A simple electric circuit
advertisement
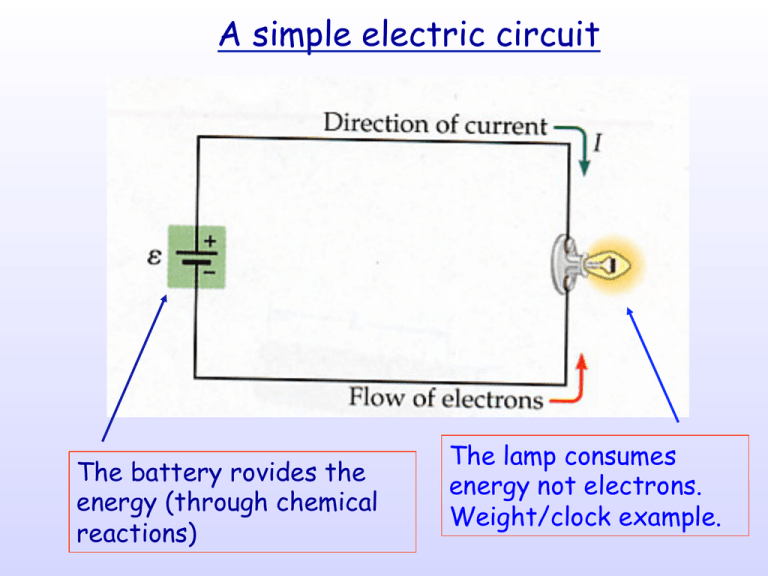
A simple electric circuit The battery rovides the energy (through chemical reactions) The lamp consumes energy not electrons. Weight/clock example. For many useful simulations on electric circuit and not only GOTO: http://phet.colorado.edu Click on ‘Simulations’ Units of Electric Potential and Electric Currents • Electric Potential Units: VOLTS – your typical AA battery has 1.5 Volts potential • Electric Current Unit: AMPERE (=1 Coulomb/sec) – Ampere is the fundamental unit NOT charge – One amp is a lot of current. It will kill you if it goes through your body – Every time you start your car the battery provides (for very short time) a current of several hundred amps A simple electric circuit The battery rovides the energy (through chemical reactions) The lamp consumes energy not electrons. Weight/clock example. Resistance (R) • Charge doesn’t flow ‘ideally’, i.e. w/out resistance (‘friction’ analog). • Resistors take energy away from the charges and convert it to heat. • AGAIN: charges are not destroyed or ‘used up’ etc. only energy. Resistance (R) • The resistance is defined as the ratio of the applied potential at the ends of the resistor, to the current flowing through the resistor V R= I Where: R is the resistance of the object (in Ohms) V the potential difference across the object, measured in Volts I is the current passing through the object, measured in Amperes Ohm's Law • For many conductors of electricity, the electric current which will flow through them is directly proportional to the voltage applied to them. When a microscopic view of Ohm's law is taken, it is found to depend upon the fact that the drift velocity of charges through the material is proportional to the electric field in the conductor. The ratio of voltage to current is called the resistance. Ohm’s law expresses electric current I which will flow through a resistor is directly proportional to the voltage V applied to it and inversely proportional to its resistance R” just the fact that “The OHM’s Law and its derivatives V R= I V = I ⋅R Examples • Simple circuit involving two resistors (lamps) – Resistors in series – Resistors in parallel Resistors in SERIES The same current, I, flows through each resistor in SERIES The total resistance is the SUM of the resistances Resistors in PARALLEL R2 Each resistor ‘sees’ the same potential The total resistance is the sum of the INVERSES and it is always less than the smallest one Example: Two 10 Ohm resistors in series are equal to 20 Ohm and in parallel equal to 5 Ohm. Examples • Simple circuit involving two resistors – Resistors in series – Resistors in parallel • Simple circuits involving lamps and switches. Applications of Resistors • Electronic circuits with vast range of applications • Non-fluorescent bulbs, Ovens, Heating elements • Resistors sensitive to Temperature – Thermistors/thermometers Superconductors • Superconductivity is a phenomenon of exactly zero electrical resistance ( and expulsion of magnetic fields) occurring in certain materials when cooled below a characteristic critical temperature • It was discovered by Heike Kamerlingh Onnes on April 8, 1911 • It is a quantum mechanical phenomenon • It occurs abruptly at the critical temperature • Recently ‘high temperature superconductors’ show promise for practical applications Magnetism • made of “poles” (instead of “charge”) • also come in two flavors (“north” and “south”) – two flavors always come in equal amounts • made of “poles” (instead of ‘charge’) • also come in two flavors (“north” and “south”) – two flavors always come in equal amounts A similar law to Coulomb law exists for magnetic forces (but only quantitatively) s Magnetic Field lines Earth is a Magnet!!!! In 1820 Hans Oersted found that a magnet is deflected by an electric wire! The unification of the electric and the magnetic force had begun electric fields can generate magnetic fields AND magnetic fields can generate electric fields • Electromagnet • dynamo (generator) • so, which came first? J.C. Maxwell (1875) • unified theory of electricity and magnetism • proved that they were different “manifestations” of electromagnetic field • proved that E-M field could travel as a wave • showed that light is just one type of Electromagnetic wave THE NATURE OF LIGHT We just answered the question of what is light? • James Clerk Maxwell (1875) – light is an electromagnetic wave • but what is a “wave”?