Journal of Management Engineering and Information Technology (JMEIT)
Volume -2, Issue- 3, Jun. 2015, ISSN: 2394 - 8124
Website: www.jmeit.com | E-mail: editorjmeit@outlook.com|jmeit@outlook.com
Design and Simulation of VFOA Based Wein
Bridge Oscillator Using NI Multisim and
Ultiboard and their Applications
Vijaylaxmi Kalyani, Shreya Surana, Summaiya Syed
Vijay laxmi Kalyani, Assistant professor, ECE department, Govt. Women Engineering College, Ajmer
vijaylaxmikalyani@yahoo.com
Shreya Surana, B.Tech Student II year, EEE branch, Govt. Women Engineering College, Ajmer
Shreyasurana1995@gmail.com
Summaiya Syed, B.Tech Student II year, EEE branch, Govt. Women Engineering College, Ajmer
Abstract:Oscillators have many applications in
the field of electronics and communication. They
are widely used in many electronic devices. They
can generate output waveform of high frequency
up to GHz. Oscillators are used to generate
waveform for testing and repairing of radio,
television, computer and in other electronic
devices. VFOA i.e. Voltage
Feedback
Operational Amplifier is a voltage controlled
amplifier. VFOA is used for most of the analog
circuit design. In this paper, we design and
analyze the Wein bridge oscillator based on
VFOA at the frequency of 102.73 KHzusing NI
Multisim software and Ultiboard. The working
and performance criteria of the circuit examined
using NI Multisim software by making use of
741IC for VFOA. In this paper, we also show the
3-D view of complete circuit and layout using
Ultiboard.
Keywords: Wein bridge oscillator, Voltage
Feedback Operational Amplifiers (VFOA), NI
Multisim Simulation Software, Ultiboard.
I. INTRODUCTION
All analog circuitry basically use VFOA. An oscillator is
basically an electronic circuit uses positive feedback
which produces repetitive waveforms of fixed amplitude
and frequency without any external input. In 1917Astable
Multivitrator, first & most widely used relaxation
oscillator was invented by French engineer Henri
Abraham and Eugene Bloach. It produced square wave
signals which were rich in harmonics.
In 1921,Barkhausen Criterion, were derived by Heinrich
George Barkhausen. In 1969, K. Kurokawa derived
necessary and sufficientconditions for oscillation in
negative resistance circuits [4], which form the basis of
modern microwave oscillator design. In this paper, the
frequency of 102.73 KHz of the Wein bridge oscillator
circuit using VFOA is analyzed. Various components use
in the VFOA circuits design gives the value of frequency,
when the selection of their values are being done. First,
the theoretical frequency range of the oscillator was found
at 102.73 KHz and then the circuit is simulated using NI
Multisim Simulation software and also shown the 3-D
view and Ultiboard design.
I.I.OSCILLATOR
An oscillator is a type of feedback amplifier in which part
of the output is fed back to the input via a feedback circuit
[1]. If the signal fed back is of proper magnitude and
phase, the circuit produces alternating currents or voltages
[1]. This is the basic principle of an oscillator. Oscillators
are used in radio, television, communication, etc. The
different types of Oscillators works on the same basic
principle. They are characterized as, audio frequency
oscillator, radio frequency oscillator and low frequency
oscillator. Ranges of these oscillators are about 16 KHz to
20 KHz, 100 KHz to 100 GHz and below 20 Hz
respectively. The electronic oscillators are of two main
types which are linear oscillators and relaxation
oscillators. Wein bridge oscillator is a type of audio
frequency oscillator used to generate sinusoidal
waveforms.
I.II.VOLTAGE FEEDBACK OPERATIONAL
AMPLIFIER (VFOA)
VFOA is a voltage feedback architecture used in op-amp
applications. In VFA, the feedback that makes them
versatile and accurate also has a tendency to make them
unstable. The operational amplifier circuit configuration
uses a high gain amplifier whose parameters are
determined by external feedback components. The
amplifier gain is so high that without these external
feedback components, slightest input signal would
saturate the amplifier output [2]. VFOA is used to produce
voltage waveform at output when voltage signal is applied
at input.
