ZVEI Guideline for Customer Notifications / PCN
advertisement

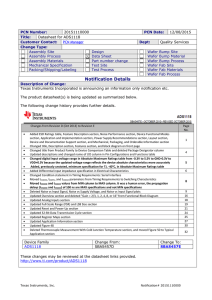
Guideline for Customer Notifications of Product and /or Process Changes (PCN) of Electronic Components specified for Automotive Applications Electronic Components and Systems (ECS) Division Impressum Product/Process Change Notification Guideline for Automotive Electronic Components Published by: ZVEI–German Electrical and Electronic Manufacturers ‘Association e.V. Electronic Components and Systems (ECS) Division Lyoner Straße 9 60528 Frankfurt am Main, Germany Phone: 069 6302 - 402 Fax: 069 6302 - 407 E-mail: zvei-be@zvei.org www.zvei.org/ecs Contact person: Dr. Rolf Winter Picture: ZVEI–German Electrical and Electronic Manufacturers‘ Association e.V. ArchMen - Fotolia.com 1st Edition, December 2006 2nd revised Edition, January 2013, Rev. 2.1 3rd revised Edition, January 2015, Rev. 2.2 This document may be reproduced according to the copyright and liability chapter free of charge in any format or medium providing that it is reproduced accurately and not used in a misleading context. The material must be acknowledged as ZVEI copyright and the title of the document has to be specified. A complimentary copy of the document where ZVEI material is quoted has to be provided. Every effort was made to ensure that the information given herein is accurate, but no legal responsibility is accepted for any errors, omissions or misleading statements in this information. The Document and supporting materials can be found on the ZVEI website www.zvei.org/PCN or at www.zvei.org under the rubric "Publikationen". 2 Content 1. Purpose / Scope 2. Preamble 3. Terminology/Definitions 4. Approach to classify product/process changes 4.1. Change Notification 4.2 Change Evaluation 5. Customer Notification Process for PCN’s 5.1 Preparation of a Product/Process Change Notification 5.2 First and second feedback from customer 5.3 Evaluation and Documentation 5.4 Finalize and Closure 5.5 Disapproval 5.6 Escalation path 6. Communication Flow for Information Notes 7. References 3 4 5 6 8 8 12 14 15 16 16 17 17 17 17 17 1. Purpose / Scope This guideline describes the specific elements of the change management process in the automotive market for product and/or process changes. The need for product/process change notifications (PCN) is defined, content and form of customer notifications is recommended. General rules and requirements are proposed for: 1. the classification of product/process changes 2. the corresponding customer change notification 3. the recommended qualification activities for suppliers and customers This guideline is aimed at suppliers who produce, assemble or test electronic components, particularly semiconductor devices, passive components and LED component which are specified between customer and supplier for automotive applications or designed for automotive applications. 4 2. Preamble Customer notifications resulting from product/process changes as described in this guideline require a close supplier/customer co-operation for which the following statements apply: (1) The supplier is entitled to perform changes to the manufacturing process and/or the product itself. For changes which require customer notification or approval as defined below the customer is informed well in advance to the intended date of implementation in order to account for the qualification and release effort on the customer side and possible OEM approval requirements. (2) The customer actively supports the change request by giving timely feedback. This feedback shall include but is not limited to (a) acknowledgement of receipt (1. feedback), (b) interim feedback (2. feedback) stating the customer's release requirements or giving a timeline by when these requirements will be available, and/or (c) change acceptance (final feedback). (3) Continuing lack of response by the customer in spite of feedback requests by the supplier will trigger appropriate escalation actions by the supplier to get customer feedback. In absence of feedback from the customer, a decision is taken by the supplier how to proceed. The customer will be informed accordingly. In cooperative and faithful supplier/customer relationship escalation will not be necessary. (4) For exceptional cases (like disaster recoveries) mutually agreed appropriate measures deviating from the outlined standard customer notification process may apply. 5 3. Terminology/Definitions Automotive Application: embedded electronic system which uses one or more of the electrical/electronic components/modules in a motor vehicle like Electronic Control Unit, Transmission Control Unit, Display, Headlamp units, etc. Board: Printed Circuit Board which is used to test electronic components or to evaluate a potential impact to processability/manufacturability at customer. Component: part manufactured by supplier or in case of modules part delivered to supplier. See also Product. Customer: see Tier1 DeQuMa: Delta Qualification Matrix is a tool to describe the requested change, the evaluation level, and the test which should be considered for qualification Evaluation Level: (as indicated in the DeQuMA) i. ”C: Component Level“: The evaluation of a change at component has to be done by the component manufacturer at the component only. Generic data from other relevant evaluations can be used. ii. ”B: Board Level“: The intended change described in the PCN may influence processability / manufacturability of the component at board level. Therefore additional evaluation by Tier1 may be necessary. iii. ”A: Application Level“: The intended change described in the PCN may influence the properties of the application (e.g. ECU). In addition to the evaluation under C or B the influence of the change in the ECU is evaluated by suitable investigations by the Tier1. The scope of the evaluation has to be aligned with the OEM. It has to be considered whether the ECU / assembly requirements are already sufficiently safeguarded by other qualifications (application-specific risk assessment). iv. ” *: will become A/B/C after decision“: Is subject to a case by case evaluation. v. ” **: Not relevant for qualification matrix“: Changes which fulfill neither A,B nor C. Fit: External dimensions and associated tolerances of the product (without packing). FMEA: Failure Mode and Effects Analysis is a methodology to identify risks in product and processes and prevent potential failure modes. Hereby the probability of occurrence of a potential failure as well as the effect of this failure in terms of its severity and the ability of detection is assessed. The so-called Risk Priority Number (RPN) is defined as the product of Severity, Occurrence and Detection and gives a measure of the overall risk associated with a planned product/process change. Form: visual appearance including shape, colour, marking, and surface finish of the product (without packing). 