Federal States in Germany
advertisement
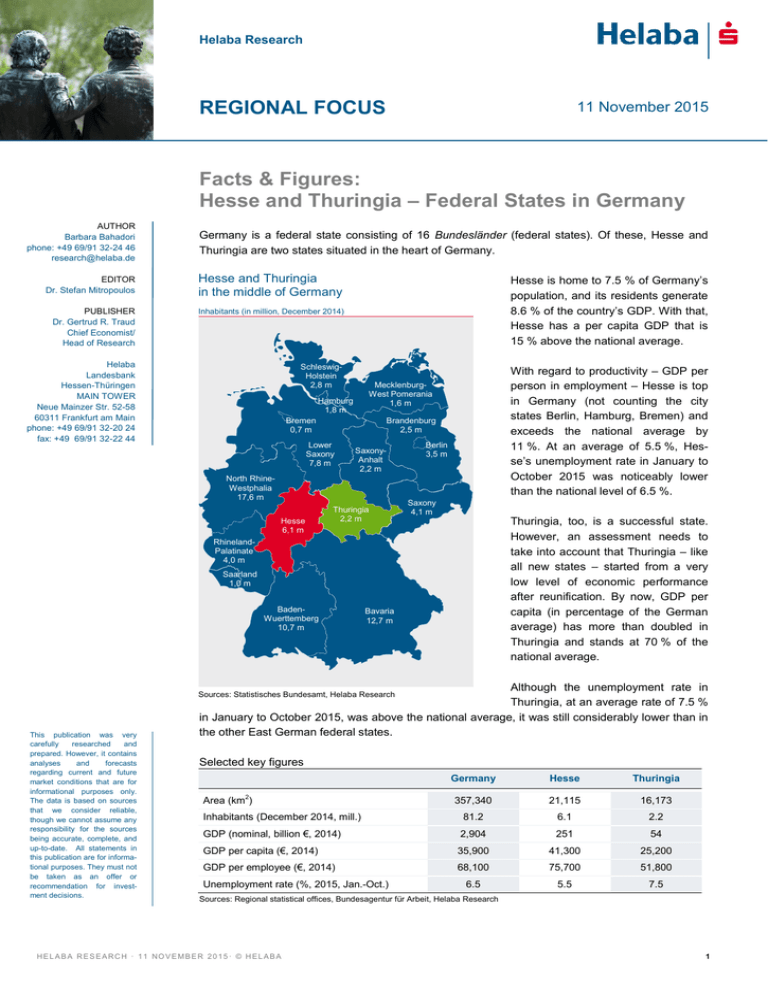
Helaba Research REGIONAL FOCUS 11 November 2015 Facts & Figures: Hesse and Thuringia – Federal States in Germany AUTHOR Barbara Bahadori phone: +49 69/91 32-24 46 research@helaba.de Germany is a federal state consisting of 16 Bundesländer (federal states). Of these, Hesse and Thuringia are two states situated in the heart of Germany. EDITOR Dr. Stefan Mitropoulos Hesse and Thuringia in the middle of Germany PUBLISHER Dr. Gertrud R. Traud Chief Economist/ Head of Research Inhabitants (in million, December 2014) Helaba Landesbank Hessen-Thüringen MAIN TOWER Neue Mainzer Str. 52-58 60311 Frankfurt am Main phone: +49 69/91 32-20 24 fax: +49 69/91 32-22 44 SchleswigHolstein 2,8 m Hesse is home to 7.5 % of Germany’s population, and its residents generate 8.6 % of the country’s GDP. With that, Hesse has a per capita GDP that is 15 % above the national average. Hamburg 1,8 m Brandenburg 2,5 m Bremen 0,7 m Lower Saxony 7,8 m SaxonyAnhalt 2,2 m North RhineWestphalia 17,6 m Hesse 6,1 m With regard to productivity – GDP per person in employment – Hesse is top in Germany (not counting the city states Berlin, Hamburg, Bremen) and exceeds the national average by 11 %. At an average of 5.5 %, Hesse’s unemployment rate in January to October 2015 was noticeably lower than the national level of 6.5 %. MecklenburgWest Pomerania 1,6 m Thuringia 2,2 m Berlin 3,5 m Saxony 4,1 m Thuringia, too, is a successful state. However, an assessment needs to take into account that Thuringia – like all new states – started from a very low level of economic performance after reunification. By now, GDP per capita (in percentage of the German average) has more than doubled in Thuringia and stands at 70 % of the national average. RhinelandPalatinate 4,0 m Saarland 1,0 m BadenWuerttemberg 10,7 m Bavaria 12,7 m Although the unemployment rate in Thuringia, at an average rate of 7.5 % in January to October 2015, was above the national average, it was still considerably lower than in the other East German federal states. Sources: Statistisches Bundesamt, Helaba Research This publication was very carefully researched and prepared. However, it contains analyses and forecasts regarding current and future market conditions that are for informational purposes only. The data is based on sources that we consider reliable, though we cannot assume any responsibility for the sources being accurate, complete, and up-to-date. All statements in this publication are for informational purposes. They must not be taken as an offer or recommendation for investment decisions. Selected key figures Area (km2) Inhabitants (December 2014, mill.) Germany Hesse Thuringia 357,340 21,115 16,173 81.2 6.1 2.2 GDP (nominal, billion €, 2014) 2,904 251 54 GDP per capita (€, 2014) 35,900 41,300 25,200 GDP per employee (€, 2014) 68,100 75,700 51,800 6.5 5.5 7.5 Unemployment rate (%, 2015, Jan.-Oct.) Sources: Regional statistical offices, Bundesagentur für Arbeit, Helaba Research HELABA RESEARCH · 11 NOVEMBER 2015 · © HELABA 1 F ACT S & FIGURES: HES SE AND THURINGIA – F EDERAL ST AT ES IN GE RMANY Hesse’s per capita GDP 50 % above the EU average These two federal states also hold up well in an international comparison. For example, Hesse’s GDP is as large as Denmark’s, and the per capita output is 50 % higher than the EU average. At 86 %, Thuringia’s economic output per capita is still slightly below the EU average. However, compared with other successor states of the former Eastern