國立臺南大學101 學年度電機工程學系碩士班招生考試電子學試題卷
advertisement

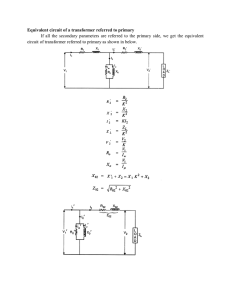
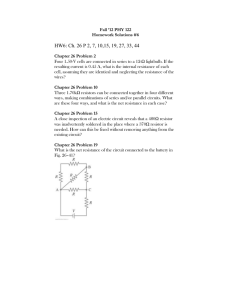
國立臺南大學 101 學年度 電機工程學系碩士班 招生考試 電子學 試題卷 ◎ 第 1 題為選擇題,請於答案卷對應空格填入選項。2-8 題為計算或問答題,需寫明過程。 1. Choose one right answer for each of the following questions. (10%) (1) The diodes in a bridge rectifier each have a maximum dc current rating of 2A. This means the dc load current can have a maximum value of (A) 1A (B) 2A (C) 4A (D) 8A (2) The device associated with voltage-controlled capacitance is a (A) Light-emitting diode (B) Photodiode (C) Varactor diode (3) Increasing the collector supply voltage will increase (A) Base current (B) Collector current (C) Emitter current (D) Zener diode (D) None of the above (4) If the base resistor has zero resistance, the transistor will probably be (A) Saturated (B) In cutoff (C) Destroyed (D) None of the above. (5) With CMOS, the upper MOSFET is (A) A passive load (B) An active load (C) Nonconducting 2. (D) Complementary Show that the series connection of MOSFETs shown in Fig. 1 behaves as a single MOSFET with Twice the length of the individual MOSFETs. (Neglect the body effect) (10%) Fig. 1 3. Show that the parallel connection of MOSFET shown in Fig. 2 behaves as a single MOSFET a width equal to the sum of the individual MOSFET’s widths. (10%) Fig. 2 第 1 頁,共 3 頁 4. What would happen to the transfer function analysis results for the circuit in Fig. 3? (10%) (a) A capacitor is added in series with R1. Why? (b) A capacitor is added in series with R2. Why? Fig. 3 5. Describe the transfer characteristic of the circuits shown in Fig. 4 (a) and (b). (10%) Fig. 4 6. An OPA circuit is shown in Fig. 5. (10%) (a) Find VO and CMRR. (b) How to set R1~ R4 for converting the circuit to differential amplifier? Fig. 5 第 2 頁,共 3 頁 7. Fig. 6 shows a circuit for charging a 12-V battery. If vs is a sinusoid with 24-V peak amplitude, find the fraction of each cycle during which the diode conducts. Also find the peak value of the diode current and the maximum reverse-bias voltage that appears. (20%) Fig. 6 8. Explain the following terms. (20%) (1) Can you set up a lighting source by only using LED diodes without any rectifier circuits (that is 110-V AC LED)? (2) What is the field effect in MOSFET? And what is the meaning of Vt of MOSFET? Sketch the structure and explain it. (3) Design a Constant-Current Source for biasing using two BJT and show the current. (4) Explain Frequency Compensation by using Bode plots. 第 3 頁,共 3 頁 電機工程學系光電工程碩士班 國立臺南大學 100 學年度 電機工程學系通訊工程碩士班 招生考試 電子學 試題卷 電機工程學系碩士班 共 10 題,每題 10 分,合計 100 分 1. Consider a common-source MOSFET amplifier in Figure 1. The transistor has μnCox(W/L)=0.25mA/V2, Vt=1.5V, VA=50V. Assume the coupling capacitors to be sufficiently large so as to act as short circuits at the signal frequencies of interest. (1) Find Rin and Vo/Vin. (2) Find the largest allowable input signal to keep the MOSFET in saturation at all times. Figure 1 2. The common source (CS) amplifier in Figure 2 has transistor parameters VTP = -2V, β= 4mA/V2 and λ=0.01V-1. Determine IDQ, VDSQ and small-signal voltage gain. Figure 2 第 1 頁,共 4 頁 3. For the circuit shown in Figure 3, R1 = R2 = 10kΩ and C1 = C2 = 100pF. Find the upper 3-dB frequency exactly. Figure 3 4. For the circuit shown in the Figure 4. Deduce the output voltage Vo in terms of input voltages Va, Vb, V1, V2, V3. Assume the used OPAMP is ideal. Figure 4 5. In Figure 5, assume the diodes D1 and D2 have the same threshold voltage VT, the forward-biased resistance Rf, and the reverse-biased resistance Rr and R >> Rf +Rr. Analyze the operation of the output Vo(t) under the below input condition. (VT=0.5V, VCC=10.0V) (1) t = 0.0~1.0sec, V1=0V and V2=0V (2) t = 1.0~2.0sec, V1= VCC and V2=0V (3) t = 2.0~3.0sec, V1=0V and V2= VCC (4) t = 