6 Function: electrical, mechanical, thermal and performance characteristics of the product (without packing). Information Note: A document sent to customers for information only, describing the change(s), the reason for the change(s), its timeline, and projected impact and containing all information as described in 5.1 (Figure 4). The Information Note can also be used for those types of datasheet modifications as specified in Tables 1 and 2 and/or for any other non-mandatory customer information. Manufacturability: see Processability/Manufacturability OEM: Car maker PCN: (Product/Process Change Notification): A document sent to customers describing change(s), the reasons for the change(s), its timeline, projected impact and containing all information as described in 5.1 (Figure 4). Processability/Manufacturability: The properties of a product to be processed according to the specified processes at customer. Product: Electrical/electronic component/module manufactured by supplier and delivered to customer including packing and associated information (e.g. labelling, barcode, shipment documents). Reliability: the capability of a product to perform specified properties over time Supplier: see Tier2 Supply Chain: Tier2 - Tier1 - OEM OEM: Car Maker Tier1: Automotive application manufacturer and direct supplier to OEM Tier2: Electronic component manufacturer and direct supplier to Tier1 In case of a more complex Supply Chain, all participants are requested to apply the regulations and processes described in this document by appropriate measures and/or contracts. Note: Minor / Major Changes: these terms are no longer used in this document. Classification of different types of notification (PCN, Information Note and no Information) is shown in table 1 and 2. 7 4. Approach to classify product/process changes 4.1. Change Notification The supplier shall have a documented method and an associated metric for assessing the technical risk of a change and its potential impact on the Supply Chain. One such method is the Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA) with the Risk Priority Number (RPN) as it’s metric. Based upon the assessment for the Change Request technical and contractual aspects have to be taken into account in order to decide whether a risk remains for the Supply Chain or not. If risk remains PCN is required. If not, an assessment of change type referring to tables 1, 2 or 3 is necessary to decide whether or which kind of Customer Notification is required. Change Request YES Risk on Supply Chain? NO PCN required acc. tables 1, 2 or 3? YES PCN (see Chapter 5) YES Information Note (see Chapter 6) NO Information Note required acc. tables 1, 2 or3 ? NO No Information Figure 1: General change assessment flow The change assessment matrix in tables 1, 2 and 3 contain examples only and should not be considered as representing all possible changes. These matrices are aimed at giving guidance in the decision process concerning the need and kind of Customer Notification. 8 Table 1: Change Assessment Matrix for semiconductor components without LED components (as referenced in “VDA Production process and Product Approval [PPA]”) Bare die Result: Remaining risks on supply No Yes P P P P P P I P I P P P P P P P I P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P – – – P P P P I I I P P P P P P P P P – P – I – – – – P P P P I P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P P – P P P Test Flow – P P Q Gate Equip ment Packing/ Shipping Assembly Process Wafer production Design Data Sheet Any 1) Change? 2) Assessment of impact on Supply Chain regarding following aspects - contractual agreements - technical interface of processability/manufacturability of customer - form, fit, function, quality performance, reliability 3) Type of change any change with impact on agreed upon contractual agreements any change with impact on processability/manufacturabiliy at customer, which is not covered below Change of datasheet parameters/electrical specification (min./max./typ. Values) and/or AC/DC spec. 1 Correction of datasheet errata Specification of additional parameters Design changes in active elements. 2) Design changes in routing. 3) Die shrink 4) Fimeware modification New / change of wafer substrate material New wafer diameter New final wafer thickness Change of electrically active doping/implantation element Change of gate material / dielectrics New / change of metallization (specifically chip backside) New / change of metallization (specifically chip frontside) New / change of passivation or die coating (without Bare Die) Change in process technology (e. g. process changes like lithography, etch, oxide deposition, diffusion, die back surface preparation/backgrind, ...) Process integrity: tuning within specification Change of wafer supplier. Change of specified wafer process sequence (deletion and/or additional process step) Move of all or part of wafer fab to a different not previously released location/site/subcontractor New final wafer thickness New / change of frontside metallization New / change of backside metallization Change of wafer setup or number of possible Good Dies on wafer. Change of optical appearance of wafer edge region (like imide coverage or edge exclusion) Die scribe or separation, change of Die size y Change in critical dimensions of package e Change of leadframe base material s Change in leadframe dimensions Change of lead frame finishing material (internal) Change of lead and heat slug plating material/plating thickness (external) Bump Material / Metall System (internal) Die attach material Change of wire bonding Change of BGA substrate Die Overcoat / Underfill Change of mold compound Change of encapsulation/sealing material Change of product marking Change in process technology Process integrity: tuning within specification Change of direct material supplier Change of specified assembly process sequence (deletion and/or additional process step) Move of all or part of assembly to a different not previously released location/site/subcontractor Packing/shipping specification change Dry pack requirements change Change of carrier (tray, reel) Change to labelling Production from a new equipment/tool which uses a different basic technology or which due to its unique form or function can be expected to influence the integrity of the final product. Production from a new equipment/tool which uses the same basic technology (replacement equipment or extension of existing equipment pool) without change of process. Change in final test equipment type that uses a different technology. Move of all or part of electrical wafer test and/or final test to a different not previously released location/site/subcontractor Change of the test coverage/testing process flow used by the supplier to ensure data sheet compliance (e.g. elimination/addition of electrical measurement/test flow block; relaxation/enhancement of monitoring procedure or sampling) – P 1) 2) 3) , 4) Not included: Editorial changes Not included: Design optimization = modification to adapt to the specified process window. Not included: sawing street/kerf/scribe line 9 Table 2: Change Assessment Matrix for passive components (as referenced in “VDA Production process and Product Approval [PPA]”) 1) Change? 