Lec 7 Current, resistance - BYU Physics and Astronomy
advertisement
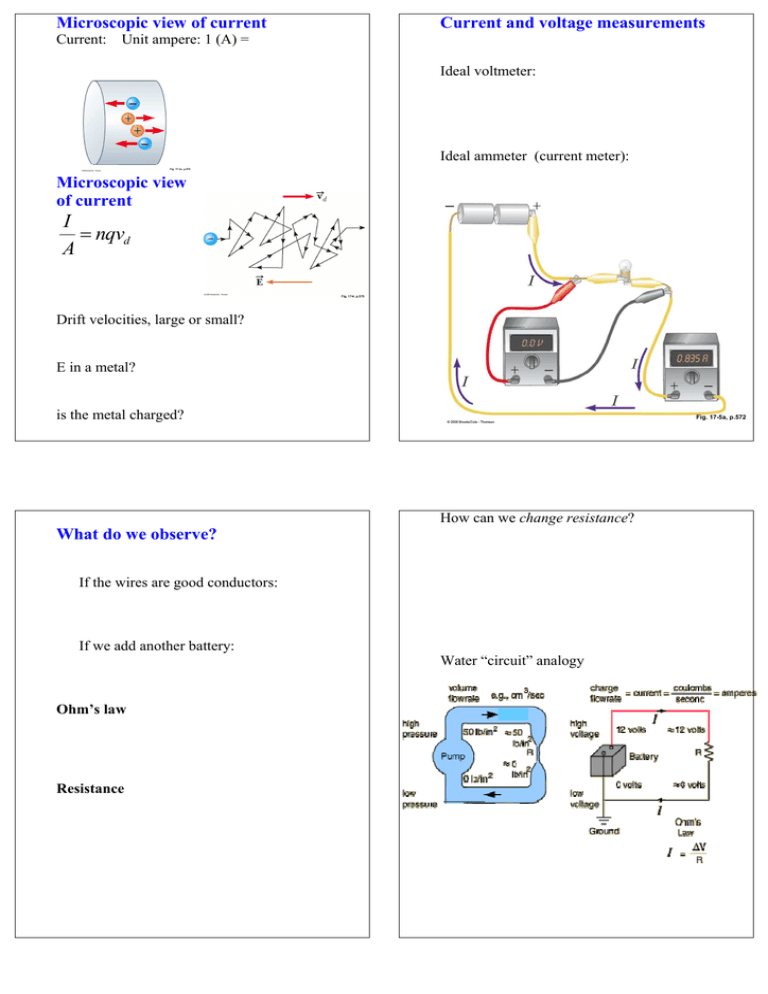
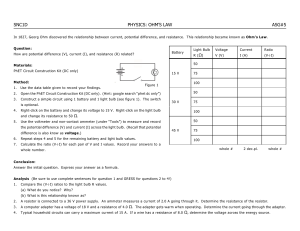
Microscopic view of current Current: Current and voltage measurements Unit ampere: 1 (A) = Ideal voltmeter: Ideal ammeter (current meter): Fig. 17-2c, p.570 Microscopic view of current I = nqvd A Fig. 17-4, p.570 Drift velocities, large or small? E in a metal? is the metal charged? Fig. 17-5a, p.572 How can we change resistance? What do we observe? If the wires are good conductors: If we add another battery: Water “circuit” analogy Ohm’s law Resistance Temperature and resistance Fig. 17-6a, p.573 1 A battery is connected in three ways. Which way(s) light(s) up the bulb (deliver(s) power)? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 1,2 E. 1,3 Fig. 17-6b, p.573 Fig. 17-6c, p.573 How much energy does each electron lose in the resistor? A high-voltage transmission line carries 1000A at 700 kV above ground voltage for a distance of 100 km. If the resistance in the wire is 1 Ω/km (each way) How much energy per second is lost by all of them? What is the voltage drop by the time it has traveled 100 miles? Power How much power is delivered to the load (a city)? P = I ∆V = I 2 ( ∆V ) R= 2 R How much power is lost in heating the transmission line? Note: Pbattery = I ∆Vbattery Energy consumed If the transmission line were at 100V above ground, what would the transmission loss be for the same power plant output? 1 kWh = 3.60 × 106 J P2. One resistor is 4 ohms. A second resistor is made of the same material, but is twice as long and has four times the conducting area, so it has a resistance of ___________ ohms A. 1 B. 2 C. 4 D. 8 E. 16 A light bulb is connected across a power source with voltage difference of 100 V. The bulb consumes 200 W of power. P3. The current is _____ A A. 2 B. 50 C. 10 D. 200 E. 500 P4. The resistance of the wire is _____ ohms A. 2 B. 50 C. 10 D. 200 E. 500 P7. Charge flows through a light bulb because of a battery. Suppose a wire which has a tiny R is connected across the bulb as shown, which has a large R. When the wire is connected, A. essentially all the charge continues to flow through the bulb. B. half the charge flows through the wire, the other half continues through the bulb. C. essentially all the charge flows through the wire. Hint: think about ohm’s law Two resistors are connected to a battery. The power consumed in each battery is shown. P5. The battery with the greatest resistance is A. top B. bottom C. same P6. The battery with the greatest current is A. top B. bottom C. same