Circuits - Little Shop of Physics
advertisement

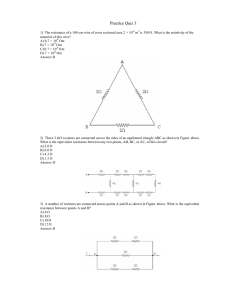
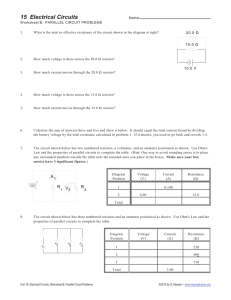
Circuits • Resistor Circuits. We’ll look at more complex circuits this week. • Capacitor Circuits. Adding a capacitor to a resistor circuit allows for timing functions. • Electricity in the Body. The physics of resistor-capacitor circuits can be used to explain signal propagation in the nervous system. Reducing Complex Circuits, Part I Rage Against the Dying of the Light. Holiday lights use simple series circuits so that the bulbs can be low voltage. Suppose there are 50 bulbs in one string. What is the voltage across each bulb? How does the string stay lit when one bulb goes out? Reducing Complex Circuits, Part II What’s the Voltage? The diagram below shows a circuit with two batteries and three resistors. What is the potential difference across the 200 Ω resistor? Understanding Circuits a. Which bulb is brightest? b. Which bulb is dimmest? Ideal Wires, Ideal Batteries, Light Bulbs are Resistors Suppose a wire is connected between points 1 and 2. Does the brightness of each bulb: ! A. !Increase ! B. !Decrease Understanding Circuits a. Which bulb is brightest? b. Which bulb is dimmest? Voltage Is, Current Flows. Suppose a wire is connected between points 1 and 2. Does the brightness of each bulb: ! A. !Increase ! B. !Decrease What’s The Current? The diagram below shows a segment of a circuit. What is the current in the 200 Ω resistor? What’s the Voltage? The diagram below shows a circuit with two batteries and three resistors. What is the potential difference across the 200 Ω resistor? What’s the Resistance? There is a current of 1.0 A in the circuit below. What is the resistance of the unknown circuit element? What’s the Current? What is the current supplied by the battery in the following circuit? Which is quicker? Series Parallel Explain which wiring will result in quicker cooking, and why. You must use a mathematical relationship. Common Combinations −1 Requivalent = R1 + R2 = 2R Requivalent ⎡1 1 ⎤ R =⎢ + ⎥ = 2 ⎣ R1 R2 ⎦ Simplifying Circuits What is the equivalent resistance of the following circuit? Measuring Voltage and Current Ammeter: Measures current. R=0 Ω; no voltage. What is the value of R? Voltmeter: Measures potential difference. R=∞ Ω; no current. What is the value of I? What is the value of R? Circuits Calculations. What is the current provided by the battery in the following circuit? Circuits Calculations. What is the current through each of the resistors in the following circuit? Voltage is. Current flows. 1)Which point, a or b, is at a higher potential? 2.0 Ω 1.0 Ω 1.0 Ω 2.0 Ω 3.0 V 2)What is the potential difference Vab? Grand Finale. What is the current through each of the resistors in the following circuit? Warming Up. the figure. Warming Up. What’s the potential at the the figure. noted point in the circuit? ! ! ! ! A. ! B. !! C. ! D. ! 10 V 6V 5V 4V Warming Up: What are the two resistors? What are the resistances of the two unknown resistors in this circuit? R1 R2 Warming Up. What is the value of resistor R in the figure? Unfinished Business. What is the current through each of the resistors in the following circuit? Capacitor formulas Unit: farad, F: Storing Charge 1)What is the capacitance of the 2 l bottle Leyden jar capacitors we use in class? 2)The capacitor is charged up to 10,000 V, then discharges in 0.01 s. What is the current? Area: ! ! ! Thickness: !! κ:!! ! ! ! ε0:!! ! ! ! 0.08 m2 0.00025 m 2.8 8.85x10-12 C2/N•m2 Capacitors in series and in parallel Which of the following combinations of capacitors has: ! 1) the highest capacitance? ! 2) the lowest capacitance? Capacitor Discharge 11 11 C 11 11 C R 22 22 22 22 I R C I 2 2 R DVC (DVC)0 I0 0 1 1 I0 t t50 0 t t50 Voltage, current decrease with time. Capacitor Discharge DVC (DVC)0 0.37(DVC)0 0.13(DVC)0 0 0 t 2t τ = RC 3t ΔVC = ( ΔVC )0 e−t /τ t Timing Circuits DVC t Intermittent Wipers Rotating the dial changes a variable resistor. Does turning the dial toward “F” increase or decrease the resistance? Half life: t1 2 = τ ln 2 RC Timing The following circuits contain capacitors charged to 5.0 V. All of the switches are closed at the same time. After 1 second has passed, which capacitor has the highest voltage? The lowest? RC Timing A 10 µF capacitor is initially charged to 20 µC. The capacitor is discharged through a 1.0 kΩ resistor. How long does it take to reduce the capacitor’s charge to 10 µC? Large Current, Short Pulse A typical defibrillator has a 32 µF capacitor charged to 5000 V. The electrodes connected to the patient are coated with a conducting gel that reduces the resistance of the skin so that the effective resistance of the patient’s torso is100 Ω. a. What is the current at the instant the switch is closed? b. What is the current 5.0 ms after the switch is closed?