2) Assessment of impact on Supply Chain regarding following aspects - contractual agreements - technical interface of processability/manufacturability of customer - form, fit, function, quality performance, reliability Result: Remaining risks of supply chain? Yes P P any change with impact on technical interface or processability/manufacturabiliy at customer P P Change of datasheet parameters/electrical specification (min./max./typ. values) and/or AC/DC specification P P Correction of data sheet I P Specification of additional parameters I P Change of material composition P P Change of supplier of material – P Changes termination, surface finish, shape, color, appearance or dimension structure I P Changes of inner construction – P Changes in process technology or manufacturing methods – P Process integrity: tuning within specification – P Packing / shipping specification change (loosening of tolerances) P P Dry pack requirements change P P Change of carrier (tray, reel) P P Change of labelling I P Change of the product marking I P Change of packing/shipping specification P P Production from a new equipment/tool which uses a different technology and which due to its unique form or function can be expected to influence the integrity of the final product. P P Production from a new equipment/tool which uses the same basic technology (replacement equipment or extension of existing equipment pool). – P Change in final test equipment type that uses a different technology P P Manufacturing site transfer or movement of a part of production process to a different, not previously released location/site P P Elimination or addition of a manufacturing process step – P Elimination of final electrical measurement / test flow block I P Change of test coverage used by the supplier to ensure data sheet compliance (e.g., elimination/addition of electrical measurement/test flow block, relaxation/enhancement of monitoring procedure or sampling) – P Equipment New Visual material, inspection crit.dimensi on* No any change with impact on special customer characteristics/contractual agreements Q Gate Process Flow Logistics/Capacity/Testing y e s Packing/Shipping Process Design Material Data Sheet Any 3) Type of change For more specified description of the change(s) see DeQuMa 10 Table 3: Change Assessment Matrix for LED components (as referenced in “VDA Production process and Product Approval [PPA]”) Q-gate Test Flow Equip ment Packing/ Bare die Shipping deliveries Assembly Process Wafer production Design Data Sheet Any 1) Change? 2) Assessment of impact on Supply Chain regarding following aspects Result: - contractual agreements Remaining - technical interface of processability/manufacturability of customer risks of - form, fit, function, quality performance, reliability supply chain? 3) Type of change No Yes Any change with impact on agreed upon contractual agreements P P Any change with impact on processability/manufacturabiliy at customer which is not covered below P P Change of datasheet parameters/electrical specification (min./max./typ. values) and/or Pulse/DC specification P P Correction of data sheet I P Specification of additional parameters I P Design changes in active area. P P Design changes in routing/layout for chip. P P Die shrink P P LED package P P New / change of wafer substrate or carrier material P P Wafer diameter P P New final wafer thickness P P Change of electrically active doping/implantation element P P Change of stacking P P Change in die coating or passivaton P P New / change of metallization (specifically chip frontside) P P New / change of metallization (specifically chip backside) P P Change in process technique (e. g. significant process changes like lithography, etch, oxide -P Process Integrity: Tuning within specification -P Change of material supplier without impact on agreed specifications -P Change of specified wafer process sequence (deletion and/or additional process step) -P New wafer production location or tranfer of wafer production to a different location/site/subcontractor P P Change of leadframe/carrier base material P P Y Change of leadframe/carrier finishing material (internal) P P E Change of lead and heat slug plating material/plating thickness (external) P P S Bump Material / Metall System (internal) P P Die attach material P P Change of bond wire material / diameter P P Change in material for sub-components (excluding LED chip & LED package related items) with impact on P agreed specifications P Die Overcoat / Underfill -P Change of mold compound/encapsulation/sealing material P P Change of conversion material P P Change of converter process technology I P Change of product marking I P Change in process technique (e.g., die attach, bonding, moulding, plating, trim and form, …) P P Process Integrity: Tuning within specification -P Change of direct supplier for converter material -P Change of direct material supplier without impact on specification -P Change of specified assembly process sequence (additional or deletion of process step) I P New assembly location or transfer of assembly to a different location/site/subcontractor P P New / change of front side metallization P P New / change of backside metallization P P Change of wafer setup or number of dies on wafer. I P Inner Packing/shipping specification change P P Outer Packing/shipping specification change I P Change of labelling I P Production from a new equipment/tool which uses a different basic technology P P Production from a new equipment/tool which uses the same basic technology (replacement equipment or -P Change in final test equipment type that uses a different technology I P Move of all or part of electrical wafer test and/or final test to a different location/site/subcontractor P P Change of the test coverage/testing process flow used by the supplier to ensure data sheet compliance (e.g. elimination/addition of electrical measurement/test flow block; relaxation/enhancement of monitoring procedure or sampling) -- P Above three “Change assessment matrices” detail both formal and technical aspects and help to select the correct type of customer notification. “P”, “I”, and “-“ stand hereby for PCN, Information Note and no customer notification, respectively. 