the Dynamic & Transient Stability Analysis report to determine/confirm that the grid remains stable and the Generation Resource remains online under typical fault conditions. If the ERCOT engineer or other TSPs desire clarification or additional information on the Dynamic &Transient Stability Analysis report, they send an email requesting clarification to the TSP producing the study within 10-days. 38 □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ If no comments are received or all comments are addressed, the TSP producing the report submits the accepted copy to the Transmission Owners Generation Interconnection list. The ERCOT engineer requests the power flow case(s) for the Dynamic & Transient Stability Analysis report, and saves the study case(s) into the study folder on System Planning/GenInterconnect. The ERCOT engineer will save the Dynamic & Transient Stability Analysis study report in the study folder on GenInterconnect. The ERCOT engineer records the date the Dynamic & Transient Stability Analysis report was accepted into the GINR database in field Dynamics Study. The ERCOT engineer will receive the Facilities Study report when submitted to the Transmission Owners Generation interconnection list. The ERCOT engineer reviews the Facilities Study report. If the ERCOT engineer or other TSPs desire clarification or additional information on the Facilities Study report, they send an email requesting clarification to the TSP producing the study within 10-days. If no comments are received or all comments are addressed, the TSP producing the report submits the accepted copy to the Transmission Owners Generation Interconnection list. The ERCOT engineer will save the Facilities Study report in the study folder The ERCOT engineer records the date the Facilities Study report was accepted into the GINR database in field Facilities Study Accepted. The ERCOT engineer reviews projected costs of interconnection and enters the estimated cost of integration into the “Estimated Integration Cost” field of the GINR database. If the cost is over $25M an Economic study is required. □ □ □ □ □ □ □ □ If an Economic Study is required, the ERCOT engineer sets the “Economic Study required” field in the database to “YES”. Otherwise he sets it to “NO”. IF an Economic Study is required, the ERCOT engineer sends an email to the ERCOT manager of Mid Term Planning requesting this study, and agrees upon a timeline for the study. IF an Economic Study is required, the ERCOT engineer notifies the interconnecting TSP and IE of the projected completion for this study. IF an Economic Study is required, when the Economic study is complete, the ERCOT engineer sends the Economic study report to the TSP resource integration group for comments within 10-days. The ERCOT engineer will save the Economic study report in the study folder If no revisions are necessary, the ERCOT engineer sends an email to the TSP and IE notifying them that the Economic study report is accepted by ERCOT. The ERCOT engineer enters the date of the Economic study acceptance in the “Economic Study Date” field of the GINR database. (If no economic study was created this field remains blank) IF the ERCOT Engineer receives an SSO study as a part of the FIS scope, the date it was received is entered into the “SSO Study Received” field of the GINR database. □ IF an SSO study is required, when the SSO study is complete, the ERCOT engineer sends the SSO study report to the TSP resource integration group for comments within 10-days. 39 □ □ □ □ □ The ERCOT engineer will save the SSO study report in the study folder. The ERCOT engineer reviews the SSO study to determine if mitigation is required by either the TSP or the resource. If no revisions are necessary, the ERCOT engineer sends an email to the TSP and IE notifying them that the SSO study report is accepted by ERCOT. The ERCOT engineer enters the date of the SSO study acceptance in the “SSO Approved” field of the GINR database. (If no SSO study was created this field remains blank) If mitigation is required, the ERCOT engineer coordinates the mitigation actions with the TSP and the IE, and records a summary in the GINR database notes. □ Once all individual studies in the FIS have been accepted, the FIS is deemed complete. The ERCOT engineer enters the date into the “FIS_approved” field of the GINR database. After the FIS is completed, the TSP and IE have 180-days to sign an IA, per ERCOT Planning Guide, 5.4.8 (5). If the resource has been registered, the ERCOT receives updated RARF information from the Resource Entity as a result of the FIS process. ERCOT loads the updated