Bloc such as Poland (40 %) and Czech Republic (54 %), this is an excellent level. Hesse’s GDP equal to Denmark’s, Thuringia’s per capita GDP higher than Central/Eastern Europe GDP (nominal, billion €, 2014) 450 GDP GDP per capita (€) 50 000 GDP per capita 400 40 000 350 300 30 000 250 200 20 000 150 100 10 000 50 0 0 Sources: Eurostat, National accounts of the federal states, Helaba Research Crucial to Hesse’s strong economic performance is the state’s special mix of sectors. No other federal state can boast simultaneously an important financial center, an international airport, and a highly-regarded international fair. This is also reflected in the statistical data: One third of gross value added is generated in the economic sector “Financing, insurance, renting, business service providers”. Another 22 % of the output comes from the sector “Trade, transport, tourism, telecommunication”. Service-provider state Hesse, industrial Thuringia Share of gross value added (2014) Public and other services 22% 20% Financing, insurance, renting, business service providers 26% 33% Trade, transport, tourism, telecommunication Construction Total industry (without construction sector) Agriculture, forestry 20% 5% 22% 29% 21% 15% 7% 4% 26% 21% Germany Hesse 26% Thuringia Sources: National accounts of the federal states, Helaba Research Sector mix in Hesse: financial center, airport, fair, chemicals/pharma The reason for the exceptional sector composition in Hesse is at first the financial centre Frankfurt. 196 domestic and foreign banks are headquartered in Frankfurt, which is 40 % of all supra-regional financial institutions active in Germany (i.e. not counting savings banks and credit unions). Another important factor for Hesse as a business location is Frankfurt Airport, which is used by 28 % of passengers and 48 % of the cargo volume in German air traffic. It is unchallenged in the first place in Germany and is the largest hub in continental Europe, with regard to transportation of goods and the second largest with regard to passengers. The Frankfurt Fair is another asset that strengthens the region’s international orientation. In terms of visitors and exhibitors, the Fair ranks first in Germany, with international exhibitors also appreciating the location. HELABA RESEARCH · 11 NOVEMBER 2015 · © HELABA 2 F ACT S & FIGURES: HES SE AND THURINGIA – F EDERAL ST AT ES IN GE RMANY Large share of industry in Thuringia At 19 % of the gross value added, the industrial sector in Hesse plays a smaller role than in Thuringia, where it accounts for 22 %. Within industrial manufacturing, there are clear focal points in Hesse: One quarter of industrial sales are generated in the sector chemical and pharmaceutical products. Motor vehicles/other transport equipment and the metals sector generated 16 %, and 12 % respectively, of Hesse’s industrial sales. With that, three sectors account for 54 % of sales. The structure of industry is more diversified in Thuringia. Thus, four sectors – food products and beverages, basic metals and metal products, electric/electronic and optical products, motor vehicles and trailers – make up 58 % of Thuringia’s industrial sales in nearly equal shares. Chemicals/pharma most important sector in Hesse Diversified industrial structure in Thuringia Share of industrial sales (January to August 2015) Share of industrial sales (January to August 2015) Motor vehicles other transport equipment 16% Machinery, Rubber/plastic equipment products 9% 9% Wood/paper 6% Non metalic Motor