11 4.2 Change Evaluation Each change has to be evaluated. For changes which are listed in Tables 1, 2 and 3 the PCN Delta Qualification Matrix (DeQuMa) has been developed by ZVEI (see Figure 2 and corresponding Excel File “DeQuMa”). This is a helpful guideline to determine which tests should be considered and which information is needed for approval of a proposed change. Based on the changes listed in Tables 1, 2 and 3 the Delta Qualification Matrix contains proposals to evaluate according to accepted standards (e.g. AEC-Q, IEC 60810). The described changes are classified for the best suitable evaluation level to verify feasible interactions between e.g. package, processability/manufacturability, and reliability. Following classifications are used: A – application level (includes component and / or board level) B – board level (includes component level) C – component level The evaluation levels are based on best knowledge of component/technology experts and are recommendations for qualification effort The Delta Qualification Matrix considers aspects as line evaluation, specification of material and remarks to the change. 12 Worked on: Max Mustermann Date: Form provided by ZVEI ‒ Revision 1.2.2 ̶ 12/2014 PCN number: Device evaluation Signature: Whisker test (IEC 60068-T2-82, JEDEC JESD201) Parameter-Analysis: Comparison of current with changed device characterization, electrical distribution LT DS IWV E7 E9 E10 E11 E12 G1-4 G5 G6 G7 G8 - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - P P Update of datesheet because of technical change of the product. - - - 1 A - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Errata sheet as information note in case of editorial changes. Errata sheet which impacts product integrity requires a PCN. A - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - A - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ● ● M - ● ● DJ - - - - - - D D D D D ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● - - F - - - - ● - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ● Lead free Internal Water Vapor DROP E5 - - Die Shear MECH E4 - - Lid Torque LF E3 - - Package Drop SER E2 - - Hermetic Package Test SC D5 - - Soft Error Rate EMC D4 - - Short Circuit Characterization CHAR D3 - - Electromagnetic Compatibility ED D2 - - Characterisation LU D1 - - Electrical Distribution CDM C6 - - Latch up HBM/MM C5 - - Electronic Discharge Charged Device Model SM C4 - - Electronic Discharge Human Body Model / Machine Model NBTI C3 - - Stress Migration HCI C2 - - Negative Bias Temperature Instability TDDB C1 - - Hot Carrier Injection EM B3 - - Time Depending Dielectric Breakdown LI B2 - - Electromigration SBS B1 - - Lead Integrity PD A6 - - Solder Ball Shear SD A5 - - Physical Dimensions WBP A4 - - Solderability WBS Potential impact on processability/manufacturing process at customers. Wire Bond Pull EDR Not relevant for technical evaluation. P Wire Bond Shear ELFR P I Early Life Failure Rate HTOL P Any change with impact on processability/manufacturabiliy at customer, which is not covered in the matrix below. High Temperature Operating Life HTSL Any change with impact on agreed upon contractual agreements SEM-AN-02 High Temperature Storage Life PTC SEM-AN-01 Power Temperature Cycling TC A3 - B ANY Headings Temperature Cycling AC Yes Further applicable conditions Autoclave or Unbiased HAST THB No Examples to explain AEC - Q100 Type of change Understanding of semiconductors experts Check of specification (for raw material only) ID Remaining risks on Supply Chain? Line evaluation (can be evaluated by data or audit/on site check) A2 ** Remarks / Comments Mark change with an "x" additional to AEC-Q10x A, B, C: Depends on change. Values: Hide Rows Values: Hide Columns Assessment of impact on Supply Chain regarding following aspects - contractual agreements - technical interface of processability/manufacturability of customer - form, fit, function, quality performance, reliability Temperature Humidity Bias or biased HAST Evaluation level A/B/C Hide Text NVM Endurance, Data Retention, and Operational Life MATERIAL PERFORMANCE TEST RESULTS (on the basis of AEC-Q100) includes integrated circuits (e.g. ASICs, µ-Controler, memories, voltage regulators, smart power devices, logic devices, analog devices,... ) AEC-Q100 A: Application level B: Boardlevel C: Component level *: will become A/B/C after decision ** : Not relevant for qualification matrix For integrated circuits or discrete semiconductors select below: Remarks DATA SHEET Headings SEM-DS-01 Change of datasheet parameters/electrical specification (min./max./typ. values) and/or AC/DC specification 1) e.g. recomendations for pull-up/pull-down or NC pins, MSL SEM-DS-02 Correction of data sheet / errata I P No technical change of the product, only correction in description (wording, drawing, …). e.g. datasheet correction because of new (I): In case of editorial changes. information about component behavior. (P): In case of impact on product integrity. SEM-DS-03 Specification of additional parameters I P Description of a new not previously covered parameter. No technical change of the product. e.g. adding new tested parameter. ) Not included: Editorial changes - DESIGN Headings SEM-DE-01 Design changes in active elements. 2) P P Any device relevant changes in design / layout of elements. Not included: design optimization e. g. change of ESD structure e. g. mask changes in active die area A, B, C: Depends on change. 2 ) Not included: Design optimization = modification to adapt to the specified process window. A SEM-DE-02 Design changes in routing. 