DTC P0200/97 INJECTOR CIRCUIT / OPEN
advertisement

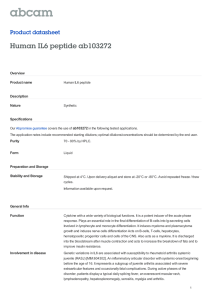
05–547 DIAGNOSTICS DTC – ECD SYSTEM (1KD–FTV)(From August, 2004) 05M58–02 P0200/97 INJECTOR CIRCUIT / OPEN HINT: S S For more information on the EDU, refer to the system description (see page 05–422). If P0200/97 is present, refer to the ”Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) Table for Common Rail System” (see page 05–547). CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION The EDU has been adopted to drive the injectors at high speeds. The EDU delivers high–speed driving under highly–pressurized fuel conditions using the DC/DC converter that provides a high–voltage, and the quick– charging system. Soon after the EDU receives an injection command (IJT) signal from the ECM, the EDU responds to the command with an injector injection confirmation (IJF) signal when the current is applied to the injector. EDU Wiring Diagram EDU COM3 From Battery COM2 DC/DC Converter Maximum 150 V Command Pulse COM1 Injector ECM IJT#1 INJ#1 IJT#4 INJ#4 IJT#2 INJ#2 Control Circuit IJT#3 INJF (IJF) INJ#3 Confirmation Pulse GND EDU Connector I5 I6 Warning: Terminals I, H, K, L, M, N are high voltage G38712 05–548 DIAGNOSTICS DTC No. – ECD SYSTEM (1KD–FTV)(From August, 2004) DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area Open or short in EDU or injector circuit After engine is started, there is no IJF signal from EDU to ECM, despite ECM sending IJT signal to EDU (1 trip detection logic) P0200/97 S Open or short in EDU circuit S Injector S EDU S ECM MONITOR DESCRIPTION P0200/97 (Open or short in EDU or injector circuit): The ECM continuously monitors both injection command (IJT) signals and injection confirmation (IJF) signals. This DTC will be set if the ECM judges that the number of IJT signals and IJF signals are inconsistent. The injectors are grounded over a Field Effect Transistor (FET) and a serial resistor. This resistor creates a voltage drop, which is monitored by the EDU (injector drive circuit), in relation to the current drawn by the injector. When the injector current becomes too high, the voltage drop over the resistor exceeds a specified level and no IJF signal for that cylinder is sent to the ECM. P0200/97 refers to a malfunction in the EDU or injector circuit. If this DTC is set, the ECM enters fail–safe mode and limits the engine power. The fail–safe mode continues until the engine switch is turned OFF. Malfunction Detection: Command Signal (IJT) ECM Confirmation Signal (IJF) EDU ON Injection Command Signal IJT Injection Confirmation Signal IJF OFF Abnormal Normal A81495 Y G37535 MONITOR STRATEGY Required sensors IJF signal from EDU Frequency of operation Continuous Duration 10 seconds MIL operation 1 driving cycle TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS Item Specification Specification Minimum Maximum Engine speed Engine is running (except engine start) – Battery voltage 11 V – Ignition switch ON ON TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS Threshold The injection missing counter* for all the cylinders, or for one individual cylinder, reaches a specified number (taking approximately 1 second from starting the engine) *: Increments when