Document
advertisement

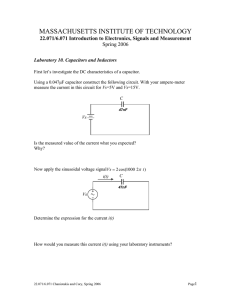
Clicker Question Right after switch S is closed, what will be the potential difference across the capacitor? A) 0 B) C) D) E) ε ε R2/(R1+ R2) ε /2 ε R1/(R1+ R2) Clicker Question Right after switch S is closed, what will be the potential difference across the capacitor? A) 0 B) C) D) E) ε ε R2/(R1+ R2) ε /2 ε R1/(R1+ R2) Clicker Question A long time after switch S is closed, what will be the charge on the capacitor? A) 0 B) Cε C) D) ε/C Cε /2 E) C/R2 Clicker Question A long time after switch S is closed, what will be the charge on the capacitor? A) 0 B) Cε C) D) ε/C Cε /2 E) C/R2 Figure 30.15 Figure 30.14 Table 30.1 Clicker Question An inductor (inductance L) and a capacitor (capacitance C) are connected as shown. If the values of both L and C are doubled, what happens to the time required for the capacitor charge to oscillate through a complete cycle? A. It becomes 4 times longer. B. It becomes twice as long. C. It is unchanged. D. It becomes 1/2 as long. E. It becomes 1/4 as long. Clicker Question An inductor (inductance L) and a capacitor (capacitance C) are connected as shown. If the values of both L and C are doubled, what happens to the time required for the capacitor charge to oscillate through a complete cycle? A. It becomes 4 times longer. B. It becomes twice as long. C. It is unchanged. D. It becomes 1/2 as long. E. It becomes 1/4 as long. Clicker Question An inductor (inductance L) and a capacitor (capacitance C) are connected as shown. The value of the capacitor charge q oscillates between positive and negative values. At any instant, the potential difference between the capacitor plates is A. proportional to q. C. proportional to d2q/dt2. E. all of A, B, and C. B. proportional to dq/dt. D. both A and C. Clicker Question An inductor (inductance L) and a capacitor (capacitance C) are connected as shown. The value of the capacitor charge q oscillates between positive and negative values. At any instant, the potential difference between the capacitor plates is A. proportional to q. C. proportional to d2q/dt2. E. all of A, B, and C. B. proportional to dq/dt. D. both A and C. Clicker Question Which phasor shows current that is positive and increasing with time? Clicker Question Which phasor shows current that is positive and increasing with time? Clicker Question Which phasor shows a current that is negative with an increasing magnitude (i.e. getting more negative?) Clicker Question Which phasor shows a current that is negative with an increasing magnitude (i.e. getting more negative?) Clicker Question A resistor is connected across an ac source as shown. For this circuit, what is the relationship between the instantaneous current i through the resistor and the instantaneous voltage vab across the resistor? A. i is maximum at the same time as vab B. i is maximum one-quarter cycle before vab C. i is maximum one-quarter cycle after vab D. not enough information given to decide Clicker Question A resistor is connected across an ac source as shown. For this circuit, what is the relationship between the instantaneous current i through the resistor and the instantaneous voltage vab across the resistor? A. i is maximum at the same time as vab B. i is maximum one-quarter cycle before vab C. i is maximum one-quarter cycle after vab D. not enough information given to decide Clicker Question An inductor is connected across an ac source as shown. For this circuit, what is the relationship between the instantaneous current i through the inductor and the instantaneous voltage vab across the inductor? A. i is maximum at the same time as vab B. i is maximum one-quarter cycle before vab C. i is maximum one-quarter cycle after vab D. not enough information given to decide Clicker Question An inductor is connected across an ac source as shown. For this circuit, what is the relationship between the instantaneous current i through the inductor and the instantaneous voltage vab across the inductor? A. i is maximum at the same time as vab B. i is maximum one-quarter cycle before vab C. i is maximum one-quarter cycle after vab D. not enough information given to decide Clicker Question A capacitor is connected across an ac source as shown. For this circuit, what is the relationship between the instantaneous current i through the capacitor and the instantaneous voltage vab across the capacitor? A. i is maximum at the same time as vab B. i is maximum one-quarter cycle before vab C. i is maximum one-quarter cycle after vab D. not enough information given to decide Clicker Question A capacitor is connected across an ac source as shown. For this circuit, what is the relationship between the instantaneous current i through the capacitor and the instantaneous voltage vab across the capacitor? A. i is maximum at the same time as vab B. i is maximum one-quarter cycle before vab C. i is maximum one-quarter cycle after vab D. not enough information given to decide Clicker Question An AC voltage source drives a sinusoidal current through two resistors. The amplitude of the sinusoidal voltage across the first resistor is 4 V. The amplitude of the sinusoidal voltage across the second resistor is 3 V. What is the amplitude of the sinusoidal voltage provided by