RC circuit, magnetic fields, magnetic force
advertisement

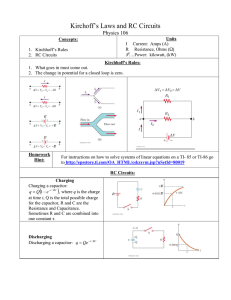
Recap Lecture 13 © Matthias Liepe, 2012 Today: • More on RC circuits • Magnets and magnetic field a i RC circuit: Charging R i i i At time t 0 the switch is C moved to position a. RC circuit: Discharging a R b i i C • The switch has been at position a for a very long time. • At time t 0 move the switch to position b. • Current i begins to flow to discharge the capacitor. RC circuit: Discharging R b i i C At time t 0 the switch is moved to position b. 120 Current i (mA) What is the 100 approximate value of 80 the time constant for 60 this decay of electric 40 current from a 20 discharging capacitor 0 in a simple RC circuit? 0 A. B. C. D. E. ~25 s ~35 s ~50 s ~100 s ~250 s 50 100 150 Time t (s) 200 250 120 A. B. C. D. E. 1.2 C 3.0 C 6.0 C 12 C 18 C 100 Current i (mA) Approximately, what was the discharging capacitor’s initial charge at time t = 0 ? 80 60 40 20 0 0 50 100 150 Time t (s) 200 250 At time t =2 , how much charge is on the capacitor? A. B. C. D. E. 0.14 qf 0.37 qf 0.63 qf 0.79 qf 0.86 qf Charge q The graph shows the electric charge on a charging capacitor in a simple RC circuit. q6 f 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 50 Charging 100 Time150 t 200 250 Magnetic Fields and Forces The Earth’s magnetic field near the surface can be approximated by the field of a bar magnet. In which direction would the magnetic north pole of Earth’s magnet point? A. B. C. D. To the geographic north pole To a point near the geographic north pole To the geographic south pole To a point near the geographic south pole Magnetic Fields and Forces How can we detect a magnetic field B?