SWR Seeing Watts Reflected by W5RH
advertisement

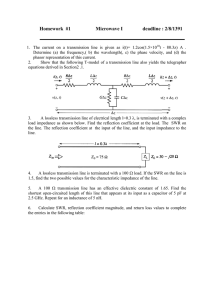
SWR Seeing Watts Reflected by Rick Hiller – W5RH SWR Seeing What’s Reflected by Rick Hiller – W5RH Agenda • • • • • The Antenna System What is SWR How it is developed How it is measured Why/How we use it Handout (See last page of PDF) The Antenna “System” Antenna The Load Transmission Line - TL Transceiver – The Source Defacto Standards • 50 ohm (nominal) coax is the most commonly used in Ham Radio RF – Transmitter outputs designed for 50 ohms – Antennas are commonly designed for 50 ohms The Requirement (our desire) • Maximum power transfer from the transmitter to the antenna (minimize losses) • This is accomplished by having a matched system – i.e. 50/50/50 ohms The Transmission Line • Also called “Feed Line” • Passive Device • Primarily, for getting RF power from an RF power source to an antenna • Characteristic Zo • Different types have differing loss numbers • Different physical configurations • ”If I had one wish in Ham Radio it would be that both my antenna and transmission line would be totally lossless…..we can get close, but no cigar. “Neither the line or the antenna actually consumes power, they are simply passing it off to something else” George Grammer, W1DF – QST -1957. What happens? Xmitter For demonstration purposes, TL is many times longer than a typical Ham Station feed line A N T E N N A What happens? FORWARD POWER Xmitter Voltage is generated by the transmitter Zero Reflected If the system is “matched” all power will be accepted by the antenna A N T E N N A What happens? FORWARD POWER Xmitter Reflected Power If the system is “NOT matched” some power will be reflected. How much is reflected is dependent on the value of the mis-match A N T E N N A What happens? Xmitter Forward wave and reflected wave travel independently, but mix/add into a static condition called the Standing Wave A N T E N N A Creating an envelope, similar to AM modulation wave form. What happens? Xmitter Standing Wave Envelope The waves will add at some places and subtract at others, producing mins and maxes It is almost as if the Reflected wave is modulating the forward wave A N T E N N A SWR Demo Bessernet Web Note: URL is on the Handout Standing Wave Envelope Maximum Minimum Standing Wave Envelope Movie -- Similarities of Wave Behavior (Note: URL is on the Handout) Standing Wave Ratio Maximum Envelope Voltage versus Minimum EnvelopeVoltage SWR = E max E min The differential of the max to the min is dependent on the size of the reflected voltage wave Standing Wave Ratio If, the differential of the max to the min is dependent on the size of the reflected voltage wave……. Then -- SWR can be used to indicate the quality of the match between the Transmission line and the antenna. SWR = E max = I max = Z Ant E min I min Z TL SWR Cardinal Rules • Always determined by the load – Load vs Zo of line (which is constant) • Does not change over the length of a lossless transmission line (theoretical) • Will change over the length of a normal line • SWR is greatest at the load SWR • Due to inherent line loss SWR will decrease as you approach the line input point • Absolute and always greater than 1 SWR= Zo / Zl or Zl / Zo • Singular – never SWR’s or s’wers How To Measure SWR? • With an SWR Meter, of course !!! • Power meter – Forward / Reflected • Cross Needle Meter • VNA Vector Network Analyzer Measuring SWR Measuring SWR – Bird Crossed Needle Meter VNA Based Meter Antenna Analyzer Also use an antenna analyzer -- with caution Very low drive signal so….. High RF fields can distort the measurements “Blame it on IZO” BVARC Tech Articles (Note: URL is on the Handout) Living in the Emperical World A few insights and caveats SWR Excursions SWR 1:1 2:1 3:1 4:1 6:1 10:1 Z 50 100/25 150/16.6 200/12.5 300/8.3 500/5 50ohm +/-j 0 36 58 75 102 142 Antenna System Philosophy • The good thing is that Hams have “bands of frequencies” to use • The bad thing is that hams have “bands of frequencies” to cover Antenna load Z’s • Unless you are rich and famous and own a self tuning antenna system (ie Stepper IR) then you do not have a resonant or matched antenna across the “Band”. • Your antenna generates a range of input feed impedances which can vary extremely. 