The Wizard Test Maker
advertisement
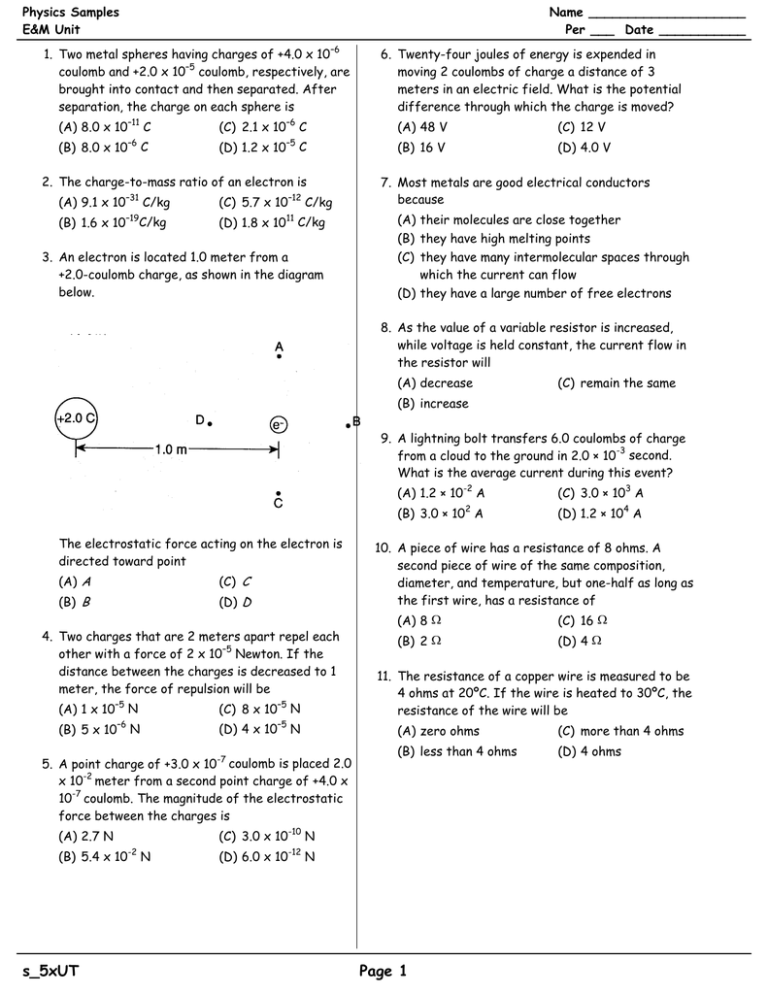
Physics Samples E&M Unit Name ____________________ Per ___ Date ___________ 1. Two metal spheres having charges of +4.0 x 10–6 coulomb and +2.0 x 10–5 coulomb, respectively, are brought into contact and then separated. After separation, the charge on each sphere is (A) 8.0 x 10–11 C (B) 8.0 x 10 –6 C (C) 2.1 x 10–6 C (D) 1.2 x 10 –5 C 2. The charge-to-mass ratio of an electron is (A) 9.1 x 10 –31 (B) 1.6 x 10 –19 C/kg C/kg (C) 5.7 x 10 –12 C/kg 11 (D) 1.8 x 10 C/kg 3. An electron is located 1.0 meter from a +2.0-coulomb charge, as shown in the diagram below. 6. Twenty-four joules of energy is expended in moving 2 coulombs of charge a distance of 3 meters in an electric field. What is the potential difference through which the charge is moved? (A) 48 V (C) 12 V (B) 16 V (D) 4.0 V 7. Most metals are good electrical conductors because (A) their molecules are close together (B) they have high melting points (C) they have many intermolecular spaces through which the current can flow (D) they have a large number of free electrons 8. As the value of a variable resistor is increased, while voltage is held constant, the current flow in the resistor will (A) decrease (C) remain the same (B) increase 9. A lightning bolt transfers 6.0 coulombs of charge from a cloud to the ground in 2.0 × 10-3 second. What is the average current during this event? The electrostatic force acting on the electron is directed toward point (A) A (C) C (B) B (D) D 4. Two charges that are 2 meters apart repel each other with a force of 2 x 10–5 Newton. If the distance between the charges is decreased to 1 meter, the force of repulsion will be (A) 1 x 10–5 N (C) 8 x 10–5 N (B) 5 x 10–6 N (D) 4 x 10–5 N 5. A point charge of +3.0 x 10-7 coulomb is placed 2.0 x 10-2 meter from a second point charge of +4.0 x 10-7 coulomb. The magnitude of the electrostatic force between the charges is (A) 2.7 N (C) 3.0 x 10-10 N (B) 5.4 x 10-2 N (D) 6.0 x 10-12 N s_5xUT (A) 1.2 × 10-2 A (C) 3.0 × 103 A (B) 3.0 × 102 A (D) 1.2 × 104 A 10. A piece of wire has a resistance of 8 ohms. A second piece of wire of the same composition, diameter, and temperature, but one-half as long as the first wire, has a resistance of (A) 8 Ω (C) 16 Ω (B) 2 Ω (D) 4 Ω 11. The resistance of a copper wire is measured to be 4 ohms at 20ºC. If the wire is heated to 30ºC, the resistance of the wire will be (A) zero ohms (C) more than 4 ohms (B) less than 4 ohms (D) 4 ohms Page 1 12. The graph below represents the relationship between potential difference and current for four different resistors. Which resistor has the greatest resistance? 16. In the circuit shown below, voltmeter V2 reads 80. volts. What is the reading of voltmeter V1? (A) A (C) C (B) B (D) D 13. If the current in a wire is 2.0 amperes and the potential difference across the wire is 10. volts, what is the resistance of the wire? (A) 5.0 Ω (C) 12 Ω (B) 8.0 Ω (D) 20 Ω 14. If the potential difference across a 30.-ohm resistor is 10. volts, what is the current through the resistor? (A) 0.25 A (C) 3.0 A (B) 0.33 A (D) 0.50 A 15. Which voltage would cause a current of 0.5 ampere in a circuit that has a resistance of 24 ohms? (A) 6.0 V (C) 24 V (B) 12 V (D) 48 V (A) 160 V (C) 40. V (B) 80. V (D) 20. V 17. Which circuit segment below has the same total resistance as the circuit segment shown in the diagram to the right? (A) (B) (C) (D) s_5xUT Page 2 18. Ammeters A1, A2 and A3 are placed in a circuit as shown below. 