Widely separated binary systems of very low mass stars Phan Bao
advertisement

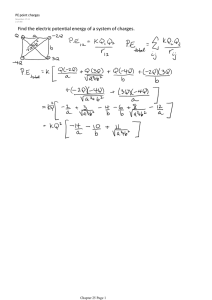
Homework (lecture 1): ● Prove the shell theorem for the electrostatic force ● 1, 3, 6, 9, 12, 20, 26, 29 (page 574-576) 1. Two equally charged particles are held 3.2x10-3 m apart and then released from rest. The initial acceleration of the first particle is observed to be 7.0 m/s2 and that of the second to be 9.0 m/s2. If the mass of the first particle is 6.3x10-7 kg, what are (a) the mass of the second particle and (b) the magnitude of the charge of each particle. F12 m2a2 F21 m1a1 F12 F21 : m2 a1 m1 F12 F21 k 2 q1q2 r 2 a2 m1a1 7 m1a1r 6.3 10 7 3.2 10 q 9 k 8.99 10 q 71 (pC) 3 2 7.110 11 (C ) 3. What must be the distance between point charge q1 = 26.0 C and point charge q2 = -47 C for the electrostatic force between them to have a magnitude of 5.70 N? F k q1q2 r 1C 10 r 6 2 q1 q2 r k F C 9 6 8.99 10 (26 10 5.7 )(47 10 6 ) 1.39 (m) 6. In the figure as shown, four particles form a square. The charges are q1 = q4 = Q and q2 = q3 = q. (a) What is Q/q if the net electrostatic force on particles 1 and 4 is zero? (b) Is there any value of q that makes the net electrostatic force on each of the four particles zero? explain. (a) q1 & q4 have the same sign, all three forces act on q1 as shown F41 F21 F31 F41 2F21 Q2 qQ Q k 2k 23 / 2 2.83 2 2 q a a 2 q (b) if the net force acting on particle 3 is also zero: 2.83 this is inconsistent with (a), so the answer is NO Q 9. Two identical conducting spheres, fixed in place, attract each other with an electrostatic force of 0.108 N when their centerto-center separation is 50.0 cm. The spheres are then connected by a thin conducting wire. When the wire is removed, the spheres repel each other with an electrostatic force of 0.036 N. Of the initial charges on the spheres, with a positive net charge, what was (a) the negative charge on one of them and (b) the positive charge on the other? Using the shell theorem: Before: F1 k q1q2 r 2 q1q2 3.0 1012 (C ) After: the net charge is positive 2 q1 q2 2 q 2 F2 k k q1 q2 2.0 10 6 2 2 r r (C ) 2 6 12 q1 2.0 10 q1 3.0 10 0 The solutions: 1st: 2nd: q1 3.0 10 6 q1 1.0 10 (C ) q2 1.0 10 6 6 (C ) q2 3.0 10 6 (C ) (C ) Note: if the net charge is negative q1 q2 2.0 10 6 (C ) the solutions should be: q1(or q2 ) 1.0 10 6 (C ) q2 (or q1) 3.0 10 6 (C ) 12. See the figure as shown, particle 1 (of charge q1) and particle 2 (of charge q2) are fixed in place on an x axis, 8.0 cm apart. Particle 3 (of charge q3 = +8.0x10-19 C) is to be placed on the line between particles 1 and 2 so that they produce a net electrostatic force F3,net on it. The diagram gives the x component of that force versus the coordinate x at which particle 3 is placed. What are (a) the sign of charge q1 and (b) the ratio q2/q1? ● at 2 cm: Fnet=0 so 1 and 2 must have the same sign. ● when q3 approaches q1,F13 increases in magnitude. Fnet increases in the positive x direction, so F13 is a repulsive force, q1 > 0 qq q q k 1 3 k 2 3 r 213 r 2 23 q2 q1 2 2 r23 6 9 2 r13 20. See the figure, particles 1 and 2 of charge q1 = q2 = +3.2x10-19 C are on a y axis at distance d = 17.0 cm from the origin. Particle 3 of charge q3 = +6.4x10-19 C is moved gradually along the x axis from x = 0 to x = +5.0 m. At what values of x will the magnitude of the electrostatic force on the third particle from the other two particles be (a) minimum and (b) maximum? what are the (c) minimum and (d) maximum magnitudes? The net force acting on particle 3: qq3 Fnet 2 k r r 2 