vehicles, mineral products trailers 4% 16% Chemicals, pharmazeutical products 4% Electric/ Other electronic/ 9% optical products 15% Food products, beverages Basic metals, 12% metal products 16% Electric/ Basic metals, electronic/ metal products optical 12% products 9% Machinery, equipment 9% Food products, beverages 7% Chemicals, pharmazeutical products 26% Rubber/plastic products 7% Other 14% Sources: Thüringer Landesamt für Statistik, Helaba Research Sources: Hessisches Statistisches Landesamt, Helaba Research The 25 largest companies The economic structure of the federal states is clearly reflected in the twenty-five largest enterpris1 es in Hesse and Thuringia, whereby our rankings were determined by a company’s workforce in the respective state, and not by its importance in Germany as a whole or worldwide. The 25 largest companies in Hesse Rank The 25 largest companies in Thuringia Com pany Sector Com pany Sector 1 Deutsche Lufthansa AG Transportation 1 Edeka Wholesale and retail trade 2 Rew e Group Wholesale and retail trade 2 Deutsche Bahn AG Transportation 3 Deutsche Bahn AG Transportation 3 Deutsche Post AG Transportation 4 Fraport Group Transportation 4 Randstad Deutschland Temporary employment company 5 Deutsche Post Group Transportation 5 Bosch Electric/electronic products 6 Commerzbank AG Banking 6 Helios Kliniken GmbH Hospitals 7 Deutsche Telekom AG Telecommunications 7 Rew e Markt Region Ost Wholesale and retail trade 8 Continental Group Automotive supplier 8 Rhön-Klinikum Hospitals 9 Volksw agen AG Automotive industry 9 Zeitungsgruppe Thüringen Publishing 10 Adam Opel AG Automotive industry 10 SWE Stadtw erke Erfurt GmbH Utility 11 Rhön-Klinikum AG Hospitals 11 Carl Zeiss AG Optical/electronic products 12 DZ Bank Gruppe Banking 12 Deutsche Telekom AG Telekommunication 13 Deutsche Bank AG Banking 13 Opel Eisenach GmbH Automotive industry 14 Merck KGaA Chemicals, pharmazeut. products 14 Continental Gruppe Automotive supplier 15 Metro Group Wholesale and retail trade 15 E.ON Thüringer Energie AG Utility 16 Sanofi Group Chemicals, pharmazeut. products 16 GeAT Temporary employment company 17 WISAG Facility Service Holding Service to buildings 17 Jenoptik-Group Optical/electronic products 18 B. Braun Melsungen AG Pharmazeutical products, medical engineering 18 Metro Group Wholesale and retail trade 20 Procter & Gamble Germany GmbH & Co. Operations oHG Siemens AG 21 Rank Chemicals 19 Electric/electronic products 20 ITT Industrie- und Transportschutz Thüringen GmbH Bertelsmann Helaba Group Banking 21 Rege Motorenteile GmbH Automotive supplier 22 Stadtw erke Frankfurt am Main Utility, Transportation 22 Stadtw erke Jena Utility 23 Bilfinger SE Construction 23 August Storck KG Food industry 24 Fresenius SE & Co. KGaA 24 Siemens Electric/electronic products 25 Evonik Industries AG 25 K+S Kali GmbH Exploitation of salt 19 Pharmazeutical products, hospitals Chemicals, utility, real estate Security firm Printing, call center Sources: Helaba Research, Hessen Agentur, LEG Thüringen 1 The ranking for Hesse is based upon the employment of 2012, and for Thuringia on 2010. However, we know from experience that the enterprises and their ranking change only slightly. HELABA RESEARCH · 11 NOVEMBER 2015 · © HELABA 3 F ACT S & FIGURES: HES SE AND THURINGIA – F EDERAL ST AT ES IN GE RMANY The export rates of the industrial enterprises have risen remarkably over the last fifteen years in both of the federal states. And Hesse, where foreign sales account for 53 % of total sales, is above-average by German