3) P P Any change in chip design / layout. Not included: design optimization e. g. change of wiring between elements in one chip which has influence on the specified parameters / function e. g. mask changes in metal fix 3 A, B, C: Depends on change. ) Not included: Design optimization = modification to adapt to the specified process window. C SEM-DE-03 Die shrink 3) P P Shrink of active area. ) Not included: sawing street/kerf/scribe line Typical shrink of die. SEM-DE-04 Firmeware modification I P (I): e.g. Firmware is programed in the memory without effect of electical performance at the customer (bug fix). (P): e.g. Firmeware update requires hardware update and new mask set. Any change with impact on internal software intergated by design or memory. e.g. different wafer material to currently released material (like change from EPI material into nonEPI material) 3 A = Impact on EMC behavior cannot be evaluated / excluded on component level. A = If impact on electrical funtion is not excluded on component level. ● ● - M - ● ● DJ - - - - - - ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● - - - - - - A, B, C: Depends on change. ) Not included: sawing street/kerf/scribe line A - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ● *For opto-electronic components only. R is valid if the current specification of device will not change. C - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ● ● - - - - - - - - - - ● Qualification effort acc. AEC-Q100: see diffusion/doping Not realistic as a single change, will become A, B, C depending on related type of change(s). C A = impact on changes in SEM-PW-09 and/or SEM-EQ-01. ● - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ● - - - - - - - - - - - - AEC-Q100: "For broad changes that involve multiple attributes (e.g., site, materials, processes), refer to section A1.3 of this appendix and section 2.3 of Q100, which allows for the selection of worst-case test vehicles to cover all the possible permutations." R (EMC): If the die grounded with backside. C A = If thermal conductivity is affected (like MOSFET; IGBT, BGA package, stacked dies, …) A = If impact on EMC or ESD behavior cannot be evaluated / excluded on component level. - - - E M - E ● - E E - - - - - - - ● - E E E ● - - - - - - - - - - - ● Not realistic as a single change, will become A, B, C depending on related type of change(s). A - - - M - ● G - - - - - - - - - - ● - ● ● ● ● - - - - - - - - - - - - - ● M - ● - DJ - - - - - - - - - ● - ● ● ● ● ● - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ● M - ● - - - - - - - - - - - - - M M ● - ● - - - - H - - H - - ● - ● ● ● M - ● - - ● ● - - - - ● - - - ● - - - ● ● - ● - - - - - - - - ● - K K ● M - ● K ● - - - - - ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● - - - - - - - - - - ● - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ● Qualification effort depends on type of change. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ● - - - - - - - - - - - ● Qualification for IC & µ-Controller difficult on product level. Characterisation on wafer level only on test structure. AEC-Q100: "For broad changes that involve multiple attributes (e.g., site, materials, processes), refer to section A1.3 of this appendix and section 2.3 ofQ100, which allows for the selection of worst-case test vehicles to cover all the possible permutations." - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - A 4 SEM-PW-01 New / change of wafer substrate material P P New wafer material. SEM-PW-02 New wafer diameter P P Change of wafer diameter resulting in equipment and process changes. ● PROCESS - WAFER PRODUCTION Headings SEM-PW-03 New final wafer thickness P P Change in final wafer thickness. SEM-PW-04 Change of electrically active doping/implantation element P P Change in electrically active doping / implantation element resulting in a new technology. SEM-PW-05 Change of gate material / dielectrics P P Change of gate material and / or gate dielectric material. Not realistic as a single change, will become A, B, C depending on related type of change(s). A SEM-PW-06 New / change of metallization (specifically chip backside) P P Change of bottom layer of die (between die and leadframe). Change in process, material, or dimensions necessary. e. g. change from Cr/NiV/Au to Cr/NiV/Ag Electr. Funct.: Depends on electrical backside function. R (EMC): If the die grounded with backside. C SEM-PW-07 New / change of metallization (specifically chip frontside) P P Change in metallization of bondpads, material, layer thickness e. g. change from AlSiCu to AlCu e. g. change in over pad metallization R (package): If impact on bond pad. R (EMC): Electr. Conductivity can be affected C SEM-PW-08 New / change of passivation or die coating (without bare die) P P Change of top layer on die (between mold compound and die). e. g. additon of polyimide R: Change of intrinsic mechanical stress might influence electrical function. C Change of intrinsic mechanical stress might influence electrical function. SEM-PW-09 Change in process technology (e. g. significant process changes like lithography, etch, oxide deposition, diffusion, die back surface preparation/backgrind, ...) -- P (--): If the change in process technology does not influence the integrety of the final product. (P): If the change in process technology can influence the integrety of the final product. E. g. change from wet to dry etching, change from horizontal to vertical oven for oxidation, change from contact litho into stepper litho, … A, B, C: Depends on change and potential impact at final product. In case of new equipment see also "Production from a new equipment/tool…" A Please also check changes described under EQUIPMENT. SEM-PW-10 Process integrity: tuning within specification -- P Variation within process specification e.g. process control SEM-PW-11 Change of wafer supplier. -- P (--): If no remaining risk in supply chain exist (e.g. same material composition and electrical behavior). e.g. change of wafer supplier. (P): New supplier, for new wafer substrate material composition. Not on component, tested on test structure (typical for IC). Interaction on component level for discrete components expected. In case of SOI substrate HF properties have to be qualified. C SEM-PW-12 Change of specified wafer process sequence (deletion and/or additional process step) -- P Any change which is not covered by another type of change. Risk is to be assessed. A, B, C: Depends on change and potential impact at final product. C - - - SEM-PW-13 Move of all or part of wafer fab to a different location/site/subcontractor A ● ● e. g. change of cleaning process in wafer production A = If thermal conductivity is affected (like MOSFET; IGBT, BGA package, stacked dies, …) A = If impact on EMC or ESD behavior cannot be evaluated / excluded on component level. GN DJ ● - - C Not on component, tested on test structure (typical for IC). Interaction on component level for discrete components expected. In case of SOI substrate HF properties have to be qualified. - ● e.g. change in final chip/die thickness P P Wafer fab transition with additional changes (described above). ● ● M - ● ● J ● ● - - - - ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● - - - - - H - - H - - SEM-BD-01 New final wafer thickness P P Change in final wafer thickness. Change in