Capacitors and Inductors
advertisement

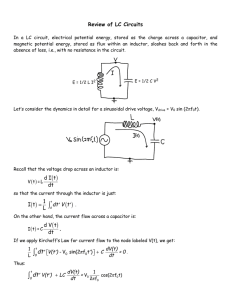
Chapter 7 Capacitors and Inductors 7.1 The Capacitors 7.2 The Inductors 7.3 Inductance and Capacitance Combination 7.4 Consequences of Linearity 7.5 Simple Op Amp Circuits with Capacitors 7.6 Duality 회로이론-І 2013년2학기 이문석 1 7.1 The Capacitors • Ideal Capacitor Model active element: an element that is capable of furnishing an average power greater than zero to some external device ideal source, op amp passive: an element that cannot supply an average power that is greater than zero over an infinite time interval resistor, capacitor, inductor → ⇒ [unit: C/V or farad(F)] 회로이론-І 2013년2학기 이문석 : permittivity 2 7.1 The Capacitors Example 7.1 Determine the current i flowing through the capacitor ( C=2 F ) → ⇒ 0 회로이론-І 2013년2학기 이문석 0 2 capacitor: open circuit to DC 3 7.1 The Capacitors • Integral Voltage-Current Relationships 1 ⇒ → ∞, ∞ Example 7.2 1 ⇒ 1 ⇒ 0 → ⇒ Determine the voltage across the capacitor ( C=2 µF ) 1 1 4000 , 0 5 1 or 1 10 20 10 회로이론-І 2013년2학기 이문석 0 8, 2 , 2 ms 4 7.1 The Capacitors • Energy Storage Power : ′ ′ 0 1 2 ′ 1 2 1 2 Example 7.3 Find maximum energy stored in capacitor. . ⇒ 1 1 20 2 2 0.1 sin 2 10 → maximuat 1 ⇒ 4 회로이론-І 2013년2학기 이문석 100 sin 2 10 10 sin 2 . 10 sin 2 2.5 100 sin 2 _ 100 5 7.1 The Capacitors 1 10 0.0001 100 2 20 2 10 0.004 cos 2 200 cos 2 0.01257 cos 2 Important Characteristics of an Ideal Capacitor 1. There is no current through a capacitor if the voltage across it is not changing with time. A capacitor is therefore an open circuit to dc. 2. A finite amount of energy can be stored in a capacitor even if the current through the capacitor is zero, such as when the voltage across it is constant. 3. It is impossible to change the voltage across a capacitor by a finite amount in zero time, for this requires an infinite current through the capacitor. (A capacitor resists an abrupt change in the voltage across it in a manner analogous to the way a spring resists an abrupt change in its displacement.) 4. A capacitor never dissipates energy, but only stores it. Although this is true for the mathematical model, it is not true for a physical capacitor due to finite resistances associates with the dielectric as well as packaging. 회로이론-І 2013년2학기 이문석 6 7.2 The Inductors • Ideal Inductor Model [unit] henry (H) Voltage is proportional to the time rate of change of the current producing the magnetic field 0 → constantcurrent ⇒short circuit to dc Example 7.4 Determine the inductor voltage. ( L = 3 H ) 3 회로이론-І 2013년2학기 이문석 7 7.2 The Inductors Example 7.5 Determine the inductor voltage. ( L = 3 H ) 3 Infinite voltage spikes are required to produce the abrupt changes in the inductor current 회로이론-І 2013년2학기 이문석 8 7.2 The Inductors • Integral Voltage-Current Relationships → ′ 1 1 1 ′⇒ 1 ⇒ 1 1 → ′ ∞, ∞ 0 Example 7.6 Determine the inductor current if i (t=-π/2)=1A. ( L = 2 H ) 6 cos 5 ⇒ 0.6 sin 5 1 2 ⇒ 2 1 6 sin 5 2 5 6 cos 5 ′ 0.6 sin 5 6 cos 5 0.6 sin 1 2 ⇒ 0.6 sin 5 0.6 sin 회로이론-І 2013년2학기 이문석 1 ⇒ 1 0.6 sin 5 1.6 Let 0.6 sin 5 5 2 5 2 1 6 sin 5 2 5 1 0.6 1.6 ∴ 0.6 sin 5 1.6 9 7.2 The Inductors • Energy Storage Power: ′ 0 ′ 1 2 1 2 ′ 