standards in 2015 (January to March). In Thuringia, too, the export shares have improved to 34 %. The economic crisis saw a sharp slump in domestic and foreign demand in 2008/2009, so that, in the end the export ratios declined slightly. German businesses, and thus also those in Hesse and Thuringia, were able to profit particularly strongly from the global economic recovery in 2010, as a result of which the export shares were surging again. After that the export ratios maintained their high levels, owing to the strengthening of the domestic demand. This year the export rations in Germany as a whole and in Thuringia are rising again whereas in Hesse, they are slightly under the last year’s level. Export ratios on a high level Export quotas on a high level Most exports go to Europe Share of foreign sales among total sales in % Share of exports (January to June 2015) 55 Hesse 50 55 50 45 Germany 40 45 40 Thuringia 35 35 France Netherlands Italy Austria Spain Belgium Other Eurozone UK 8% 6% 5% 5% 4% 4% 8% 8% Other EU 10% 30 30 USA 13% 25 25 China 5% 20 20 Other Asia 12% 15 Other countries Russia 1,5% 14% 15 99 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15* *Average January to August 2015 Sources: Statistisches Bundesamt, Helaba Research 7% 5% 6% 5% Other Eurozone 13% UK Hungary Czech Republic Poland Other EU USA China Other Asien 7% 7% 5% 5% 5% 7% 6% 9% Other Countries 14% Russia 1,7% Thuringia Sources: Regional statistical offices, Helaba Research The Euro Zone is the main target for exports in 2015: 36 % of Hessian and Thuringian exports were sent there, with the neighbouring states and Italy among the top customers. Europe as a whole received 65 % and 71 %, respectively, of the exports of Hesse and Thuringia. Asia was the second-largest target region (share of exports: 16 % and 15 %, respectively), with China as the chief importer. The US played an important role for the companies in Hesse, as it was the country with the highest single share of exports. For Thuringia, by contrast, were the neighbours to the East – Hungary, the Czech Republic and Poland – important customer countries for its products. Main export target: Europe Germany 2015: economic growth on the same level Stable labour markets Real change in GDP compared to previous year in % 6 4 Hesse France Italy Austria Spain Germany Unemployment rate in % of labour force Thuringia 2 0 6 20 4 18 2 16 0 Hesse -2 -2 -4 -4 -6 -6 -8 -8 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 1st half-year Sources: Statistisches Bundesamt, Helaba Research 14 12 10 8 6 4 Eastern Germany 20 18 16 Thuringia Germany Western G. Hesse 98 99 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 14 15 * 14 12 10 8 6 4 *Average January to October 2015 Sources: Bundesagentur für Arbeit, Helaba Research After the economic downturn in 2009, the German federal states of Hesse and Thuringia achieved strong growth rates in the next two years that followed. After that the economy cooled down and Hesse and Thuringia were more strongly affected. But in contrast to the development in Germany as a whole, the braking effect wore off more quickly in Hesse and led to a recovery in 2013; in Thuringia there was no improvement. The recovery in 2014 made positive growth rates in every German federal state. Thuringia with 1.6 % reached the German average and Hesse was slightly HELABA RESEARCH · 11 NOVEMBER 2015 · © HELABA 4 F ACT S & FIGURES: HES SE AND THURINGIA – F EDERAL ST AT ES IN GE RMANY GDP-growth 2014: Germany 1.6 % Rising employment below with 