final chip/die thickness A - - - E M - E ● - E E - - - - - - - ● - E E E ● - - - - - - - - - - - ● SEM-BD-02 New / change of frontside metallization P P e. g. change from AlSiCu to AlCu e. g. change in over pad metalization R(reliability): Verify Bond parameter B - ● ● ● M - ● - - - - - ● - - - - - - - - - - ● ● - ● - - - - - - - - - SEM-BD-03 New / change of backside metallization P P Change in bondpads, material, pad pitch, surface changes, layer thickness Change of bottom layer of die (between die and leadframe). Change in process, material, or dimensions. e. g. change from Cr/NiV/Au to Cr/NiV/Ag R(electrical function & reliability): for power semiconductors A - - - ● M - ● - - - - ● ● - - - - - - - - - - ● ● - ● - - - - - ● - - ● SEM-BD-04 Change of wafer setup or number of possible good dies on wafer. I P Needed information for pick & place machine. e. g. information change for pick & place machine. R (processability): Can the machine handle the wafer. B - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - SEM-BD-05 Change of optical appearance of wafer edge region (like imide coverage or edge exclusion) I P Selection of dies in wafer edge region which have full electrical functionality. B - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ● SEM-BD-06 Die scribe or separation I P Needed information for sawing and pick & place machine. e. g. information change for pick & place machine. R (processability): Can the machine handle the wafer. e. g. information change for sawing machine. B - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - B - ● ● ● M - - - - - - - ● - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - B - - ● ● M ● - - - - ● ● ● - ● - - - - - - - - - - - ● - L H - - H - ● - - - ● ● M - - - - - - ● ● - ● - - - - - - - - - - - ● - L H - - - - - ● AEC-Q100: "For broad changes that involve multiple attributes (e.g., site, materials, processes), refer to section A1.3 of this appendix and section 2.3 of Q100, which allows for the selection of worst-case test vehicles to cover all the possible permutations." BARE DIE Headings R: To assure process uniformity. PROCESS - ASSEMBLY Headings Change in critical dimensions of package P P Change in dimensions of existing package. SEM-PA-02 Change of leadframe base material P P New leadframe material in new composition. e. g. change from alloy42 to copper e. g. change between two different copper alloys SEM-PA-03 Change in leadframe dimensions P P Change in leadframe dimensions which has impact to the specified electrical parameter acc. data sheet or specification (e.g. heat sink, pin e. g. change in lead frame geometry dimensions, die paddle size, ...) Not included: Variation within specification. e. g. change from Ag flash to NiP protection layer e. g. change from Ag spot to Au spot R (EMC): if internal resistance is affected. e. g. increase of silver plating area C - ● ● ● M ● - - - - C ● - ● - - - - - - - - - - - - - L H - - H - - - B - ● ● ● M ● - - - - C ● - - ● - - - - - - - - - - - - - L H - - H - - - C - ● ● ● M ● ● - - - - - ● ● - - - - - - - - - - - - - ● L - - - - - - - - ● ● ● M - ● - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ● - - ● - L H - - H H - ● ● ● ● ● Q ● - - - ● ● - - - - - - - - - - - - M - - ● - - H - - - - - ● - - Change of lead frame finishing material / area (internal) P P SEM-PA-05 Change of lead and heat slug plating material/plating thickness (external) P P Change in material and process technique for final pin termination (e.g. pure tin). e.g. change in heat slug stack e.g. change from Sn into Ni/Pd/Au e.g. change of layer thickness SEM-PA-06 Bump Material / Metall System (internal) P P Stack die or die to substrate (flip chip) e. g. change to Pb-free material e. g. change of copper pillars SEM-PA-07 Die attach material P P Change of die attach material (e.g. soft solder, epoxy, etc) P P Material, diameter, change in process technique and / or bonding diagram Change of wire bonding e. g. change from Au to Cu material e. g. change from 25µm to 23µm diameter e. g. change from single to double bond Package, processability and reliability on board level can be verified by generic data. B EMC behavior is influenced if electrical connection to leadframe is affected (non conducting to conducting). Otherwise verification on component level is sufficient. C Has to be discussed with Pb-Matrix team (ESD influence). R (EMC): Influence expected if number of bond contacts > 100 or significant change of bond wire change (>30%). C A, B, C: Depends on change. B SEM-PA-09 Change of BGA substrate P P Change of BGA substrate SEM-PA-10 Die Overcoat / Underfill -- P Supporting layers for complex packages like flip chip. SEM-PA-11 Change of mold compound P P Change of mold compound. e.g. change to green mold compound e. g. change of filler particles Electrical function affected in case of mechanical stress distribution change. AOI, wave soldering and board coating has to be assessed. MSL might be changed. B SEM-PA-12 Change of encapsulation/sealing material -- P Metal cap and ceramic package e.g. of metal cap composition To be individually assessed by change (e.g. of metal cap composition) B SEM-PA-13 Change of product marking I P Marking on device. e. g. change from inked marking to laser marking e. g. marking of pin 1 e. g. change of appearance (additional marking) AOI check necessary! B SEM-PA-14 Change in process technology (e.g., die attach, bonding, moulding, plating, trim and form, lead frame preperation, …) -- P (--): If the change in process technology does not influence the integrety of the final product. (P): If the change in process technology can influence the integrety of the final product. A, B, C: Depends on change. A SEM-PA-15 Process integrity: tuning within specification -- P Variation within process specification e.g. process control SEM-PA-16 Change of direct material supplier -- P Change of suppliers e.g. for lead frames, wire material, die attach … Change of suppliers e.g. for lead frames, wire material, … SEM-PA-17 Change of specified assembly process sequence (deletion and/or additional process step) -- P E.g. lead finishing post trim & form changed to preplated lead frame. e. g. additional cleaning step (plasma etching) or deletion of optical inspection SEM-PA-18 Move of all or part of assembly to a different location/site/subcontractor. P P Assembly transfer or relocation Dual source strategy SEM-PS-01 Packing/shipping specification change P P SEM-PS-02 Dry pack requirements change P SEM-PS-03 Change of carrier (tray, reel) SEM-PS-04 Change of labelling ESD investigations are only necessary if internal ground and power supply connection of leadframe is affected. A = If impact on EMC behavior cannot be evaluated / excluded on component level. A = If impact on EMC behavior cannot be evaluated / excluded on component level (if die attach has impact on electrical conductivity). A = Impact on EMC behavior cannot be evaluated / excluded on component level. A = If impact on electrical funtion is not excluded on component level. C A = impact of thermo mechanical stress caused by mismatch of mold compound, interconnecting technology and carrier is evident. A = impact on EMC behavior cannot be evaluated / excluded on component level (if encapsulation / sealing has impact on electrical conductivity). Please also check changes described under EQUIPMENT (SEM-EQ-01). - - - - ● ● ● M ● ● - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ● - - - - - H - - - ● ● ● M ● ● ● - - - ● ● - ● - - - - - - - - - - - - ● L - - - - - - ● - - ● ● - ● - - - - - - ● - ● - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ● - ● - ● - ● - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - For wire bond strengh test preconditioning needed (AEC-Q101). Parameter Analysis: Strictly required only for Power devices. In general: Site audit for material change with impact on bondprocess (e.g. from Au to Cu) recommended. AEC-Q100: "For broad changes that involve multiple attributes (e.g., site, materials, processes), refer to section A1.3 of this appendix and section 2.3 of Q100, which allows for the selection of worst-case test vehicles to cover all the possible permutations." - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - C - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Assumption that change material specification remains unchanged. Otherwise see change of material. C - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - See change of material. Single case assessment necessary to identify possible interactions or risk. C - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ● Qualification depends on specific change. Transfer of known technology and equipment. C ● ● ● ● M - ● ● - ● ● ● ● T ● - - - - - - - - ● - - - - L H - - H H - ● Packing/shipping specification change. Will approve by logistic and/or purchasing. ** - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - P Change of dry pack requirements (e.g. change of MSL) As defined in PPAP documentation. ** - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - P P Change of carrier (tray, reel) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ● SEM-PA-08 Investigation for ESD is only necessary if internal ground and power supply connection of leadframe is affected. If risk for EMC is assessed, qualification on application level (A) is necessary. ● SEM-PA-04 Change of surface material of die attach pad and second bond area (e.g. influence in adhesion to mold compound, wedge bond reliability) R: Influence in package change and processability should be assessed. ● SEM-PA-01 e. g. changes in package dimensions (further development). - Whisker tests have to be done on monitoring basis! A or B = impact on other type of changes described under PROCESS ASSEMBLY and EQUIPMENT (SEM-EQ-01). AEC-Q100: "For broad changes that involve multiple attributes (e.g., site, materials, processes), refer to section A1.3 of this appendix and section 2.3 of Q100, which allows for the selection of worst-case test vehicles to cover all the possible permutations." PACKING/SHIPPING Headings B I P Change of labelling also on reel. (I) e.g. additional information (RoHS stamp) (P) e.g. change of customer specific information Update in customer specification/documentation necessary. Processabillity check in production flow. B - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - SEM-EQ-01 Production from a new equipment/tool which uses a different basic technology or which due to its unique form or function can be expected to influence the integrity of the final product P P Change in process technique which is not already covered above. Change from single wafer to batch process (e.g. over pad metalisation) e.g. dambar cutting (mechanical to laser cutting) A, B, C: Change is described in all manufacturing and testing areas. Therefore the affected change is to check. A - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ● - - - - - - - - - - - - SEM-EQ-02 Production from a new equipment/tool which uses the same basic technology (replacement equipment or extension of existing equipment pool) without change of process. -- P e. g. change from single site to multi site handler. A, B, C: Depends on sensitivity of component and affected parameters. C - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ● Change in final test equipment type that uses a different technology P P Change of tester platform (e.g. new test program, new tester interface, …). e. g. change tester equipment from LTX to Teradyne Gage R&R / delta correlation / spike analysis needed. C - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ● - - - - - - - - - - - ● Gage R&R / delta correlation P P Tester transfer or relocation. Check impact on SEM-AN-01 Dual source strategy Gage R&R / delta correlation C ● - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ● - - - - - - - - - - - ● Gage R&R / delta correlation -- P E. g. test flow block, reduction from three E. g. test flow block, reduction from three R (electr. funct.): test coverage temperature measurements to two temperature temperature measurements to two temperature R (reliability) only for change in burn in process measurements, change in burn in / run in process. measurements, change in burn in / run in process. C - - - - - - - * - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ● - - - - - - - - - - - ● - EQUIPMENT Headings SEM-EQ-03 PCN required for dedicated equipment for sensitive component production. Affected process change is to check. TEST FLOW Headings SEM-TF-01 Move of all or part of electrical wafer test and/or final test to a different location/site/subcontractor Q-GATE Headings SEM-QG-01 Change of the test coverage/testing process flow used by the supplier to ensure data sheet compliance (e.g. elimination/addition of electrical measurement/test flow block; relaxation/enhancement of monitoring procedure or sampling) - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Tests, which should be considered for the appropriate process change after selection of condition table. - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - Suppliers performed tests (mark with an 'X' for done or 'G' for generic) Reason for exception of tests: -I P Not required. Information Note required. PCN required. A letter or "●" indicates that performance of that stress test should be considered for