Tabulation to determine diameter of the copper wire
advertisement

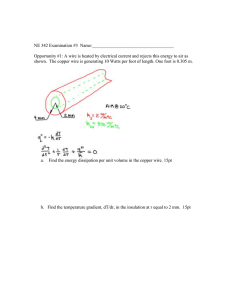
EXPERIMENTAL ARRANGEMENT OF FERMI ENERGY OBSERVATION: Determination of radius of the copper wire (r): Zero Error = Zero Correction = Least Count I In mA Value of 1 Pitch Scale Division Total No. of Head Scale Divisions = mm 0 Voltage in volt Tabulation to determine diameter of the copper wire (d): Trial No. PSR In mm HSR ZE ZC TR= PSR+ ( HSR + ZC ) X LC In mm 1. 2. Radius of the given copper wire Length of the Specimen wire Tabulation to Determination of Fermi Energy Trial No. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Voltage V In volt r = d/2 =………..mm l= 2.0metre Current I In mA Fermi Energy Aim: Determination of Fermi Energy of the given copper wire. Apparatus: Copper wire, screw gauge, sample wire, ammeter, voltmeter, battery eliminator etc,. Formula: Fermi Energy 3.95x10 2 x Slope 2 xr 4 Ef eV L2 Where Ef = Fermi energy in eV V slope From graph I R = radius of the copper wire in mm L = length of the copper wire in m Formula of Screw Gauge TR = PSR + (HSR+ZC)xLC TR = Total Reading in mm PSR = Pitch Scale Reading in mm HSR = Head Scale Reading ZC = Zero Correction LC = Least Count in mm Theory: The Fermi energy is the maximum energy occupied by an electron at 0K. By the Pauli Exclusion Principle, we know that the electrons will fill all available energy levels, and the top of that "Fermi Sea" of electrons is called the Fermi energy or Fermi level. The conduction electron population for a metal is calculated by multiplying the density of conduction electron states g(E) times the Fermi function f (E). Procedure: 1. The circuit arrangement is made as shown in figure. 2. The voltage is varied gradually and the corresponding current values are noted down. 3. A graph can be plotted with the voltage along Y-axis and the current along the X-axis. 4. The slope of the graph gives the resistance of the given copper material. 5. The radius of the copper wire is measured using a screw gauge and the values are tabulated. 6. Length of the wire is measured by using a meter scale. Determination of radius of the specimen wire using screw gauge 1. To find zero error, bring two metallic studs in contact and observe if the zero of the head scale lies ‘n’ divisions above the horizontal (pitch) line then ZE= -n & ZC = +n, if the zero of the head scale lies ‘n’ divisions below the pitch line then ZE =+n & ZC = -n, in case if the zero of the head scale exactly coincides with pitch line then instrument has no zero error. i.e., ZE=0. 2. Keep the specimen between the metallic studs and bring it into gentle contact with the help of head, note down the no. of division uncovered on pitch scale by the sleeve is the PSR, and the division on the head scale is coinciding with the pitch line is the HSR, repeat the same procedure for next trial, tabulate the readings & diameter of the wire is calculated and average value of radius is obtained. Result: Fermi Energy of the given copper wire is given by =………….eV.