Almatex 2007 Brochure - Anderson Development
advertisement

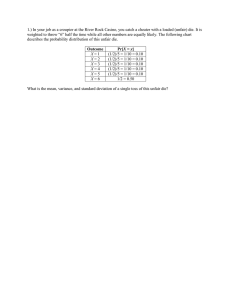
ALMATEX ® A C R Y L I C Premium Performance Durable R E S I N S Novel Dependable Acrylic Resins P R E M I U M Keeping that shine on your automobile is important to you. Our products help you maintain it. Our innovative acrylic resins are used extensively in powder coating applications in the automotive industry. Other markets include aluminum wheels, outdoor furniture, lawn and garden equipment, and various architectural uses. Printed with permission of BMW AG Applications: Automotive Wheel Clear Top Coats Auto Primer Pigmented Coatings These resins contain glycidyl functional groups which, when combined with polycarboxylic acid compounds as the curing agent, exhibit excellent properties for coating materials. Architectural Powder coating made from Almatex ® GMA acrylics is especially noted for weatherability, gloss, crystal clarity, chemical resistance, and smooth finish. The resins exhibit excellent over bake tolerance, good caking stability, excellent electrical insulation properties, and an outstanding performance in electrostatic spraying equipment. These products are also more environmentally friendly than solvent based products. Wood and MDF Outdoor Furniture Powder on Plastic UV Curable Coatings Plumbing Fixtures Industrial Plastics and other Heat Sensitive Substrates Lawn & Garden Agricultural Machinery PERFORMANCE Chemistry of GMA Acrylic Resins Almatex® GMA Acrylic Resins are made by free radical, solution copolymerization of Glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) with other acrylic or vinyl aromatic co-monomers. H3C Free Radical Copolymerization O C C H2C O H2C CH O + CH2 Acrylate or Methacrylate Monomers and other Unsaturated Monomers 1 w1 ______ w2 ______ w3 ... ______ + ∞= ∞+ ∞+ Tgc Tg1 Tg2 Tg∞3 Printed with permission of Goodrich Technology Corporation Degree of Functionality Monomer Composition O Initiator Type O The stable -C-C- polymer backbone of GMA resins confers good outdoor weathering & chemical resistance. Unlike liquid coatings, powder coating resins are restricted to monomer selection and molecular weight (MW) to inhibit sintering and provide good flow during melt and cure. Hence, the glass transition temperature (Tg) of the final resin is designed to be above some minimum value (usually 40-45 oC) to insure physical stability of the powder coating. Tg of GMA acrylic powder resin is controlled by two equations: ______ Variables: ∞ C Tgc = Tgc_ ____ MW By controlling monomer compositions and molecular weight, Almatex GMA resins can be designed with a wide range of melt viscosities, Tg, epoxy equivalent weight, and functionality for different application needs. The selection of monomers and polymer modification processes can produce Almatex® GMA acrylic resins with a variety of properties such as enhanced pigmentation, compatibility and flexibility. Removal of solvent and unreacted monomers from resin product syrup is important to maintain the essentially zero VOC advantage of powder coatings. The volatile contents of Almatex resins are well controlled to below 0.5%. Anderson Development Company is installing a revolutionary continuous devolatilization capability in 2007 to further cut the residuals and low molecular weight portion (LMWP) in Almatex® GMA Acrylic Resins. ADC and its parent company Mitsui Chemicals Inc. have full capability to tailor-make Almatex GMA acrylic powder resins to fit various special application needs. Molecular Weight Glass Transition Temperature Advantages: Excellent Long-term Weatherability & UV Durability Superb Chemical Resistance Crystal Clarity Outstanding Hardness Low to High Gloss Superb Smoothness & Appearance D U R A B L E GMA Powder Coating Formulation Since GMA acrylic powder coating resins are epoxy functional, any curing mechanism for epoxy resins will also function with GMA resins. At this time the preferred curative for GMA acrylic powder resins is 1,12dodecanedioic acid (DDDA) due to its combination of favorable melting point, cure rate & viscosity reduction. DDDA also provides cured coatings with excellent clarity, chemical resistance and weatherability. Other polycarboxylic acids or anhydrides may be used as curatives or additives to modify cure rate or coating properties. Many additives used in the powder coating industry may also be used in GMA acrylic powder formulations. These additives include: flow control agents (FCA), de-gassing agents, UVAs, and HALS. For clearcoat applications, non-silica dispersed FCA’s or special solid FCA’s are preferred. The selection of UVA/HALS can also effect the yellowing and degree of outdoor