PHY 2049 - Assignment 22
advertisement

PHY 2054 – Test I review
Name: ___________________________
Show all work in the spaces provided where appropriate. Final numerical answer should be given with
the appropriate units, when applicable.
1. A metallic object has been given a negative charge of – 2.40 µC by the process of induction using a
grounding wire. How many excess electrons does this object have?
_________________________
2. An electron traveling horizontally enters a region where there is a constant E field directed upward
(north). What is the direction (N, S, E, W) of the force exerted on the electron once it has entered the
field?
_____________________________
3. Why do bits of paper become attracted to a negatively charged plastic comb?
______________________________________________________________________
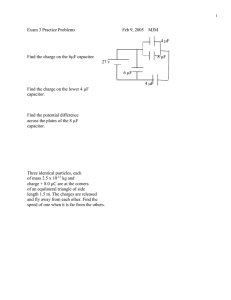
4. A helium nucleus is floating between the plates of a charged parallel-plate capacitor shown below.
The nucleus has a charge of +2e and a mass of mn = 6.60 x 10-27 kg. {Hint: floating means that the
charge is in equilibrium, i.e., electric force is = gravitational force}
a. How many Coulombs of charge does the helium nucleus have?
______________________________
b. What is the magnitude of the electric field?
______________________________
1
5. Three charges: q1 = - 2.00 x 10-6 C, q2 = - 3.20 x 10-6 C, and q3 = + 1.50 x 10-6 C are located along the
x-axis at the following positions: x1 = - 4.00 m, x2 = 2.00 m and x3 = 8.00 m. What is the magnitude
and direction of the net force on q2 due to the other charges, q1 and q3?
q1 = - 2.00 µC
x1 = -4.00 m
ΣF2 = _________________________
q2 = - 3.20 µC
x2 = 2.00 m
q3 = + 1. 50 µC
x3 = 8.00 m
direction ___________________________
2
6. Three charges have equal magnitudes, except two are positive (C & B) and one is negative (A). These
charges are fixed to the corners of an equilateral triangle as shown below. Which of the following
gives the correct direction for the net force on charge B?
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
h.
7. The drawing below shows 3 charges arranged at the same distance from the origin O. Which of the
following gives the correct direction for the net electric field at the origin due to the source charges
shown below?
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
3
f.
g.
h.
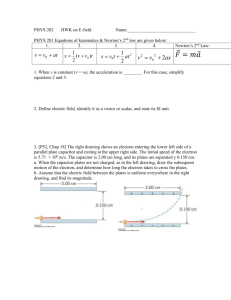
8. Three point charges are arranged on an xy-axis as shown below.
y
y=2m
q2 = - 20.0 µC
q3 = - 16.0 µC
x
x=1m
y=-2m
q1 = + 40.0 µC
a. What is the net electric field E (magnitude and direction) at the origin due to charges q1 q2 and q3?
E = ____________________________
b. If a + 5.00 µC were placed at the origin, what would be the net force F (magnitude and direction)
that it would experience? {Hint: you do not need to recalculate using Coulomb’s Law, just make
use of the results that you found in part a, and the relation between E and F}
F = ____________________________
4
9. The figure below shows a charged parallel-plate capacitor. The magnitude of charge on each plate is
q = 9.00 x 10-8 C, and the area of each plate is A = 3.00 x 10-2 m2.
a. Draw an arrow on the diagram to indicate the direction of the electric field E at the point P.
b. What is the magnitude of the electric field E at the point P?
E = ______________________
c. If a charge of q = - 3.00 µC is placed at the point P, what is the magnitude and direction of the
force on it?
F = ______________________
direction _________________________
5
10. Each case below shows the potential at two points in space, point A and point B.
A
•
150 V
B
•
50 V
Case 1
A
B
•
•
- 25 V
25 V
Case 2
A
•
- 10 V
B
•
- 50 V
Case 3
(a) For each case, determine the potential difference between the points A and B. {Be sure to indicate ±
signs}
Case 1: VB – VA = ________________________
Case 2: VB – VA = ________________________
Case 3: VB – VA = ________________________
(b) For Case 1, determine how much work the electric force has to do in moving a proton from point A to
point B. {Be sure to indicate ± signs}
Case 1: _________________________
(c) For Case2, determine the change in potential energy of an electron from point A to point B. {Be sure
to indicate ± signs}
Case 2: _________________________
11. Which of the following statements is True and which is False regarding equipotential surfaces:
a. Equipotential surfaces are sometimes parallel to the electric field E
T/F _________
b. No work is done in moving a charge along an equipotential surface.