the appropriate process change. CONDITIONS A Only for peripheral routing B For symbol rework, new cure time, temp C If bond to leadfinger D Design rule change E Thickness only F MEMS element only G Only from non-100% burned-in parts H Hermetic only J EPROM or EEPROM K Passivation only M For devices requiring PTC N Passivation and gate oxide P Passivation and interlevel dielectric Q Wire diameter decrease S Required for plastic SMD only T Only for Solder Ball SMD => Please mark 'NO' with 'x', default is 'YES' Comments Figure 2: Parameter Analysis: Delta correlation * For "burn in" changes ELFR recommended Tests, which should be considered for the appropriate process change. Worksheet “Active Components” of the corresponding Excel File “Delta Qualification Matrix (DeQuMa)” The recommended Communication Flow between Tier2 and Tier1 is described in chapter 5 (PCN) and chapter 6 (Information Notes) of this document (corresponding to VDA Volume 2 “Production process and Product approval (PPA)”). Note: The communication between and within all parties is crucial for the total throughput time of the PCN Process within the supply chain (Tier2–Tier1–OEM). 13 5. Customer Notification Process for PCN’s In general the PCN notification process can be understood as shown in Figure 3. Total through put time for complete PCN process should not exceed the projected through put time as described in Table 3. All parties are asked to support short through put times. Figure 3: Generic PCN process flow 14 5.1 Preparation of a Product/Process Change Notification ZVEI recommends to use the tools (Excel Files) “PCN Form” (Figure 4) and “Delta Qualification Matrix” (completion of mandatory content, relevant attachments like datasheet and qualification results, …). Both available at www.zvei.org/PCN. However, if the “PCN Form” is not used, all mandatory information indicated in the “PCN Form” have be provided and the Qualification has to correspond to the Delta Qualification Matrix. The PCN has to be forwarded to the appointed PCN contact at customer. Note: Complete Information is crucial to avoid a delay in the PCN process. Standardized Information for Process/Product Change Notification (PCN) ZVEI - Zentralverband Elektrotechnik- und Elektronikindustrie e.V. ZVEI - German Electrical and Electronic Manufacturers`Association 1.2 PCN No. 1.3 Title of PCN 1.4 Product Category e.g.CM1234567 e.g. Change of mold compound into green mold for SOT23 Semiconductor Components 1.5 Issue date 2012.01.01 1.6 PCN revision history (optional) 1.7 Issue date of previous revision (optional) 1.8 Delta to previous revision (optional) e.g. CM1234566 2011.01.01 e.g. Change of mold compound into green mold for D2PAK 2. PCN Team 2.1 Contact supplier 2.1.1 Name 2.1.2 Phone 2.1.3 Email 2.2 Team supplier 2.2.1 Name (optional) Carl Clever Mr. Mustermann +49 123 456789 max.mustermann@newcompany.com 2.2.2 Phone (optional) +49 123 987654 2.2.3 Email (optional) carl.clever@newcompany.com 3. Changes 3.1 Category 3.2 Type of change Change #1 Process Assembly-new Material-Mould compound, encapsulation/sealing material Change #2 Datasheet Correction of datasheet Figure 4: Standardized Information for Process/Product Change Notification (excerpt) 15 Form provided by ZVEI - Revision 1.8b 1. PCN basic data 1.1 Company 5.2 First and second feedback from customer Customer should acknowledge receipt of the PCN and provide a first feedback latest within 2 weeks from delivery of the PCN according to the attached customer feedback form displayed in the ZVEI PCN template. In case of no reaction from customer within 3 weeks from delivery of the PCN an escalation will be started by the supplier (see Chapter 5.6). After customer has finished their assessment according to the PCN Delta Qualification Matrix, a second feedback to the supplier will be given according to the attached customer feedback form displayed in the ZVEI PCN template indicating: - acknowledge evaluation level, additional information, needed samples, estimated closing date for PCN. The total through-put time for both feedbacks from customer should not be longer than 6 weeks from delivery of the PCN. If the second feedback is the final feedback the customer is asked to send the approval to the supplier immediately. Table 4: Projected through-put time Evaluation Level 1st Feedback 2nd Feedback Evaluation and Documentation(1) Finalize and Closure projected through put time ** 2 weeks 4 weeks 2 weeks 2 weeks 10 weeks C 2 weeks 4 weeks 4 weeks 2 weeks 12 weeks B 2 weeks 4 weeks 12 weeks 2 weeks 20 weeks A 2 weeks 4 weeks depends on application 2 weeks depends on application (1) starts with sample availability at customer (if required) 5.3 Evaluation and Documentation Based on customer feedback and assessment the identified action points need to be done. To assure the fastest throughput time a good cooperation and communication between supplier and customer is mandatory. The evaluation by the customer results in an approval or disapproval of the proposed change. In case the projected throughput time (see table 4) is jeopardized an escalation will be started by supplier or customer (see Chapter 5.6). 16 5.4 Finalize and Closure If the proposed change can be agreed, the customer will send an approval in writing to the supplier within two weeks. The supplier will implement the change and will indicate the first delivery of the changed product. 5.5 Disapproval Disapproval will end in a supplier decision how to proceed with the change. The customer will be informed accordingly. 5.6 Escalation path Lack of response by the customer within the projected throughput time will trigger appropriate escalation actions by the supplier. In absence of feedback from the customer, a decision is taken by the supplier how to proceed. The customer will be informed accordingly. 6. Communication Flow for Information Notes If an Information Note is required (see Figure 1 and Tables 1, 2 and 3), ZVEI recommends to use the attached “Information Note” form. However, if the “Information Note” form is not used, all mandatory information indicated in the “Information Note” form should be provided. The Information Note has to be forwarded to the appointed PCN contact at customer (if not otherwise defined) in a timely manner. Confirmation of receipt is recommended. 7. References All mentioned documents are available at ZVEI Homepage under www.zvei.org/PCN 17 Published by: ZVEI–German Electrical and Electronic Manufacturers‘ Association e.V. Electronic Components and Systems (ECS) Division Lyoner Straße 9 60528 Frankfurt am Main, Germany Phone: 069 6302 - 402 Fax: 069 6302 - 407 E-mail: zvei-be@zvei.org www.zvei.org/ecs