cos x x d ; cos r 2 2 Fnet 2kqq3 x x 2 d 2 3/ 2 r x 0 : minimum F net 0 d 2 x 0 x d / 2 : maximum ' 2 2 http://www.function-grapher.com/index.php 26. Calculate the number of coulombs of positive charge in 250 cm3 of (neutral) water. (Hint: A hydrogen atom contains one proton; an oxygen atom contains eight protons) The mass of the sample: m V 1 250 250( g ) The number of moles: m 250 n 13.9 M molar 18 The positive charge: Q nN Aq 23 13.9 6.023 10 10 1.6 10 19 7 1.34 10 (C ) 29. In crystals of the salt cesium chloride, cesium ions Cs+ form the eight corners of a cube and a chlorine ion Cl- is at the cube’s center. The edge length of the cube is 0.4 nm. The Cs+ ions are each deficient by one electron (and thus each has a charge of +e), and the Cl- ion has one excess electron (and thus has a charge of –e). (a) What is the magnitude of the net electrostatic force exerted on the Cl- ion by the eight Cs+ ions? (b) If one of the Cs+ ions is missing, the crystal is said to have a defect, what is the magnitude of the net force exerted on the Cl- ion by the seven remaining Cs+ ions? (a) The net force is zero due to the symmetric distribution of the eight Cs+ around Cl2 e (b) F7Cs F1Cs k 2 r 2 2 r a (a 2 ) ; a 0.4nm 2 2 F7Cs k e (3 / 4)a 2 Homework (lecture 2): 1, 3, 5, 8, 12, 19, 22, 24, 27, 31, 34, 46, 50, 53 (page 598-601) 1. Sketch qualitatively the electric field lines both between and outside two concentric conducting spherical shells when a uniform positive charge q1 is on the inner shell and a uniform negative charge –q2 is on the outer. Consider the cases q1 > q2, q1 = q2, and q1 < q2. E=0 q1 > q 2 E=0 q1 = q 2 q1 < q 2 3. Sketch qualitatively the electric field lines for a thin, circular, uniformly charged disk of radius R. (Hint: Consider as limiting cases points very close to the disk, where the electric field is directed perpendicular to the surface, and points very far from it, where the electric field is like that of a point charge) Edge-on view 5. What is the magnitude of a point charge whose electric field 50 cm away has the magnitude 2.0 N/C? E kq 2 r Er q k 2 2 0.5 2 9 8.99 10 5.6 10 11 (C ) 8. See the figure, particle 1 of charge q1 = -5.0q and particle 2 of charge q2 = +2.0q are fixed to an x axis. (a) As a multiple of distance L, at what coordinate on the axis is the net electric field of the particles zero? (b) Sketch the net electric field lines. + E1 k q1 x 2 x L 2 x2 E2 E2 E1 k q2 x L 2 2 x 2.72 L 5 12. The three particles are fixed in place and have charges q1 = q2 = +e and q3 = +2e. Distance a = 6.0 m. What are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction of the net electric field at point P due to the particles? E1 E2 0 Enet E3 E3 2e a 2 E3 k ; OP 2 2 OP 9 E3 8.99 10 4 1.6 10 19 6.02 1012 0 E3 160( N / C ); ( E3 , Ox) 45 19. The figure shows an electric dipole. What are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction (relative to the positive direction of the x axis) of the dipole’s electric field at point P, located at distance r >> d? Enet 2k q r 2 cos kqd r 3 p qd : electric dipole moment Enet • • If x>>d: kp d 2 x 2 Enet points 2 3/ 2 Enet kp x 3 in the negative direction of the y axis Enet 22. The figure shows two parallel nonconducting rings with their central axes along a common line. Ring 1 has uniform charge q1 and radius R; ring 2 has uniform charge q2 and the same radius R. The rings are separated by distance d = 3.0R. The net electric field at point P on the common line, at distance R from ring 1, is zero. What is the ratio q1/q2? E