information into the RARF Planning Hub. If the resource has not been registered, the ERCOT engineer receives the updated RARF data and stores it in the project folder on SystemPlanning/GenInterconnect 40 APPENDIX I: PROJECT PROTOCOL REVIEW CHECKLIST Background: The Standard Generation Interconnection Agreement or SGIA (commonly referred to as the “IA”) is signed by the Transmission Service Provider (TSP) and the Interconnecting Entity (IE). This review is also triggered if the IA is amended by one or both parties. In either case, The TSP informs the Public Utilities Commission and ERCOT of the agreement via email to GINR@ERCOT.com. The TSP is required by ERCOT Planning Guide 5.5.1 to do so within 10days in ERCOT’s case, and within 30-days in the case of the PUC. The GINR coordinator enters into the GINR database the SGIA signature date and ERCOT receipt date, and notifies the Resource Integration Manager via email (triggers assignment of review). These are important dates, because the receipt date starts the 60 day review period within which ERCOT must review the projects compliance with protocol and other binding requirements. These dates also enable the RI Manager to determine the efficiency of the IA review process. The GINR coordinator sends a form letter to the IE with a list of data requirements required to analyze compliance with ERCOT Protocols and other binding documents and for inclusion in the SSWG, SPWG, and DWG planning models. The RI Manager directs the ERCOT engineer already assigned to project preform the Protocol and Guide reliability review. (1) The ERCOT engineer retrieves the IA from the GINR mailbox, and utilizing the IA information, RARF information, and FIS study results (including study cases), evaluates the compliance of the resource development with protocol requirements. A list of items checked is listed in Appendix E of this document. (2) The ERCOT engineer scans a copy of the completed protocol review results (Appendix E) to the project folder and fills in the results in the GINR database. (3) The ERCOT engineer sends a letter documenting compliance to Legal Department for review, before sending letter out to TSP and IE. A template for this letter is attached as Appendix L. (4) Upon authorization from Legal Department, the engineer sends the letter to the TSP and IE via email. The ERCOT engineer copies ERCOT Client Services on the email. (5) The Engineer notifies the RI Manager of protocol checklist completion and of the results. a. If the ERCOT engineer’s decision was negative, or “not enough information”, the IE is directed to send information necessary to the same engineer. In case of “not enough information” ERCOT engineer must specify which changes need to be made. (6) The ERCOT engineer updates the GINR database the day the letter is sent to the TSP and IE, entering the date in the appropriate field, and saves a copy of the IA review in the project folder. a. If the engineer’s decision was “Insufficient information at this time” or “Not meeting standards”, engineer repeats steps 1 through 6 as needed until all requirements are met, at which time; engineer updates the GINR database with the date of IA approval. (7) ERCOT engineer informs Operations Support Engineering Supervisor that Protocol review is completed successfully. ERCOT engineer informs GINR coordinator via email that protocol review (protocol 16.5 (3)) requirements have been met. 41 APPENDIX J: ERCOT NOTICE FOR COMMISSIONING PLAN Prior to submitting a request for approval to energize a new generation facility, ERCOT may request a written plan describing commissioning of the new generation facility from submittal of PART 1 of the Checklist to ERCOT through anticipated approval of PART 3 of the Checklist. ERCOT Nodal Protocols Section 16.5 allows ERCOT to refuse initial energization if the new generation facility cannot demonstrate compliance with the operational standards established in the Protocols, Planning Guide, Nodal Operating Guides and Other Binding Documents (including the Nodal ICCP Communication Handbook). ERCOT may review the commissioning plan and provide feedback if the plan indicates possible non-compliance with such operational standards. Once ERCOT has reviewed and provided feedback on the Commissioning Plan, and the Resource Entity and QSE have considered ERCOT’s comments, the QSE may submit PART 1 of the Checklist if the Generation Resource is ready for initial energization, pursuant to the Stage 3 criteria of the Generation Interconnection Process. The Commissioning Plan should have sufficient detail which explains how the new Generation Resource will manage