I.III. OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
Linear IC’s were developed in early 1960, when arrays
were first fabricated on a single silicon chip. Arrays were
combination of isolated components (diodes, transistors or
individual stages).
All rights reserved © www.jmeit.com
24
Journal of Management Engineering and Information Technology (JMEIT)
Volume -2, Issue- 3, Jun. 2015, ISSN: 2394 - 8124
Website: www.jmeit.com | E-mail: editorjmeit@outlook.com|jmeit@outlook.com
gain equal to 1. If the feedback impedances are chosen
Before, Op-amp’s were invented have many problems
properly, there will be some frequency at which there is
such as:zero phase shift in the signal fed back to the op-ampnon•
No short- circuit protection.
inverting terminal input. Because the amplifier is non•
A possible latch up problem.
inverting, it also attributes to zero phase shift, so the total
phase shift around the loop is 0 at that frequency as
•
Require an external frequency compensating
required for oscillation. Thus total phase shift must be
network.
zero.This condition occurs only when bridge is balanced.
This balancing condition is called resonance.The
In 1968, introduction of Fairchild µA741, an internally
frequency of oscillation fo is exactly the resonant
compensated op-amp. It doesn’t have above discussed
frequency of the balanced Wien bridge oscillator [1].
problems. It also has very high input resistance (2MΩ,
typically), high gain voltage, and offset null capability.741
is second generation op-amp. Other examples of second
generation op-amp are LM101, LM307, µA748 and
MC1558 etc.
Operational amplifier or op-amp is a multi-terminal
device. An operational amplifier is a direct- coupled high
gain amplifier usually consisting of one or more
differential amplifiers and usually followed by a level
translator and an output stage [1]. The output stage is
generally a push-pull or push-pull complementarysymmetry pair. It is a circuit which was originally
designed to perform various mathematical operations as
well as amplification of some ac or dc signals. By
introducing suitable feedback components, the op-amp
acquires a variety of applications such as ac and dc
amplification, filters, oscillators, comparators, etc.
Fig.2 Wien bridge oscillator
fo=
Since the oscillator is working in non-inverting mode, so
gain Av= 1+
For sustained oscillation condition the gain is:
Av=3
And Rf =2Rg
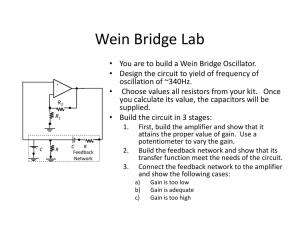
II.1 Designing steps for Wein bridge oscillator:
Fig.1 Equivalent circuit of an op-amp.
II. WEIN BRIDGE OSCILLATOR
Wien bridge oscillator is a type of audio frequency (AF)
oscillators. It provides a stable low distortion sinusoidal
output over a wide range of frequency [3]. It uses RC
circuit to produce sinusoidal outputs. Generally, RC
feedback oscillators are used for frequencies up to about 1
MHzWien bridge oscillatoris very popular type of
oscillator for this range of frequencies.In Wien bridge
oscillatorthe op-amp is used in a non-inverting
configuration and the impedance blocks i.e. Z1 and Z2
forms a voltage divider that determines the feedback ratio.
A portion of the output voltage is feedback through this
impedance divider to thenon-inverting of op-amp.
Resistors R g and Rf are used to determine the amplifier
gain and are selected to make the magnitude of the loop
II.1.1. Choose the value of R as 0.031kΩ
II.1.2. Select the value of capacitance C (C≤1µF) as
0.05µF.
II.1.3. Calculate the value of fousing the formula of
fo=
Hence fo=102.73kHz.