no IJF signal is received from the EDU despite the ECM sending IJT signals 05–549 DIAGNOSTICS – ECD SYSTEM (1KD–FTV)(From August, 2004) WIRING DIAGRAM (*1) (*2) 10 C4 IM4 IC4 B Engine Room R/B B J22 J/C B 1 E14 +B B C C17 IC4 W–G ECM C 8 E14 MREL W–G 2 B EF1 Relay D D J22 J23 (*1) (*2) L L 2 W–B 2 5 3 2 1 2 B 2 2 B 1 2 5 3 2 1 1 2 2 B 2 B 2 B 8 C8 IM4 IC4 (*1) (*2) L L B BR J2 J/C 2 EB1 25 E17 24 E17 23 E17 22 E17 21 E17 BR B–W L R–L Y W I6 Injector 1 2 INJF #1 #2 #3 #4 B 1 I9 Injector 4 3 INJ#4 E3 1 EB1 B B BR B 2 INJ#2 E3 8 E3 COM2 (*3) W–B B BR EB 10 E14 IREL B–W 7 IJF E4 6 IJT#1 E4 3 IJT#2 E4 2 IJT#3 E4 5 IJT#4 E4 4 INJ#1 E3 5 COM1 E3 (*3) W–B 2 E15 BATT L EDU EF1 L D D J22 J23 (*1) (*2) A5 IC4 B–W C/OPN or EDU Relay J/C Battery EG P 2 1 INJ#3 E3 Y 1 GND E4 W–B 8 E3 +B *1: LHD *2: RHD *3: Shielded I7 Injector 2 L 1 I8 Injector 3 2 L 2 E W–B E EF J11 J/C G38697 05–550 DIAGNOSTICS – ECD SYSTEM (1KD–FTV)(From August, 2004) PULSE GENERATION INSPECTION HINT: Problem areas can be located by checking the waveform at the following terminals. Warning: Terminals COM1, COM2, and INJ#1 to 4 are high–voltage ECM High–voltage Area EDU C IJF INJF D COM2 Injector COM1 IJT#1 INJ#1 IJT#4 INJ#4 #2 IJT#2 INJ#2 #3 IJT#3 INJ#3 #1 #4 B A A81508 HINT: In order to save time during the inspection, follow these instructions. When checking the ECM side first, inspect the trouble areas listed to the right of A to D (in that order). Malfunction Point Trouble Area A ECM B (if A is normal) Open or short in ”#1 to #4 (ECM)” – ”IJT#1 to IJT#4 (EDU)” harness or connector C (if A and B are normal) S Open or short in ”INJ#1 to INJ#4 (EDU)” – ”COM1 and/or COM2” (EDU) circuit S Injector S EDU D (if A, B and C are normal) Open or short in ”INJ (EDU)” – ”INJF (ECM)” circuit (a) Signal Waveform #1 5 V/ Division #3 #4 #2 20 msec./Division A09438 Reference: Inspection using an oscilloscope. While idling the engine, the correct waveform is shown in the diagram on the left. Inspection Points Specified Condition A and B Correct waveform is shown 05–551 DIAGNOSTICS (b) Signal Waveform 2 V/ Division INJF 20 msec./Division – ECD SYSTEM (1KD–FTV)(From August, 2004) Reference: Inspection using an oscilloscope. While idling the engine, the correct waveform is shown in the diagram on the left. Inspection Points Specified Condition C and D Correct waveform is shown A09437 INSPECTION PROCEDURE HINT: Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester II. Freeze frame data records the engine conditions when a malfunction is detected. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data can help determine if the vehicle was running or stopped, if the engine was warmed up or not, and other data from the time the malfunction occurred. 1 INSPECT INJECTOR ASSY (a) (b) Injector Assy Disconnect the I6, I7, I8 and I9 injector connectors. Measure the resistance of the injector. Standard: 2 1 NG A81503 OK Tester Connection Specified Condition 1–2 0.85 to 1.05 Ω at 20_C (68_F) REPLACE INJECTOR ASSY (See page 11–52) 05–552 DIAGNOSTICS 2 – ECD SYSTEM (1KD–FTV)(From August, 2004) CHECK WIRE HARNESS (EDU – INJECTOR ASSY) (a) Wire Harness Side I6 I7 I8 I9 Injector 1 2 Check the wire harness between the injector and EDU (INJ terminal). (1) Disconnect