the testing of generation and systems while supporting grid security in accordance with the ERCOT Nodal Protocols and Operating Guides. At a minimum, the Commissioning Plan should provide relevant high-level facility information, such as maximum generation and load capabilities and generator fuel type (e.g. wind, solar, combined-cycle, etc). In addition, a schedule in tabular format should be included, detailing estimated dates for the following: 1. Energization of the POI, if new 2. Submittal of each PART of the Checklist 3. Initiation of energization, synchronization, and QSE-declared commercial operation 4. Availability of control systems and other equipment (e.g. static reactive devices, AVR, PFR, PSS, etc.) needed to support grid security 5. Testing the facility to meet Checklist PART 3 requirements (e.g. leading/lagging reactive capability, AVR, PFR, etc.) The Commissioning Plan should also provide details and a schedule for the following: A. Dates on estimated number of generating units planned to be online in ONTEST mode for testing per specified period (Hour Ending and Operating Day, etc.). An explanation of what tests are being run during periods the Generation Resource is reported to ERCOT with resource status as “ONTEST” shall also be provided. B. Explanation of sequence and length of time for 1.) Orderly shutdown; and 2.) Urgent shutdown, in the event it is necessary for ERCOT to issue a verbal instruction to suspend testing and shutdown due to system reliability event for which the capability of new generation is not available due to commissioning. C. Explanation of how the QSE and Resource Entity will confirm telemetry quality during commissioning period through validation, monitoring performance, and troubleshooting. 42 If changes are made by the Resource Entity to the plan then the Resource Entity must communicate those changes to ERCOT and ERCOT shall determine if a modified Commissioning Plan should be resubmitted. In accordance with Protocol Section 16.5(4), ERCOT reviews facility design capability. The current capabilities reviewed are listed below. ERCOT recommends that the Commissioning Plan provides sufficient detail to evaluate the availability of capabilities that will be available during the commissioning period and explanation of associated response times in accordance with ERCOT Nodal Operating Guides 2.2.10. Confirm design will produce ±0.95 Power factor reactive at all MW levels between LSL and HSL Protocol section 8.1.1.2.1.4. Confirm a Power System Stabilizer or equivalent is included in the design: Protocol section 3.15.3[4] Confirm the Generation Resource will provide frequency response: Protocol section 8.5.1.1 and 8.5.1.3 Confirm the Generation Resource will dynamically provide voltage regulation: Protocol section 3.15 Confirm breaker interruption capability is suitable to fault duty Confirm transient voltage ride through per Protocols and operating guides: Operating Guide section 2.9 Confirm AVR is included in the design, and it can be operated in voltage control mode. Protocol section (3.15.3 & 3.15 [5]) Confirm Generation Resource can respond to changes in the voltage profile. Protocol section 3.15 Confirm reactive capability is based upon the ability to deliver to the HIGH side of the step-up transformer. Protocol section (3.15 [3]) Confirm the Generation Resource is able to receive control signals from its QSE in an upward and downward direction. (Normally referred to as AGC; Protocol section 8.1.1.2.1.1 and 8.1.1.4.1(7-8)) Confirm under-frequency relays installed meet the requirements of operating Guide 2.6.2 Frequency Range Delay to Trip Above 59.4 Hz No automatic tripping (Continuous operation) Above 58.4 Hz up to And including 59.4 Hz Not less than 9 minutes Above 58.0 Hz up to And including 58.4 Hz Not less than 30 seconds Above 57.5 Hz up to And including 58.0 Hz Not less than 2 seconds 57.5 Hz or below No time delay required Additional documentation that supports the information requested in items A-C above is encouraged. Please note if any technical documents referenced in the Commissioning Plan were already provided to ERCOT during the engineering design study in accordance with Protocol Section 16.5 (3). 