II.1.4. Choose the value of Rgand Rf with the help of gain
Av.
Hence the gain is 3 for Wein bridge oscillator so we have
chosen the value of R1as 12kΩ and Rf as 24kΩ.
II.2.Design and Simulation of Wein bridge oscillator
using 741IC
All rights reserved © www.jmeit.com
25
Journal of Management Engineering and Information Technology (JMEIT)
Volume -2, Issue- 3, Jun. 2015, ISSN: 2394 - 8124
Website: www.jmeit.com | E-mail: editorjmeit@outlook.com|jmeit@outlook.com
R7
C2
.031kΩ
.05µF
VCC
15V
U2
XSC1
Ext Trig
+
Op-Amp_741
C3
.05µF
D3
1N4007G
R10
10kΩ
_
B
A
+
_
+
_
D2
1N4007G
R8
R9
R1 12kΩ
.031kΩ
24kΩ
R6
VEE
Fig.6: 3-D view of Wein Bridge Oscillator
-15V
50kΩ 50 %
Key=A
Fig. 3: circuit diagram of Wein bridge oscillator.
III. ADVANTAGES AND APPLICATIONS OF
WEIN BRIDGE OSCILLATOR
Wein bridge oscillator is an audio frequency oscillator
which is simple and stable. Absence of inductors and
transformers makes the circuit simple and cheap. It
provides a stable low frequency distortion sinusoidal
output over a wide range of frequency. The frequency of
oscillation can be changed by varying the two capacitors
or by using variable resistors. It has various applications.
It is used in electronic components. Its applications
includes television, radio, computers, etc.
III. RESULT
We have calculated the value of frequency as 102.73kΩ
using the value of R and C. We also obtained the output
waveform for the given frequency as shown in fig3.
V. FUTURE SCOPE
We can also use current conveyor based ICs, so that we
increase the range of frequency in MHz
Fig.4: output waves of wein bridge oscillator.
II.4. Layout using Ultiboard
CONCLUSION
We design the Wein bridge oscillator at frequency of
102.73 KHz using NI Multisim Simulation software and
also show the layout using Ultiboard and the 3-D view of
the circuit. Because of limitation of 741IC is its low slew
rate(.5v/us), so, we design the Wein bridge oscillator in
particular frequency ranges in KHz.
VI. REFERENCES
Fig.5: layout using Ultiboard
II.5.3-D View of the Circuit
[1] Ramakant A. Gayakwad, Op-amps and Linear Integrated
Circuits,
fourth
ed.,
2005.
[2] Vijaylaxmi Kalyani, Aayushi Arya, “Design and Simulation
of VFA and CFA Based Integrator and Differentiator using NI
Multisim and their Comparison”, IJARECE vol. 3, no.8, August
2014.
[3] Dr. Rajiv Tiwari,”Electronic Devices & Circuit-II, ninth
edition”,2015.
[4] Kurokawa, K. (July 1969). "Some Basic Characteristics of
Broadband Negative Resistance Oscillator Circuits"
All rights reserved © www.jmeit.com
26
Journal of Management Engineering and Information Technology (JMEIT)
Volume -2, Issue- 3, Jun. 2015, ISSN: 2394 - 8124
Website: www.jmeit.com | E-mail: editorjmeit@outlook.com|jmeit@outlook.com
AUTHOR’S DETAIL
Vijay Laxmi Kalyani is currently working as
AssistantProfessor in the department of ECE in GWEC,
Ajmer.She hasattended various workshops, conferences,
FDP,STC and alsopublished many research papers inVarious
International Journals, NationalJournals and Conferences,
Member-IAENG.
Shreya Surana is pursuing B.Tech. (II-year) in Electrical
and Electronics Engineering in GWEC, Ajmer.
Summaiya Syed is pursuing B.Tech. (II-year) in Electrical
and Electronics Engineering in GWEC, Ajmer.
All rights reserved © www.jmeit.com
27