23. The diagram below represents lines of magnetic flux within a region of space. What is the reading on ammeter A3? (A) 1.0 A (C) 3.0 A (B) 2.0 A (D) 5.0 A 19. Two resistors are connected in parallel to a 12-volt battery as shown in the diagram. The magnetic field strength is greatest at point (A) A (C) C (B) B (D) D 24. The diagram below shows the magnetic field that results when a piece of iron is placed between unlike magnetic poles. If the current in resistance R is 3.0 amperes, the rate at which R consumes electrical energy is (A) 1.1 x 102 W (C) 24 W (B) 36 W (D) 4.0 W 20. An electric motor draws 150 amperes of current while operating at 240 volts. What is the power rating of this motor? (A) 1.6 W (C) 3.6 × 104 W (B) 3.8 × 102 W (D) 5.4 × 106 W 21. The heating element on an electric stove dissipates 4.0 × 102 watts of power when connected to a 120-volt source. What is the electrical resistance of this heating element? (A) .028 Ω (C) 3.3 Ω (B) .60 Ω (D) 36 Ω At which point is the magnetic field strength greatest? (A) A (C) C (B) B (D) D 25. Which diagram best illustrates the direction of the magnetic field between the unlike poles of two bar magnets? (A) (C) (B) (D) 22. An electric dryer consumes 6.0 x 106 joules of energy when operating at 220 volts for 30. minutes (1800 seconds). During operation, the dryer draws a current of approximately (A) 10. A (C) 20. A (B) 15 A (D) 25 A s_5xUT Page 3 26. An electron current (e–) moving upward through a straight conductor creates a magnetic field. Which diagram below correctly represents this magnetic field? (A) (C) (B) (D) 29. The diagram to the right represents a conductor carrying a current in which the electron flow is from left to right. The conductor is located in a magnetic field which is directed into the page. The direction of the magnetic force on the conductor will be (A) (B) (C) (D) 27. Electrons flow in a loop of wire as shown in the diagram. What is the direction of the magnetic field at point A? (A) into the paper (C) toward the left (B) out of the paper (D) toward the right 28. The accompanying diagram shows an electron moving through a magnetic field. into the page out of the page toward the top of the page toward the bottom of the page Base your answers to questions 30 through 33 on the diagram below. The reading of voltmeter V1 is 26 volts, and the reading of ammeter A1 is 2 amperes. 30. What is the reading of voltmeter V2? (A) 52 V (C) 13 V (B) 26 V (D) 8 V 31. What is the total resistance of the circuit? If the electron is moving out of the page, in which direction will it be deflected by the magnetic field? (A) (B) (C) (D) s_5xUT toward the top of the page toward the bottom of the page to the left to the right (A) ¾ Ω (C) 10 Ω (B) 4/3 Ω (D) 13 Ω 32. The reading of ammeter A2 is (A) 6 A (C) 3 A (B) 2 A (D) 52 A Page 4 33. If additional resistances are added in series and the applied voltage is kept constant, the reading of voltmeter V3 will (A) decrease Base your answers to questions 39 through 43 on the electric circuit below. The switch is in the open position. (C) remain the same (B) increase Base your answers to questions 34 through 38 on the diagram below which represents an electrical circuit. 