1.4 %. The economic recovery continues in 2015, as the German growth rate of 1.4 % in the first half-year shows. The development in Germany is mainly driven by domestic consumption, which is growing dynamically in particular due to higher real wage increases and the strong immigration. The expansive monetary policy and the historically low interest rates should also support the economy a little bit. The situation in many countries of the euro area is getting better, whereas the global growth is quite weak. Therefore the investment in equipment is increasing only slightly. So growth prospects remain for Hesse at the projected national average of 1.7 %. For Thuringia less growth is expected, due to the weak first half of 2015; in the coming year, the gap should narrow again. On the Hessian and Thuringian labour markets, the high level of output of recent years is still having an impact. The unemployment rate in Hesse stayed for four years on the same level. In Thuringia, it is falling futhermore and getting closer to the national average. Besides capacity utilization demographic factors play an important role in the improvement of the labour market especially in the eastern federal states of Germany. The stability in the labor market is also reflected in the positive employment trend which lasts for almost five years now. Not only domestic workers found a new job, but companies could hire immigrant job seekers according to their requirements. Debt: Hesse about average, Thuringia slightly above average 783 Total Saxony Bavaria Baden- Mecklenb.- Hesse Wuertt. W. Pom. Lower Saxony Branden- Thuringia burg 9 533 9 142 8 170 7 783 7 339 7 254 6 826 6 788 5 870 4 286 1 991 6 778 14 100 Debt of federal states per capita in €, December 2014 North Rhinel.- Saxony- Schlesw.Rhine- Palatinate Anhalt Holstein Westphalia Saarland Sources: Bundesfinanzministerium, Helaba Research The economically strong federal states have noticeably higher tax revenues. For example, in Hesse the financial strength per capita is 22 % above the national average with regard to the income and corporate tax. By contrast, Thuringia reaches only 53 % of the average. Since Germany is, on the one hand, a federal state and, on the other hand, pays attention to the uniformity of living standards, the VAT is distributed according to other criteria, as a result of which the financially weak federal states catch up. The financial equalization between the federal states leads to a further equalization of revenue per capita, which is then boosted even more by the general federal supplementary grants. Thus, the financial strength per capita in Hesse is only 2 % above average after the redistribution, while Thuringia reaches 94 % of the average. Hesse well positioned because of financial strength The financial equalization system between the states and the guarantee of the federal states’ existence in the constitution have prompted the ratings agency Fitch to tie the ratings of the federal states to that of Germany. Hesse and Thuringia, therefore, could get a Triple A-rating, if, as an issuer, they themselves were rated by Fitch. Standard & Poor’s takes into account the economic productivity and the debt situation of the various federal states and differentiates accordingly: Hesse receives an “AA” rating, because it has high tax revenues thanks to its economic strength, whereas its per capita debt is not below the average as in Bavaria and Saxony (Thuringia is only rated by Fitch). HELABA RESEARCH · 11 NOVEMBER 2015 · © HELABA 5