1 2 ⇒ Assume 0 Example 7.7 Find the maximum energy stored in the inductor 1 2 0.1 12 sin 회로이론-І 2013년2학기 이문석 6 1 2 3 12 sin at 0: 0 0 at 3: 3 216 sin at 6: 6 0 ⇒ 216 sin 6 216 2 14.4 sin 6 6 maximum 43.2 10 7.2 The Inductors Important Characteristics of an Ideal Inductor 1. There is no voltage across an inductor if the current through it is not changing with time. An inductor is therefore a short circuit to dc. 2. A finite amount of energy can be stored in an inductor even if the voltage across the inductor is zero, such as when the current through it is constant. 3. It is impossible to change the current through in inductor by a finite amount in zero time, for this requires an infinite voltage across the inductor. (An inductor resists an abrupt change in the current across it in a manner analogous to the way a mass resists an abrupt change in its velocity.) 4. The inductor never dissipates energy, but only stores it. Although this is true for the mathematical model, it is not true for a physical inductor due to series resistances. 회로이론-І 2013년2학기 이문석 11 7.3 Inductance and Capacitance Combination • Inductors in Series ⋯ • ⋯ ⋯ Inductors in Parallel 1 1 1 ⇒ 1 회로이론-І 2013년2학기 이문석 1 1 1 ⋯ 1 1 12 7.3 Inductance and Capacitance Combination • Capacitors in Series 1 1 ⇒ 1 1 • 1 1 1 ⋯ 1 1 Capacitors in Parallel ⋯ ⋯ ⋯ 회로이론-І 2013년2학기 이문석 13 7.3 Inductance and Capacitance Combination Example 7.8 Simplify the network using series-parallel combinations. 1 1 6 1 1 2 1 3 0.8 1 5 6 0.8 2 1 2.0 1 3 1 3 6 6 3 2.0 3.0 No series or parallel combinations of either the inductors or the capacitors. can’t be simplified. 회로이론-І 2013년2학기 이문석 14 7.4 Consequences of Linearity Example 7.9 Write appropriate nodal equations for the circuit. ⇒ 1 ⇒ ′ 0 1 ′ 1 1. Inductors and capacitors are linear elements. 2. The principle of proportionality between source and response can be extended to the general RLC circuit, and it follows that the principle of superposition also applies. 3. Initial inductor current and capacitor voltages must be treated as independent sources in applying the superposition principle. 4. Thevénin and Norton’s theorem can be applied to linear RLC circuits, if we wish. 회로이론-І 2013년2학기 이문석 15 7.5 Simple Op Amp Circuits with Capacitors • Integrator 0, → ⇒ • 0, 1 0 Differentiator → ⇒ 회로이론-І 2013년2학기 이문석 16 7.6 Duality • Duality Two circuits are “dual” if the mesh equations that characterize one of them have the same mathematical form as the nodal equations that characterize the other. 3 0 10 4 회로이론-І 2013년2학기 이문석 10 2 cos 6 , 4 4 1 8 4 4 1 8 3 0 4 4 4 0 5 5 0 10 2 cos 6 , 4 4 1 8 4 4 1 8 0 5 5 0 10 17 7.6 Duality Voltage Serial Resistor Capacitor ↔ ↔ ↔ ↔ 회로이론-І 2013년2학기 이문석 Current Parallel 1/Resistor Inductor 18 7.6 Duality Practice 7.11 6 8e 10 t 0.2 10 10ia 10ib 0 ia ib d dt 1 10ia 10ib ib dt 0 C 6 i 80e 10 t ia a 8e 106 t ib b a 0.1 i a b 6 8e 10 t 0.1i 0.2 di dt i 10a 10b 0 10a 10b 6 8e 10 t 0.1 80e 10 16e 6 t 106 t 1 b dt 0 L Homework : 7장 Exercises 5의 배수 문제 (64번 문제까지) 회로이론-І 2013년2학기 이문석 19 이 자료에 나오는 모든 그림은 McGraw·hill 출판사로부터 제공받은 그림을 사 용하였음. All figures at this slide file are provided from The McGraw-hill company. 회로이론-І 2013년2학기 이문석