43 APPENDIX K: MODELING REQUIREMENTS FOR SYNCHRONIZATION WITH THE GRID In order to describe the “Approval to Energize Process” two concepts must be defined. The first concept is the model-ready date (MRD) which is required in the RARF’s Unit Info tab-sheet. The MRD corresponds with the energization date associated with a NOMCR. The MRD is the date that the new piece of equipment first appears in the ERCOT Network Operations Model production environment. The MRD must correspond with a Scheduled Model load date (http://www.ercot.com/gridinfo/transmission/opsys-change-schedule.html). The MRD will also correspond with the date that new piece of equipment must initially be outaged (for most cases, or for a few rare cases: Outaged-with-Closed state as to not affect existing power flows) in the ERCOT Outage Scheduler. Resources must email the ERCOT Outage Coordinators to have outages entered in the Outage Scheduler. The second term is the date that corresponds with the field-energization of a piece of new equipment. The field-energization date is the date the new equipment is energized in the field and is ready for normal or test service. The energization of new equipment in the production environment will be preceded by two conditions. First, the equipment must be modeled in NMMS in its final normal state. Secondly, a Planned Outage exists in the Outage Scheduler with an end time that corresponds to the energization of the new equipment. Relocated equipment that is moved from one location to another, or is re-energized in a new configuration in the same substation should be processed through the same A2E process as new equipment. The relocated equipment should be modeled as new equipment. Training on use of the outage scheduler is available through ERCOT training services. A catalogue of available courses is posted on the ERCOT website at: http://www.ercot.com/services/training/courses.html The outage scheduler user manual is available on the ERCOT website at: http://www.ercot.com/content/services/mdt/userguides/wholesale/ERCOT%20Nodal%20Outage%20Sche duler%20User%20Guide%20for%20QSE%20v1.1.pdf To begin the approval-to-energize process; ERCOT Operations will review Part 1 Request to Commission Point of Interconnection checklist, and if all is in order, agree to allow energization on a specific date. The interconnecting TSP shall revise the outages in the Outage Scheduler to schedule the transmission equipment as in service on the energization date. ERCOT outage schedulers review on a daily basis equipment that is to be energized in seven days. Equipment that is reported as ready for energization in seven days will be studied as energized in the current production model. If no problems are anticipated, ERCOT will send an email to the owner of the equipment stating that the Approval to Energize is expected to occur and that no problems are anticipated. If upon investigation of the current production model problems are found, then the email sent to the owner of the equipment will detail the problems and state that the Approval to Energize could be delayed if the problems are not fixed prior to the requested energization date. Market Participants are required to contact ERCOT Operations when the problems are corrected. When problems have been corrected, ERCOT will verify, and send an email that the new equipment can be energized as scheduled. 44 In some cases the future equipment that is to be energized may not be in the current production model. The operator will receive a notice stating the equipment to be energized in seven days is not in the current model and that the Approval to Energize may be delayed. In these circumstances, the operator of the equipment is required to call ERCOT Operations and provide details as to when the equipment is expected to be loaded into the production environment. With the appropriate communication, the energization date for the new equipment will not be delayed. Once ERCOT has verified the equipment is in the production model and meets the Approval to Energize standards, an email will be sent to the owner of the new equipment confirming that it can be energized as scheduled. When interconnection requirements are met, ERCOT Operations will contact the ERCOT Shift Supervisor and notify them of the expected energization dates and any other recommended actions. Market Participants are required to request approval from the ERCOT Shift Supervisor for the activation of any new equipment or a relocated transmission facility that is connected to the ERCOT Transmission Grid, according to ERCOT Protocols Section 3.3.1. The request notification shall be by phone from the Market Participant to the ERCOT Shift Supervisor or designee on the day of the energization. If the ERCOT Shift Supervisor or his designee and ERCOT Operations are in agreement, then he/she will allow the equipment to be energized. Below is an example of the Approval to Energize process. 