16.1 The Characteristic Curve of Zener Diodes Task
advertisement

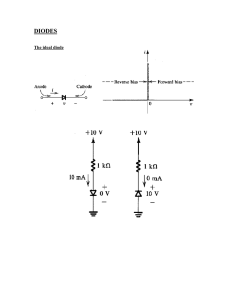
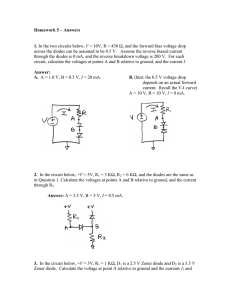
Science - Physics - Electricity and Electronics - 16 Diodes, Part 2 (P1377900) 16.1 The Characteristic Curve of Zener Diodes Experiment by: MAGNETISM Printed: Jan 10, 2011 1:12:18 PM interTESS (Version 10.03 B132, Export 1678) Task Task How do Zener diodes differ from normal rectifier diodes? Investigate the relationship between current and voltage for a Zener diode in forward and reverse direction. Use the space below for your own notes. Logged in as a teacher you will find a button below for additional information. -1- Material Material Material from "Student equipment set electricity/electronics 1" (Order No. 05600.88) and Material from "Student equipment set electricity/electronics 2" (Order No. 05601.88) Position No. Material Order No. Quantity 1 Connector, straight, module SB 05601.01 3 2 Connector, angled, module SB 05601.02 3 3 Connector, T-shaped, module SB 05601.03 2 4 Connector, interrupted, module SB 05601.04 2 5 Connector, straight with socket, module SB 05601.11 1 6 Connector, angled with socket, module SB 05601.12 1 7 Resistor 50 Ohm, SB 05612.50 1 8 Resistor 100 Ohm, SB 05613.10 2 9 Z-diode, ZF 4.7, SB 05652.00 1 10 Connecting cord, 32 A, 250 mm, red 07360.01 1 11 Connecting cord, 32 A, 250 mm, blue 07360.04 1 12 Connecting cord, 32 A, 500 mm, red 07361.01 2 13 Connecting cord, 32 A, 500 mm, blue 07361.04 2 14 Multi-range meter, analogue 07028.01 2 15 Power Supply, 0...12 V DC/ 6 V, 12 V AC 13505.93 1 Additional Material Material required for the experiment -2- -3- Setup Setup First experiment Set up the circuit according to the schematic diagram 1 as shown in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2. Connect the Zener diode in forward direction. Select a measurement range of 1 V- and 30 mA-. Make sure that the polarity on the meters is correct and that the meters are connected properly. schematic diagram 1 Fig. 1 Fig. 2 Second experiment Set up the circuit according to the schematic diagram 2 as shown in Fig. 3 and Fig. 4. Note: Make sure to change the polarity of the Zener diode. Switch the measurement range for the voltage to 10 V-. -4- schematic diagram 2 Fig. 3 Fig. 4 -5- Action Action First experiment • Switch on the power supply unit. Increase the voltage UP on the power supply unit from 0 V to 10 V in increments of 1 V. Measure both forward voltage UF and forward current IF. Enter the measurements in Table 1 on the Results page. • Switch off the power supply unit. Second experiment • Switch on the power supply unit and increase the voltage UP from 0 V to 10 V in increments of 1 V once again. Measure both reverse voltage UR and reverse current IR. Since you inverted the Zener diode polarity, you will have to enter the values measured as negative values in Table 2 on the Results page. • Switch off the power supply unit. -6- Results Results Table 1 Voltage level on power supply unit Forward voltage Forward current UF in V IF in mA 0 nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 1 nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 2 nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 3 nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 4 nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 5 nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 6 nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 7 nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 8 nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 9 nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 10 nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn UP in V -7- Table 2 Voltage level on Reverse voltage Reverse current power supply unit UR in V IR in mA UP in V (with negative sign) (with negative sign) 0 nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 1 nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 2 nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 3 nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 4 nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 5 nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 6 nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 7 nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 8 nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 9 nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn 10 nnnnnnnnnn nnnnnnnnnn -8- Evaluation Evaluation Question 1: Describe the behaviour of a Zener diode in a circuit. Use the term breakdown voltage in your explanation. Breakdown voltage is the voltage at which a diode connected in reverse direction loses its blocking ability. Question 2: How do Zener diodes differ from normal rectifier diodes? Question 3: What purpose does the multiplier R3 serve? -9- Question 4: Look at the characteristic curve in Diagram 1 on the Results page. The left arm of the graph represents the voltage UR and the lower arm the current IR (the minus signs for both arms are just for the technical realisation of displaying the graph). Determine the change in voltage in the reverse direction when the current is increased from 20 mA to 30 mA. How can this characteristic of Zener diodes be used in practice? - 10 -