2.2.Main Structural Elements of DC Machine
advertisement

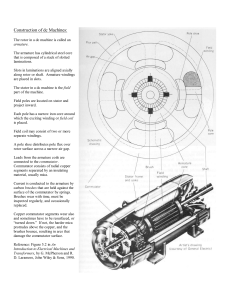
ECEg439:-Electrical Machine II 2.2 Main Structural Elements of DC Machine By Sintayehu Challa Construction of DC Machines A DC machine consists of two main parts 1. Stationary Part (Stator):-It is designed mainly for producing a magnetic flux. The stationary part of a DC Machine consists of a) b) c) Main poles:-Designed to create the magnetic flux Commutating poles interposed between the main poles and designed to ensure sparkless operation of the brushes at the commutator Frame (Yoke):The Frame is the stationary part of the machine to which are fixed the main and commutating poles and by means of which the machine is bolted to its bed plate. The Yoke is the ring shaped portion which serves as the path for the main and commuting pole fluxes 2. Rotating Part (Rotor):-It is called the armature, where the mechanical energy is converted into Electrical(as Generator) or conversily,Electrical Energy into mechanical (as Motor). Air-Gap :-The stator and Rotor are separated from each other by small air gap. By Sintayehu Challa ECEg439:Electrical Machine II DC Machine Construction By Sintayehu Challa ECEg439:Electrical Machine II 3 DC Machines ? The stator of the dc motor has poles, which are excited by dc current to produce magnetic fields. ? In the neutral zone, in the middle between the poles, commutating poles are placed to reduce sparking of the commutator. The commutating poles are supplied by dc current. ? Compensating windings are mounted on the main poles. These short-circuited windings damp rotor oscillations. ? The object of the Field System (Series and Shunt) is to create a uniform magnetic field, within which the armature rotates. By Sintayehu Challa ECEg439:Electrical Machine II 4 DC Machines ? The poles are mounted on an iron core that provides a closed magnetic circuit. ? The motor housing supports the iron core, the brushes and the bearings. ? The rotor has a ring-shaped laminated iron core with slots. ? Coils with several turns are placed in the slots. The distance between the two legs of the coil is about 180 electric degrees. By Sintayehu Challa ECEg439:Electrical Machine II 5 DC Machines ? The coils are connected in series through the commutator segments. The ends of each coil are connected to a commutator segment. ? The commutator is a form of rotating mechanical switch placed between the armature and the external circuit and so arranged that it will reverse the connection with the external circuit at the instant of each reversal of current in the armature. The commutator consists of insulated copper segments mounted on an insulated tube. ? The function of brushes is to collect current from the commutator and supply it to the external load circuit. By Sintayehu Challa ECEg439:Electrical Machine II 6 DC Machines ? ? ? ? The rotor has a ringshaped laminated iron core with slots. The commutator consists of insulated copper segments mounted on an insulated tube. Two brushes are pressed to the commutator to permit current flow. The brushes are placed in the neutral zone, where the magnetic field is close to zero, to reduce arcing. By Sintayehu Challa ECEg439:Electrical Machine II 7 DC Machine Construction Rotation Ir_dc/2 Brush Ir_dc/2 Ir_dc Shaft Pole winding | 1 2 8 N 3 7 6 S 4 5 Insulation Rotor Winding Ir_dc Copper segment Figure Commutator with the rotor coils connections. By Sintayehu Challa ECEg439:Electrical Machine II 8 DC Machine Construction Figure Details of the commutator of a dc motor. By Sintayehu Challa ECEg439:Electrical Machine II 9 DC Machine Construction Figure DC motor stator with poles visible. By Sintayehu Challa ECEg439:Electrical Machine II 10 DC Machine Construction Figure Rotor of a dc motor. By Sintayehu Challa ECEg439:Electrical Machine II 11 DC Machine Construction Figure Cutaway view of a dc motor. By Sintayehu Challa ECEg439:Electrical Machine II 12