3.0~4.0sec, V1= VCC and V2= VCC Figure 5 第 2 頁,共 4 頁 6. For the circuit in Fig.6, derive an expression for the transfer function Vo(s)/Vi(s). Show that the transfer function is that of a low-pass STC circuit. Find the dc gain and 3-dB frequency. Design the circuit to obtain a dc gain of 40 dB, a 3-dB frequency of 1 kHz, and an input resistance of 1 kΩ. At what frequency does the magnitude of transmission become unity? What is the phase angle at this frequency? Figure 6 7. The 6.8 V Zener diode in the circuit of Fig.7 is specified to have VZ=6.8 V at IZ=5 mA, rZ=20 Ω, and IZE=0.2 mA. The supply voltage V+ is nominally 10 V but can vary by ±1 V. (a) Find VO with no load and with V+ at its nominal value. (b) Find the change in VO when RL=2kΩ. (c) Find the value of VO when RL=0.5kΩ. (d) What is the minimum value of RL for which the diode still operates in the breakdown region? Figure 7 第 3 頁,共 4 頁 8.For the circuit in Fig.8, find VB and VE for VI=0 V, +3 V, -5 V, and -10 V. The BJT have β=100. Figure 8 9. Using the feedback method to find the voltage gain VO/VS, the input resistance Rin, and the output resistance Rout of the inverting op-amp configuration of Fig.9. Let the op amp have open-loop gain μ=104V/V, Rid=100 kΩ, and rO=1 kΩ. (Hint: The feedback is of the shunt-shunt type) Figure 9 10. (a)The superdiode shown as following, please sketch the transfer function and explain why it has almost-ideal characteristics. Figure 10 (b) Sketch the circuit of CMOS inverter and its voltage transfer characteristic. If the inverter is switched at the rate of f cycle per second, please list the dynamic power dissipation. (c) Design a MOS current mirror circuit. 第 4 頁,共 4 頁 國立臺南大學 99 學年度 電 機 工 程 學 系 碩 士 班 招生考試 電子學 試題卷 1. The NMOS and PMOS transistors in the circuit of Fig.1 are matched with k’n(Wn/Ln)=k’p(Wp/Lp)=1 mA/V2 and Vtn=-Vtp=1V. Find the drain currents iDN and iDP, as well as the voltage vo, for vI=0 V, +2.5 V, and -2.5 V. (10 分) Fig.1 2. For the constant-current source circuit shown in Fig.2, find the collector current I and the output resistance. The BJT is specified to have β=100 and VA=100 V. If the collector voltage undergoes a change of 10 V while the remains in the active mode, what is the corresponding change in collector current. (10 分) Fig.2 第 1 頁,共 5 頁 3. Complete the follwing questions: (10 分) (a) For a typical n-MOSFET, please sketch Ids as a function of Vds for various Vgs values with Vgs1>Vgs2>Vgs3>VT, and explain it. (b) What is the “body effect” in a MOSFET? (c) Draw the BJT Darlington configuration and show its current gain? (d) Why is the Miller-effect compensation often employ to compensate an op amp? 4. For the circuit in Fig.4, assuming 100 , find (a) Rin , (b) Rout (10 分) Fig. 4 5. For the circuit in Fig.5, assuming 100 , find V B and V E for (a) v I 0 , (b) v I 10 (10 分) Fig.5 第 2 頁,共 5 頁 6. For the circuit in Fig.6, the NMOS transistor is biased to have gm=1 mA/V and ID=1 mA, neglecting r0, what is the voltage gain vO =? (10 分) vi Fig. 6 7. For the circuit in Fig.7, find the labeled node voltages (V3, V4, and V5). The NMOS transistors have Vt 1 V and k n' W / L 2mA / V 2 Fig. 7 第 3 頁,共 5 頁 (10 分) 8. The OP amp in the circuit of Fig.8 is ideal with output saturation levels of ±12V. The diodes exhibit a constant 0.7-V drop when conducting. Find V_, VA, and VO for: (a) vI=+1V, (b)vI=+2V, (3)vI=-1V, (d)vI=-2V (10 分) Fig.8 9. An active-loaded MOS differential amplifier of the type shown in Fig.9 is specified as follows: (W/L)n=100, (W/L)p=200, μpCox=0.2 mA/V2, VAn=|VAp|=20 V, I=0.8 mA, RSS=25 kΩ. Calculate Gm, Ro, Ad, |Acm|, and CMRR. (10 分) Fig.9 第 4 頁,共 5 頁 10. Fig. 10 is the circuit diagram of a CMOS inverter. Sketch the CMOS circuit diagrams to realize the following functions: (a) Y AB CD (b) Y A B C D (10 分) Fig. 10 第 5 頁,共 5 頁