durability. Anderson has tackled many of the misnomers that surround GMA powder coatings. Our resin designs and powder coating formulations have improved flexibility, allowed robust pigmentation, proved to be effective in obtaining a wide range of matte and gloss finishes and can be combined with other powder chemistries. Anderson Development Company and its parent company Mitsui Chemicals Inc. have over 30 years experience with GMA powder coatings for various applications, and would be glad to design private label resins or assist in formulating for specific coating applications. Formulation Process: PREMIX ALMATEX® GMA acrylic resin is initially mixed with crosslinking agents, pigments, other additives and thoroughly dry blended. MELT-BLENDING The premix is then milled and blended with an extruder in a molten state. Properties of acrylic powder coating may vary depending on the compounding technique used. PULVERIZING After cooling the melt blended compound is crushed and passed through classification process for desirable particle size (typically 150-200 mesh). APPLICATION The powder is charged and sprayed with an electrostatic spray gun on a grounded substrate. Typical substrates include aluminum, steel, wood, MDF, plastic and other heat sensitive substrates. GMA powder coatings are typically baked at 130 to 180OC for 10 to 40 minutes depending on the powder formulation. O V E L 62 ® Heat Flow Endo Up (mW) N Typical DSC Thermogram of GMA Powder Coating DDDA Melt Region Heating Conditions: 10oC/min 60 Inherent nature of Low Temp. Cure (<140oC) and good storage stability 58 56 54 Global Support Glass Transition Region Complete Powder Coating Laboratory 52 Powder Softening Region 50 48 Anderson R&D Support Capabilities: Curing Reaction Region 15 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 Temperature (oC) ● Premix through Oven Cure Complete Powder Testing Facility ● Thermal Analysis ● GPC ● GC ● FTIR GMA vs 2K Clearcoat Functional Quality (Mechanical / Chemical) GMA PCC 10 2K CC Cleaning & Chemicals 8 Formulation Development Optical Quality 6 Printed with permission of Smart GmbH Problem Solving 4 2 Material Utilization & Recyclability Actual Cost (Material, Operation & Maintenance) Process Stability No Solvent Emissions No Waste Water Lab to Pilot Scale DEPENDABLE GMA vs Other Powder Coating Chemistry in Weatherability Percent 60 Gloss Retention 120 Anderson Production Capabilities: 100 80 Continuous Devolatilization 60 40 GMA Acrylic Superdurable Polyester HFA Acrylic Semidurable Polyester Standard Polyester 20 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 4000 4500 Xenon Arc Weatherometer (KJ/m) ● Heat Sensitive & UV Curable Resins Masterbatching Bulk Packaging Comparison of Powder Melting-Curing Profile of GMA & Polyester Powder Coatings 1E+6 Complex Viscosity. PaS Higher cross-linking density 1E+5 1E+4 1E+3 GMA Powder Coating Polyester Powder Coating 1E+2 1E+1 Rapid melt & Lower flow viscosity Heating Conditions: Ramp from 80oC to 145oC @ 10oC/min & hold @ 145oC 1E+0 0 120 240 360 480 600 720 840 960 1080 1200 Time, sec ● Supersacks ● Drums Private Label Manufacturing ● Solid Acrylic Resins ● Liquid Acrylic Toll Resins Iso 9001:2000 Certified General Purpose Almatex® Resins PD-7610 High Tg Short Gel-time Better Pigmentation Better Adhesion Lower Odor & Cost Higher Reactivity Lower GMA Content Dual Functionality GMA-Hydroxy Polyester Compatible & Better Pigmentation Almatex® Resin Properties PD-6300 Epoxy ALMATEX® Equivalent Resin (g/eq) PD-7690 PD-4219 PD-9200 PD-1700 Improved Flow PD-4409 PD-4411 High Performance Almatex® Resins PD-3402 Better Flow Higher Crosslinking Density PD-3402X PD-4408 PD-4418 Higher Acid Etch Resistance PD-4421 Developmental (Semi-Commercial) Almatex Resins ® • UV Curable Solid Acrylic Resins (AP-4410, AP-4414, AP-4416) • Polyester Powder Coating Compatible GMA Resins (AP-4411) • Hydroxy Functional Acrylic Resin (HA-2001) • Crystalline Aliphatic Polyester for High Flexibility (AP-8500) • Other Experimental Resins (AP-XXXX) Tg (oC) Melt Melt Index Viscosity (g/10 min) (poise) (@ 125oC) Applications o (@ 150 C) PD-7610 510-560 42-46 46-54 200-240 General Purpose, Wheel, Auto Trim, Auto Primer, High Durability PD-6300 510-560 55-58 10-16 >500 Wheel, Polyester Matting Indoor or Outdoor PD-6400 385-415 46-51 30-43 240-310 General Purpose, Polyester Matting PD-7690 450-500 44-46 43-54 200-250 General Purpose, Wheel, Auto Trim, Auto Primer, High Durability PD-4219 430-470 44-46 45-60 180-260 General Purpose, Wheel, Auto Trim, Auto Primer, High Durability PD-9200 650-690 43-48 45-60 180-280 Lower Cost, General Purpose PD-1700 570-625 950-1150* 48-50 35-45 250-310 Pigmented PC, Polyester