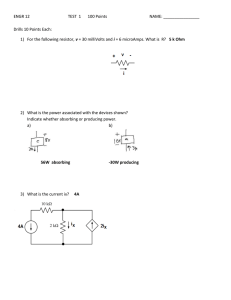
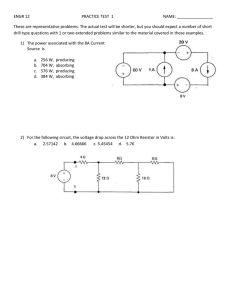
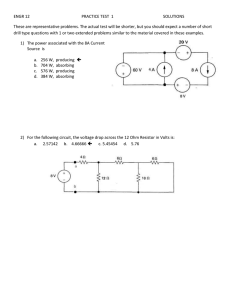
I 3.
advertisement

Chapter 2-2 •Nodes and Paths •KCL and KVL Node A node: is a point where two or more circuit elements meet. Kirchhoff’s Current Law (KCL): This law states that the algebraic sum of the currents at a node must be equal to zero. Our sign convention will be: Assign a negative sign to a current entering a node Assign a positive sign to a current leaving a node i3 i i2 i1 Find I1, I2, and I3. I1 200mA + 500mA – 100mA I2 I3 50mA R1 R2 R3 R4 Closed Path or Loop A closed path: Starting at an arbitrary node we trace a path through selected circuit elements and return to the original node, without passing through any single point more than once Kirchhoff’s Voltage Law (KVL): states that for any closed loop in a circuit, the algebraic sum of the voltages around the loop must be equal to zero. 10 Ohm 10 Ohm 10 V A 20 Ohm B Find io and voltage across 50 ohm Find vo using Kirchhoff’s laws and Ohm's law. vs = 10 V Find the value of ia. Given vg = 40 V , Rg = 3 Ω , Ra = 30 Ω , and Rb = 100 Ω Circuits with Dependent Sources Find vo Find vo Find vo What you should know 1. 2. KCL and KVL Application of them Another View