80 Meter Dipole Feed Z Excursions 5.29 SWR 43 –j86 ohms 3.95 SWR 79 +j88 ohms 1.18 SWR 59 +j1.3 Should we worry about low SWR? Should we worry about high SWR? Should we worry about low SWR? YES Should we worry about high SWR? Yes SWR is best at the Xmitter X M I T T E R A N T Mis-matched loss graph A d d I T I O N A I L O S S SWR At Antenna 4 2.25 SWR By example – Reference Sheet It’s all math Transmission Line Apps • TL Details Dan McGuire AC6LA • Provides a Smith Chart on a computer • ARRL TLW – Dean Straw • ARRL Antenna Book CD SWR Vs. Reflected E & P Loss -- dB vs Watts 100 watt reference dB watts(loss) 0= 0 -1 = 10 -2 = 37 -3 = 50 – half power -4 = 40 -5 = 69 -6 = 75 – 1 ‘S’ Unit -10 = 90 Where should I put my ATU? If you want to minimize loss, place the ATU at the antenna feedpoint. What if I can’t ? In-line matching No Matching Xmitter High SWR at xmitter Reduced power output A N T E N N A In-line matching Matched ATU Xmitter SWR 1:1 SWR 4:1 A N T E N N A Matched TL losses between xmitter and ATU Additional losses in TL between ATU and Antenna In-line matching Matched ATU Xmitter SWR 1:1 SWR 4:1 A N T E N N A Reflected power is re-reflected at the ATU Circulating current between ATU and antenna All power, except for losses, makes it to the antenna Re-reflected Power Video – “Standing Up for Standing Waves” (Note: URL is on the Handout) Mis-matched loss graph A d d I T I O N A I L O S S Loss -- dB vs Watts 100 watt reference dB watts(loss) 0= 0 -1 = 10 -2 = 37 -3 = 50 – half power -4 = 40 -5 = 69 -6 = 75 – 1 ‘S’ Unit -10 = 90 Summary • Understand what your SWR measurement is trying to tell you. • Use the published TL specifications to establish a base line for losses. • Further you knowledge of antennas and TL’s by reading more and using the free tools available to you. Get hold of the ARVN Video “SWR…etc. Summary • Use the appropriate coax for the situation. • Use the best that you can afford. • In general -- The length of transmission line that is recommenred in the length that gets you from your transceiver to tyour antenna – not 1/2wl, not 1/wl, etc. • . Summary • Remember the antenna and TL and matching network are a “system”. • Better Antenna Systems mean more contacts……….. – More contacts mean more fun • .......and that is what this hobby is all about!!!!!!! The End SWR Seeing Watts Reflected Rick Hiller – W5RH SWR—Seeing Watts Reflected HamCom SWR—Seeing Watts Reflected June 12, 13 2015 HamCom by W5RH – Rick Hiller rhiller@sdicgm.com June 12, 13 2015 by W5RH – Rick Hiller rhiller@sdicgm.com Terms and Definitions Terms and Definitions Incident (Forward) Power – the power delivered to the feed line input by the source/generator/transmitter Reflected Power – the portion of the incident (forward) power, sent back toward the generator from the load, as a result of the mismatch between the line characteristic Zo and the load Z. Standing Wave – the wave created on a transmission line, being not terminated in its’ characteristic impedance, by the sum of the incident and reflected voltage waves. VSWR (SWR) -- Voltage Standing Wave Ratio – the mathematical ratio of the standing wave’s voltage max to voltage min. It is an easily made measurement that is used as a reference to define the quality of the line to load match. ================================= Incident (Forward) Power – the power delivered to the feed line input by the source/generator/transmitter Reflected Power – the portion of the incident (forward) power, sent back toward the generator from the load, as a result of the mismatch between the line characteristic Zo and the load Z. Standing Wave – the wave created on a transmission line, being not terminated in its’ characteristic impedance, by the sum of the incident and reflected voltage waves. VSWR (SWR) -- Voltage Standing Wave Ratio – the mathematical ratio of the standing waves voltage max. to voltage min. It is an easily made measurement that is used as a reference to define the quality of the line to load match. ================================= Reference Articles and Publications *The Why’s of Transmission Lines – Series George Grammer QST Jan, Feb. March 1965 *Understanding SWR By Example – Darrin Walraven – K5DVW – QST November 2006 *SWR, Reflected Power—What Do They Mean – Joel Hallas, W1ZR, QST June 2011 *Reflections (I, II and III) – Walt Maxwell, World Radio Books Publishing *Transmission Lines, Antennas and Wave Guides— King, Mimno and Wing – 1945 US Army *ARRL Antenna Handbook – ARRL Publishing -- Any printing from 1939 to 2007 Reference Articles and Publications *The Why’s of Transmission Lines – Series George Grammer QST Jan, Feb. March 1965 *Understanding SWR By Example – Darrin Walraven – K5DVW – QST November 2006 *SWR, Reflected Power—What Do They Mean – Joel Hallas, W1ZR, QST June 2011 *Reflections (I, II and III) – Walt Maxwell, World Radio Books Publishing *Transmission Lines, Antennas and Wave Guides— King, Mimno and Wing – 1945 US Army *ARRL Antenna Handbook – ARRL Publishing -- Any printing from 1939 to 2007 * Web Sites * SWR DEMO -- http://www.bessernet.com/Ereflecto/tutorialFrameset.htm * Bell Labs Movie -- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DovunOxlY1k * Standing Waves Video --http://arvideonews.com/hrn/HRN_Episode_0199.html * TL Details Download -- http://www.ac6la.com/tldetails.html * BVARC Articles -- http://www.bvarc.org/index.php?page=tech Web Sites * SWR DEMO -- http://www.bessernet.com/Ereflecto/tutorialFrameset.htm * Bell Labs Movie -- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DovunOxlY1k * Standing Waves Video --http://arvideonews.com/hrn/HRN_Episode_0199.html * TL Details Download -- http://www.ac6la.com/tldetails.html * BVARC Articles -- http://www.bvarc.org/index.php?page=tech