T/F _________
c. Charges can experience a change in their KE while moving along an equipotential
T/F _________
d. If V is constant in a region of space, then ∆V = 0 in that region
T/F _________
e. If V is constant in a region of space, then E = 0 in that region
T/F _________
6
12. The positive terminal (anode) of an X-ray tube is at a potential of Va = + 125,000 Volts and the
negative terminal (cathode) is at a potential Vc = 25,000 Volts. Electrons at the cathode accelerate
toward the anode when subjected to the potential difference between these two terminals. As they
crash into the anode, X-rays are generated.
(a) What is the change in the potential energy of an electron as it goes from the cathode to the anode?
________________________
(b) Assuming that an electron starts from rest at the cathode, what is its final speed when it arrives at the
anode?
________________________
7
13. The plates of an air-filled parallel plate capacitor each have an area of 0.240 m2. When the capacitor
is charged with a 12.0 volt battery, the capacitor stores q = ± 5.00 x 10-9 C of charge in each plate,
respectively.
a. What is the capacitance of this capacitor?
_____________________________
b. What is the distance of separation between the plates?
_______________________________
c. What is the value of the electric field between the plates?
________________________________
d. How much energy is stored between the plates?
_____________________________
Suppose now that a dielectric slab is inserted between the plates of the isolated capacitor (disconnected
from the battery) and its potential difference drops to 8.00 Volts.
e. What is the new value of capacitance?
________________________________
f. What is the value of the dielectric constant?
κ = ________________________________
8
14. An air-filled parallel-plate capacitor with plates of area A and separation d is charged so that the
potential difference between its plates is V. The capacitor is then isolated (from the battery) and its
plates are pulled further apart to a separation 2d. After the plates are separated indicate if the
quantities below (a) increase, (b) decrease, or (c) remain the same
C’ = _____________________________
q’ = _____________________________
V’ = _____________________________
15. A parallel-plate capacitor is fully charged to a potential difference V. A dielectric with constant κ = 5
is inserted between the plates while the battery is still connected to the capacitor. Indicate which is
True (T) and which is False (F) for the following:
a. The capacitance increases by a factor of 5
T/F _____________
b. The magnitude of charge on the plates increases by a factor of 5
T/F _____________
c. The potential difference between the plates decreases by a factor of 5
T/F _____________
d. The electric field between the plates remains constant
T/F _____________
e. The energy between the plates of the capacitor remains unchanged
T/F _____________
9
ANSWERS
1) 1.50 x 1013 electrons
2) South
3) Because they become polarized – their charge separates – so that the opposite charge is attracted to
the charge on the comb. However, the bits of paper are still neutral.
4) (a) 3.20 x 10-19 C
(b) 2.02 x 10-7 N/C
5) |ΣF| = 2.80 x 10-3 N, θ = 0° (+ x dir)
6) b.
7) f.
8) (a) |ΣE| = 1.97 x 105 N/C, θ = 43.2° (b) |ΣF| = 9.85 x 10-1 N, θ = 43.2°
9) (a)
(b) |E| = 3.39 x 105 N/C
10) (a) -100 V, + 50.0 V, -40.0 V
11) (a) F
(b) T (c) F
12) (a) – 1.60 x 10-14 J
(c) F = +1.02 N, upward
(b) + 1.60 x 10-17 J
(c) - 8.00 x10-18 J
(d) T (e) T
(b) 1.88 x 108 m/s
13) (a) 4.17 x10-10 F (b) 5.10 x 10-3 m (c) 2.35 x 103 V/m (d) 3.00 x 10-8 J
(e) 6.25 x 10-10 F (f) 1.50
14) C’ decreases, q’ constant, V’ increases
15) (a) T
(b) T (c) F
(d) T (e) F
10