Additive, Dual Functional PD-4409 720-760 950-1200* 38-42 >110 75-120 Cationic UV Curable PC, Thermoset PC, Dual Functional AP-4411 500-550 2900-3200* 42-46 45-60 180-250 Polyester compatible, Dual Functional AP-2025 280-310 66-70 1-2 >500 Low Gloss GMA PC PD-3402 360-400 45-50 50-70 180-250 Automotive CC, Wheel PD-4408 350-380 42-46 60-80 125-175 Automotive CC PD-4418 300-330 41-45 >110 85-125 Automotive CC PD-4421 300-330 40-43 >110 85-125 Automotive CC AP-4410 730-770** 40-45 90-110 90-140 Free Radical UV Curable PC AP-4414 520-560** 40-45 >110 75-130 Free Radical UV Curable PC AP-4416 740-780 42-46 NA 80-120 Cationic UV Curable PC HA-2001 652-748* 45-50 40-60 200-250 Hydroxy Functional Acrylic, Urethane-Acrylic PC * Hydroxy Equivalent Weight **Double Bond Equivalent Weight ALMATEX® GMA resins contain the lowest volitiles available in the industry (<0.5%). Color (Gardner) <2 The resin data shown in this table is only for resin selection guideline not for QC specification. “AP” and “HA” indicates the Almatex grade is a developmental or semi-commercial resin. Bibliography Select Cure-curve of Almatex® GMA Resins 400 350 Viscosity, poise 300 250 200 150 100 50 0 0 50 100 150 Time, seconds 200 250 PD-7610 PD-6300 PD-7690 PD-4219 PD-9200 PD-1700 AP-4411 AP-4418 PD-3402 (MI=56) PD-3402 (MI=77) 300 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. US3752870 “Powder Coating Compositions Containing Polymer of Ethylenically Unsaturated Glycidyl Esters, Dicarboxylic Acids, and Flow Control Agents” by Ford; 1973. JP78 105,533 “Metallic Finish Powder Coating Utilizing Commercial Almatex PD-2310 Resin and Aluminum Powder” by Kansai Paint; 1978. US4091048 “Powder Coating Compositions Containing Glycidyl Ester Copolymers and Organic Carboxylic Acid Anhydride Crosslinking Agent” by Ford; 1978. US Re32,261 “Process for Producing Thermosetting Finishing Powder” by Mitsui Toatsu Chemicals; 1986. US5270391 “Composition for Thermosetting Powder Coatings” by Mitsui Toatsu Chemicals; 1993. “New Generation Body Powder Primer Surfacer and Body Pillar Blackout Material” by General Motors; IBEC-94, Automotive Body Painting; p82-85. “Acrylic Powder Clear Coat for Automotive OEM” by Hoechst AG; EuroCoat 9/1994; p574-579. “Physical Chemistry of Acrylic Powder Coatings” by Zeneca Resins, Waterborne & High-solids, and Powder Coatings Symposium; 1995; p310-319. US5407747 “Filiform Corrosion Resistance Aluminum Automotive Road Wheel” by Morton; 1995. US5744522 “Low Gloss Coating Compositions” by Mitsui Toatsu Chemicals/Anderson Development Company; 1998. “Advances in High-Performance Powder Coatings for Automotive Exterior Trim” by Ferro; Metal Finishing May 1999; p14-18. “Development Status of Powder Coatings for OEM Automotive Applications” by Seibert Powder Coatings, Powder R&D Winter/2000; p3-7. US6077608 “Multilayered Coating with Powder Clear Coating and Substrates Therewith and Method” by PPG; 2000. “Automotive OEM Powder Clearcoat” by PPG; PCI, Paint & Coating Industry; April 2000. “Powder Clearcoat, a Leap in Paint Technology” by Editor of Aei Feb 2001; p204-208. “Technology Broadens Horizons for Acrylic Powder Coating” by PPG; Powder Coatings March 2001; p25-32. “GMA Powder Coatings: Driving the Future of Automotive Clear Topcoats” by Editor of Paint & Coatings Industry; May 2001; p54-56. US6479588 “Graft Copolymer of Polyamide and A Glycidyl Group-containing Acrylate Copolymer, Process for Preparation and Coating Composition Containing the Graft Copolymer” by Anderson Development Company, 2002. US6670411, WO02/28945A1 “Process for Devolatilizing an Acrylic Resin for Preparing a Powder Coating Composition and Composition Capable of Being Formed into a Powder Coating Comp” by Anderson Development Company, 2003. US2003/0212216 “Thermosetting Powder Coating Composition, Method for Forming Coating Film of the Composition, and Coating Film” by Mitsui Chemicals, Inc., 2003. US6762259 “Process for the Production of Living (co)Polymers and Use of the (co)Polymers” by Mitsui Chemicals, Inc., 2004. US2004/0265494 “Glycidyl (meth)Acrylate Powder Coating Compositions Containing Caprolactonederived Side Chain” by Anderson Development Company, 2004. ALMATEX® is a registered trademark of Mitsui Chemicals Inc. The information contained in this bulletin we believe to be accurate, but no warranty is given nor is anything to be construed as a recommendation to infringe upon any existing patent. Since conditions of use are beyond our control, all risks of use are assumed by the user. ALMATEX ® A C R Y L I C R E S I N S Anderson Development • 1415 E. Michigan Road • Adrian, MI 49221 Tel: 517.263.2121 • Fax: 517.263.1000 • www.andersondevelopment.com