qz 4 0 ( z R ) 2 kq1R 2 2 3/ 2 2 3/ 2 kq2 2 R 2 2 3/ 2 (R R ) (4 R R ) q1 4 2 0.51 q2 5 5 Note: q1 and q2 must have the same sign to produce a net electric field equal to zero 24. Two curved plastic rods, one of charge +q and the other of charge –q, form a circle of radius R = 8.5 cm in an xy plane. The x axis passes through both of the connecting points, and the charge is distributed uniformly on both rods. If q = 15.0 pC, what are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction (relative to the positive direction of the x axis) of the electric field produced at P, the center of the circle? Consider a differential charge dq: dq ds ( Rd ) (ds) k dE1rod k cos cos dθ 2 For two rods: dq R R k dE2rods 2 cos dθ R k E2rods 2 R E2rods 90 4k 4kq cos dθ 2 R R 90 4 8.99 109 15 1012 3.14 8.52 10 4 dE 23.8( N / C ) 27. A nonconducting rod of length L = 8.15 cm has charge –q = -4.23 fC uniformly distributed along its length. (a) What is the linear charge density of the rod? What are the (b) magnitude and (c) direction (relative to the positive direction of the x axis) of the electric field produced at point P, at a = 12.0 cm from the rod? What is the electric field magnitude at a = 50 m by (d) the rod and (e) a particle of charge –q = -4.23 fC that replaces the rod? (a) q 4.23 1015 0,519 1013 (C / m) L 8.15 10 2 (b) dE x k dx L a x 2 q 3 E x k 1.6 10 ( N / C ) a L a (c) the negative direction of the x axis La : E x k Ex 1.5 10 q a 2 8 ( N / C) (d) for a distant point, the rod acts like a point charge, so the electric field of the point charge is the same as that of the rod: Ex 1.5 10 8 ( N / C) 31. At what distance along the central perpendicular axis of a uniformly charged plastic disk of radius 0.6 m is the magnitude of the electric field equal to one-half the magnitude of the field at the center of the surface of the disk? Ez 2 0 1 2 2 z R z At the center (very close to the center): 1 E z Ec : 2 Ec 2 0 1 z R/ z 1 2 2 2 z R 3 0.35(m) 34. An alpha particle (the nucleus of a helium atom) has a mass of 6.64 x 10-27 kg and a charge of +2e. What are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction of the electric field that will balance the gravitational force on the particle? E qE mg Fg mg E 2e 46. An electron is shot at an initial speed of v0=2.0x106 m/s, at angle 0 = 400 from an x axis. It moves through a uniform electric field E (5.0 N/C) ˆj. A screen for detecting electrons is positioned parallel to the y axis, at distance x = 3.0 m. In unit vector notation, what is the velocity of the electron when it hits the screen? Fg 9 1030 ( N ) F 8 1019 ( N ) So, we ignore gravity eE 1.6 1019 5.0 ay m 9.111031 8.78 1011 (m / s 2 ) Time to F x 3 6 t 1 . 96 10 ( s) hit the screen: v0 cos 0 2 106 cos 400 v y v0 y a yt v0 sin at 0.44 106 (m / s) v 1.53 106 (m / s)iˆ 0.44 106 (m / s) ˆj 50. An electric dipole consists of charges +2e and -2e separated by 0.78 nm. It is in an electric field of strength 3.4 x 106 N/C. Calculate the magnitude of the torque on the dipole when the dipole moment is (a) parallel to, (b) perpendicular to, and (c) antiparallel to the electric field. r F pE sin (a) (b) (c) net 0 ( 0) net 2edE 2 1.6 1019 0.78 109 3.4 106 net 8.5 1022 ( N .m) 0 net 0 ( 180 ) 53. How much work is required to turn an electric dipole 1800 in a uniform electric field of magnitude E = 46.0 N/C if p = 3.02 x 10-25 C.m and the initial angle is 640? U pE cos Wapplied WE U Wapplied U 0 U 0 pE cos(1800 640 ) pE cos 640 Wapplied 2 pE cos 640 Wapplied 2 3.02 10 25 46.0 0.438 Wapplied 1.22 10 23 (J )