the I6, I7, I8 and I9 injector connectors. (2) Disconnect the E3 EDU connector. (3) Measure the resistance of the wire harness side connectors. Standard: E3 EDU INJ#2 INJ#4 INJ#3 A80992 A84815 INJ#1 COM1 COM2 A99847 NG OK Tester Connection Specified Condition I6–2 – E3–4 (INJ#1) Below 1 Ω I7–2 – E3–2 (INJ#2) Below 1 Ω I8–2 – E3–1 (INJ#3) Below 1 Ω I9–2 – E3–3 (INJ#4) Below 1 Ω I6–1 – E3–5 (COM1) Below 1 Ω I7–1 – E3–6 (COM2) Below 1 Ω I8–1 – E3–6 (COM2) Below 1 Ω I9–1 – E3–5 (COM1) Below 1 Ω I6–2 or E3–4 (INJ#1) – Body ground 10 kΩ or higher I7–2 or E3–2 (INJ#2) – Body ground 10 kΩ or higher I8–2 or E3–1 (INJ#3) – Body ground 10 kΩ or higher I9–2 or E3–3 (INJ#4) – Body ground 10 kΩ or higher I6–1 or E3–5 (COM1) – Body ground 10 kΩ or higher I7–1 or E3–6 (COM2) – Body ground 10 kΩ or higher I8–1 or E3–6 (COM2) – Body ground 10 kΩ or higher I9–1 or E3–5 (COM1) – Body ground 10 kΩ or higher REPAIR OR CONNECTOR REPLACE HARNESS AND 05–553 DIAGNOSTICS 3 – ECD SYSTEM (1KD–FTV)(From August, 2004) CHECK WIRE HARNESS (EDU – ECM) Wire Harness Side IJT#3 E4 EDU IJT#2 (a) (b) (c) IJF IJT#4 Disconnect the E4 EDU connector. Disconnect the E17 ECM connector. Measure the resistance of the wire harness side connectors. Standard: IJT#1 E17 #2 INJF #4 Tester Connection Specified Condition E4–6 (IJT#1) – E17–24 (#1) Below 1 Ω E4–3 (IJT#2) – E17–23 (#2) Below 1 Ω E4–2 (IJT#3) – E17–22 (#3) Below 1 Ω E4–5 (IJT#4) – E17–21 (#4) Below 1 Ω E4–7 (IJF) – E17–25 (INJF) Below 1 Ω E4–6 (IJT#1) or E17–24 (#1) – Body ground 10 kΩ or higher E4–3 (IJT#2) or E17–23 (#2) – Body ground 10 kΩ or higher E4–2 (IJT#3) or E17–22 (#3) – Body ground 10 kΩ or higher E4–5 (IJT#4) or E17–21 (#4) – Body ground 10 kΩ or higher E4–7 (IJF) or E17–25 (INJF) – Body ground 10 kΩ or higher #1 A80994 A80456 #3 A99849 NG REPAIR OR CONNECTOR REPLACE HARNESS AND OK 4 CHECK INJECTOR DRIVER (BATTERY VOLTAGE) Wire Harness Side BATTERY (+) E3 EDU (a) (b) (c) Disconnect the E3 and E4 EDU connectors. Turn the ignition switch ON. Measure the voltage of the wire harness side connectors. Standard: Tester Connection Specified Condition E3–8 (BATTERY) – E4–1 (GND) 9 to 14 V GND (–) E4 EDU A81845 A80994 NG A99850 OK CHECK INJECTOR DRIVER POWER SOURCE CIRCUIT (BATTERY – EDU) 05–554 DIAGNOSTICS 5 – ECD SYSTEM (1KD–FTV)(From August, 2004) CHECK ECM (INJECTOR VOLTAGE) (a) E17 INJF #1 #2 #3 E16 #4 While idling the engine, check the waveform of the ECM connectors using an oscilloscope. Standard: Tester Connection Specified Condition E17–24 (#1) – E16–7 (E1) Correct waveform is shown E17–23 (#2) – E16–7 (E1) Correct waveform is shown E17–22 (#3) – E16–7 (E1) Correct waveform is shown E17–21 (#4) – E16–7 (E1) Correct waveform is shown E17–25 (INJF) – E16–7 (E1) Correct waveform is shown E1 #1 5 V/ Division #3 #4 #2 20 msec./Division 2 V/ Division INJF A66060 A09438 A09437 20 msec./Division NG A99851 REPLACE ECM (See Pub. No. RM990E, page 10–34) NOTICE: After replacing the ECM, allow for ECM learning start the engine and idle it until it is fully warmed up. OK 6 REPLACE INJECTOR DRIVER NEXT CHECK IF DTC OUTPUT RECURS (DTC P0200/97) HINT: After clearing the DTC, start the engine and let it idle for 30 seconds. Confirm that P0200/97 is not output again.