39. What is the reading of ammeter A1? (A) 1/6 ampere (C) 60. amperes (B) 6.0 amperes (D) 600 amperes 40. What is the reading of ammeter A2? 34. The equivalent resistance of the circuit is (A) 25 Ω (C) 5.0 Ω (B) 6.0 Ω (D) 0.17 Ω 35. The potential difference across R2 is (A) 1.0 V (C) 10. V (B) 2.0 V (D) 12 V 36. The magnitude of the current in ammeter A1 is (A) 120 A (C) 1.2 A (B) 2.0 A (D) 0.83 A 37. Compared to the current in A1, the current in A2 is (A) less (C) the same (B) greater 38. If another resistance were added to the circuit in parallel, the equivalent resistance of the circuit (A) decrease (C) remain the same (A) 9.0 amperes (C) 12 amperes (B) 2.0 amperes (D) 18 amperes 41. What power is developed in the 10.-ohm resistor? (A) 600 watts (C) 60. watts (B) 360 watts (D) 6.0 watts 42. Compared to the potential drop across the 10.-ohm resistor, the potential drop across the 20.-ohm resistor is (A) less (C) the same (B) greater 43. Compared to the current passing through ammeter A1 when the switch is open, the current passing through ammeter A1 when the switch is closed will be (A) less (C) the same (B) greater (B) increase 44. Which segment of copper wire has the highest resistance at room temperature? (A) 1.0 m length, area (B) 2.0 m length, area (C) 1.0 m length, area (D) 2.0 m length, area s_5xUT Page 5 2 1.0 x 10–6 m cross-sectional 2 1.0 x 10–6 m cross-sectional 2 3.0 x 10–6 m cross-sectional 3.0 x 10–6 m 2 cross-sectional 45. If both the cross-sectional area and the length of a metallic conductor were doubled, the resistance of the conductor would be (A) halved (C) unchanged (B) doubled (D) quadrupled 50. the diagram below. 46. The ratio of the potential difference across a metallic conductor to the current in the conductor is known as (A) potential drop (C) resistance (B) conductivity (D) electromagnetic force 47. A wire carries a current of 6.0 amperes. How much charge passes a point in the wire in 120 seconds? (A) 6.0 C (C) 360 C (B) 20. C (D) 720 C The total resistance in the circuit is (A) 9 Ω (C) 3 Ω (B) 6 Ω (D) less than 3 Ω 48. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below. What is the total resistance of the circuit? (A) 6.6 Ω (C) 20 Ω (B) 10 Ω (D) 30 Ω 49. When the circuit shown below is completed what will be the reading on the ammeter at B? (A) less than the reading at A (B) greater than the reading at A (C) the same as the reading at A s_5xUT Page 6 Physics Samples E&M Unit D 1. _________ 2. _________ D D 3. _________ C 4. _________ A 5. _________ 6. _________ C D 7. _________ A 8. _________ C 9. _________ 10. _________ D C 11. _________ D 12. _________ A 13. _________ 14. _________ B B 15. _________ A 16. _________ B 17. _________ 18. _________ A B 19. _________ C 20. _________ D 21. _________ 22. _________ B B 23. _________ C 24. _________ B 25. _________ s_5xUT Name ____________________ Per ___ Date ___________ Answer Key 26. _________ D B 27. _________ A 28. _________ D 29. _________ 30. _________ D D 31. _________ B 32. _________ A 33. _________ 34. _________ B D 35. _________ C 36. _________ A 37. _________ 38. _________ A B 39. _________ A 40. _________ B 41. _________ 42. _________ C C 43. _________ B 44. _________ C 45. _________ 46. _________ C D 47. _________ D 48. _________ C 49. _________ 50. _________ D