the source? A) 0 V B) 1 V 4Ω C) 5 V D) 7 V E) 12 V 3Ω Clicker Question An AC voltage source drives a sinusoidal current through two resistors. The amplitude of the sinusoidal voltage across the first resistor is 4 V. The amplitude of the sinusoidal voltage across the second resistor is 3 V. What is the amplitude of the sinusoidal voltage provided by the source? A) 0 V B) 1 V 4Ω C) 5 V D) 7 V E) 12 V 3Ω Clicker Question An AC voltage source drives a sinusoidal current through a resistor and an inductor in series. The amplitude of the sinusoidal voltage across the resistor is 4 V. The amplitude of the sinusoidal voltage across the inductor is 3 V. What is the amplitude of the sinusoidal voltage provided by the source? A) 0 V B) 1 V 4V C) 5 V D) 7 V E) 12 V 3V Clicker Question An AC voltage source drives a sinusoidal current through a resistor and an inductor in series. The amplitude of the sinusoidal voltage across the resistor is 4 V. The amplitude of the sinusoidal voltage across the inductor is 3 V. What is the amplitude of the sinusoidal voltage provided by the source? A) 0 V B) 1 V 4V C) 5 V D) 7 V E) 12 V 3V Clicker Question An AC voltage source drives a sinusoidal current through a capacitor and a resistor in series. The amplitude of the sinusoidal voltage across the capacitor is 4 V. The amplitude of the sinusoidal voltage across the resistor is 3 V. What is the amplitude of the sinusoidal voltage provided by the source? A) 0 V B) 1 V C) 5 V D) 7 V E) 12 V Clicker Question An AC voltage source drives a sinusoidal current through a capacitor and a resistor in series. The amplitude of the sinusoidal voltage across the capacitor is 4 V. The amplitude of the sinusoidal voltage across the resistor is 3 V. What is the amplitude of the sinusoidal voltage provided by the source? A) 0 V B) 1 V C) 5 V D) 7 V E) 12 V Clicker Question An AC voltage source drives a sinusoidal current through a capacitor and an inductor in series. The amplitude of the sinusoidal voltage across the capacitor is 4 V. The amplitude of the sinusoidal voltage across the inductor is 3 V. What is the amplitude of the sinusoidal voltage provided by the source? A) 0 V B) 1 V C) 5 V D) 7 V E) 12 V Clicker Question An AC voltage source drives a sinusoidal current through a capacitor and an inductor in series. The amplitude of the sinusoidal voltage across the capacitor is 4 V. The amplitude of the sinusoidal voltage across the inductor is 3 V. What is the amplitude of the sinusoidal voltage provided by the source? A) 0 V B) 1 V C) 5 V D) 7 V E) 12 V Clicker Question An L-R-C series circuit as shown is operating at its resonant frequency. At this frequency, how are the values of the capacitive reactance XC, the inductive reactance XL, and the resistance R related to each other? A) XL = R; XC can have any value. B) XC = R; XL can have any value. C) XC = XL; R can have any value. D) XC = XL = R. E) none of the above Clicker Question An L-R-C series circuit as shown is operating at its resonant frequency. At this frequency, how are the values of the capacitive reactance XC, the inductive reactance XL, and the resistance R related to each other? A) XL = R; XC can have any value. B) XC = R; XL can have any value. C) XC = XL; R can have any value. D) XC = XL = R. E) none of the above Clicker Question In an L-R-C series circuit as shown, the current has a very small amplitude if the ac source oscillates at a very high frequency. Which circuit element causes this behavior? A. the resistor R B. the inductor L C. the capacitor C D. misleading question — the current actually has a very large amplitude if the frequency is very high Clicker Question In an L-R-C series circuit as shown, the current has a very small amplitude if the ac source oscillates at a very high frequency. Which circuit element causes this behavior? A. the resistor R B. the inductor L C. the capacitor C D. misleading question — the current actually has a very large amplitude if the frequency is very high Clicker Question In an L-R-C series circuit as shown, there is a phase angle between the instantaneous current through the circuit and the instantaneous voltage vad across the entire circuit. For what value of the phase angle is the greatest power delivered to the resistor? A. zero B. 90° C. 180° D. 270° E. none of the above Clicker Question In an L-R-C series circuit as shown, there is a phase angle between the instantaneous current through the circuit and the instantaneous voltage vad across the entire circuit. For what value of the phase angle is the greatest power delivered to the resistor? A. zero B. 90° C. 180° D. 270° E. none of the above Clicker Question In an L-R-C series circuit as shown, suppose that the angular frequency of the ac source equals the resonance angular frequency. In this case, the circuit impedance A. is maximum. B. is minimum, but not zero. C. is zero. D. is neither a maximum nor a minimum. E. not enough information give to decide Clicker Question In an L-R-C series circuit as shown, suppose that the angular frequency of the ac source equals the resonance angular frequency. In this case, the circuit impedance A. is maximum. B. is minimum, but not zero. C. is zero. D. is neither a maximum nor a minimum. E. not enough information give to decide