45 APPENDIX L: LETTER TEMPLATE SENT UPON EXECUTION OF IA Dear <Person’s first name>: Sixty days after ERCOT receives notification of a generating resource having signed an Interconnection Agreement, ERCOT is required by Nodal Protocols Section 16.5 (3) to assess whether the Resource, as proposed, would violate any operational standards established in the Protocols, Planning Guide, Nodal Operating Guides, and other binding documents. This letter is in response to your recent signing of an Interconnection Agreement. In addition to the protocol review, ERCOT is required to include resources meeting the requirements of ERCOT Planning Guide Section 6.9 in the ERCOT planning cases for SSWG, SPWG, and DWG. The creation of these planning cases requires additional resource data that is detailed in the Resource Registration Glossary. In order to effectively perform this review, ERCOT needs key pieces of information. It is to your advantage to submit this information early so that ERCOT can provide more useful feedback regarding the compliance of your resource. Key documentation required: 1. Resource Asset Registration Form (RARF). A complete RARF is not required for this review; refer to Resource Registration Glossary for fields required for Planning Model. 2. Impedance data of step-up transformer. 3. For generators with a collector system (e.g. wind farms, solar farms): Power flow model (including short circuit data) of collector system (PSSE RAW and SEQ file formats preferred). 4. Statement of intention to provide dynamic and automatic voltage regulation service. 5. Statement of intention to provide frequency response. (Statement not necessary if governor droop settings are provided in the RARF.) 6. Statement of intention to install and operate a power system stabilizer. (Required for all synchronous generators.) 7. Results of FIS Stability and Short Circuit studies. 8. Results of FIS Sub synchronous study, if required. If you have already submitted completed documents, resubmission is not necessary. Upon starting the review, an engineer will contact you and verify what has been received. ERCOT requests you provide these documents within three weeks of the date of this letter in order to be sure they will be included in the review. Please email your documents to GINR@ercot.com. While fully completed documents are ideal, we realize that resources may not have all the necessary information at this time. ERCOT will accept incomplete documents, with the understanding that: (1) Protocol compliance will be evaluated based only on the information provided, (2) complete and validated filings must be submitted with ERCOT sufficiently in advance of resource commissioning, and (3) PreRARF data required for the Planning Models will include typical or representative data where actual design or construction information is not available and will be updated as soon as such data is available. For your reference, Attachment 1 lists the protocol requirements that are included in this review. ERCOT appreciates your prompt attention in providing documentation. If you have any questions, please do not hesitate to contact us. 46 Attachment 1 Protocol Requirements Included in this Review Following is a list of Protocol and Operating Guide requirements included in this review. This is NOT intended to be an exhaustive list for compliance purposes. Note that the Protocols and Operating Guides can change from time to time, and it is up to the resource owner / QSE to be sure that it meets updated requirements on an on-going basis. Parameters in RARF match assumptions in Full Interconnection Study. Resource capable of producing 0.95 leading and lagging power factor of Pmax at all MW levels between LSL and HSL, as measured at the Point of Interconnection, where Pmax represents the maximum net power to be supplied to the ERCOT transmission grid. Protocol section 3.15 and 8.1.1.2.1.4. Resource includes a Power System Stabilizer. Protocol section 3.15.3[4] and Operating Guide 2.2.6. Resource provides frequency response. Protocol section 8.5.1.1 and 8.5.1.3 and Operating Guide Section 2.2.7. Resource provides dynamic voltage regulation. Protocol section 3.15. Transmission breaker(s) interruption capability is suitable to fault duty. Resource capable of voltage ride through, per Protocols and Operating Guides. Specifically Operating Guide section 2.9. Automatic Voltage Regulator is included and can be operated in voltage control mode. Protocol section 3.15.3 & 3.15. Resource responds to changes in the voltage profile. Protocol section 3.15. Sub synchronous issues have been reviewed and resolved, if any. Planning Model modeling information provided in accordance with Operating Guide 5.1, Planning Guide section 6.9. 47