(TM) Rail-to-Rail Output Wide-Input-Voltage Op
advertisement

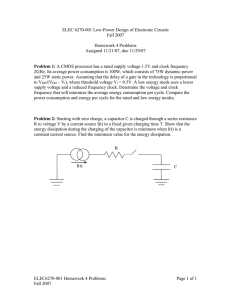
TLV2442-Q1,, TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 www.ti.com........................................................................................................................................... SGLS181C – SEPTEMBER 2003 – REVISED AUGUST 2009 Advanced LinCMOS™ RAIL-TO-RAIL OUTPUT WIDE-INPUT-VOLTAGE OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS FEATURES 1 • Qualified for Automotive Applications • ESD Protection Exceeds 2000 V Per MIL-STD-883, Method 3015; Exceeds 200 V Using Machine Model (C = 200 pF, R = 0) • Output Swing Includes Both Supply Rails • Extended Common-Mode Input Voltage Range: 0 V to 4.25 V (Min) at 5-V Single Supply • No Phase Inversion 23 • • • • • • • Low Noise: 16 nV/√Hz Typ at f = 1 kHz Low Input Offset Voltage: 950 µV Max at TA = 25°C (TLV244xA) Low Input Bias Current: 1 pA (Typ) 600-Ω Output Drive High-Gain Bandwidth: 1.8 MHz (Typ) Low Supply Current: 750 µA Per Channel (Typ) Macromodel Included HIGH-LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE vs HIGH-LEVEL OUTPUT CURRENT DESCRIPTION 3 VDD = 3 V VOH − High-Level Output Voltage − V The TLV244x and TLV244xA are low-voltage operational amplifiers from Texas Instruments. The common-mode input voltage range of these devices has been extended over typical standard CMOS amplifiers, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. In addition, these devices do not phase invert when the common-mode input is driven to the supply rails. This satisfies most design requirements without paying a premium for rail-to-rail input performance. They also exhibit rail-to-rail output performance for increased dynamic range in singleor split-supply applications. This family is fully characterized at 3-V and 5-V supplies and is optimized for low-voltage operation. Both devices offer comparable ac performance while having lower noise, input offset voltage, and power dissipation than existing CMOS operational amplifiers. The TLV244x has increased output drive over previous rail-to-rail operational amplifiers and can drive 600-Ω loads for telecommunications applications. 2.5 2 TA = − 40°C 1.5 1 TA = 125°C 0.5 TA = 85°C TA = 25°C 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 IOH − High-Level Output Current − mA The other members in the TLV244x family are the low-power, TLV243x, and micro-power, TLV2422, Figure 1. versions. The TLV244x, exhibiting high input impedance and low noise, is excellent for small-signal conditioning for high-impedance sources, such as piezoelectric transducers. Because of the micropower dissipation levels and low-voltage operation, these devices work well in hand-held monitoring and remote-sensing applications. In addition, the rail-to-rail output feature with single- or split-supplies makes this family a great choice when interfacing with analog-to-digital converters (ADCs). For precision applications, the TLV244xA is available with a maximum input offset voltage of 950 µV. If the design requires single operational amplifiers, see the TI TLV2211/21/31. This is a family of rail-to-rail output operational amplifiers in the SOT-23 package. Their small size and low power consumption make them ideal for high-density battery-powered equipment. 1 2 3 Please be aware that an important notice concerning availability, standard warranty, and use in critical applications of Texas Instruments semiconductor products and disclaimers thereto appears at the end of this data sheet. Advanced LinCMOS is a trademark of Texas Instruments. PSpice, Parts are trademarks of MicroSim. PRODUCTION DATA information is current as of publication date. Products conform to specifications per the terms of the Texas Instruments standard warranty. Production processing does not necessarily include testing of all parameters. Copyright © 2003–2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated TLV2442-Q1,, TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 SGLS181C – SEPTEMBER 2003 – REVISED AUGUST 2009........................................................................................................................................... www.ti.com ORDERING INFORMATION (1) TA VIOmax AT 25=C 950 µV –40°C to 125°C Dual 2.5 mV Dual 950 µV (1) (2) ORDERABLE PART NUMBER PACKAGE (2) Quad SOIC – D Reel of 2500 TLV2442AQDRQ1 2442AQ TSSOP – PW Reel of 2000 TLV2442AQPWRQ1 2442AQ MSOP – DGK Reel of 2500 TLV2442QDGKRQ1 OBR SOIC – D Reel of 2500 TLV2442QDRQ1 2442Q1 TSSOP – PW Reel of 2000 TLV2442QPWRQ1 2442Q1 TSSOP – PW Reel of 2000 TLV2444AQPWRQ1 2444AQ For the most current package and ordering information, see the Package Option Addendum at the end of this document, or see the TI web site at www.ti.com. Package drawings, thermal data, and symbolization are available at www.ti.com/packaging. TLV2444 PW PACKAGE (TOP VIEW) TLV2442 D, DGK, OR PW PACKAGE (TOP VIEW) 1OUT 1IN 1IN+ VDD - /GND 2 TOP-SIDE MARKING Submit Documentation Feedback 1 8 2 7 3 6 4 5 VDD + 2OUT 2IN2IN+ 1OUT 1IN1IN+ VDD+ 2IN+ 2IN2OUT 1 14 2 13 3 12 4 11 5 10 6 9 7 8 4OUT 4IN4IN+ VDD- /GND 3IN+ 3IN3OUT Copyright © 2003–2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated Product Folder Link(s): TLV2442-Q1 TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 TLV2442-Q1,, TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 www.ti.com........................................................................................................................................... SGLS181C – SEPTEMBER 2003 – REVISED AUGUST 2009 Q21 C3 C2 Q19 R6 R5 C1 R3 Copyright © 2003–2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated R2 R1 VB2 IN+ IN- VB1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1 Q23 Q22 R9 Q5 Q7 Q6 Q25 Q24 VB3 Q8 Q9 R4 Q26 Q27 Q11 Q12 Q10 VB4 Q13 D1 Q29 Q30 Q14 Q17 Q16 Q15 Q33 Q32 VB3 R10 Q18 Q35 VB2 Q34 Q31 R8 OUT Q20 Q37 Q36 R7 VB4 VDD+ VDD- /GND 69 5 26 6 Transistors Diodes Resistors Capacitors COMPONENT COUNT EQUIVALENT SCHEMATIC (EACH AMPLIFIER) Submit Documentation Feedback Product Folder Link(s): TLV2442-Q1 TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 3 TLV2442-Q1,, TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 SGLS181C – SEPTEMBER 2003 – REVISED AUGUST 2009........................................................................................................................................... www.ti.com ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS (1) over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted) VDD Supply voltage (2) 12 V VID Differential input voltage (3) ±VDD VI Input voltage (any input) (2) –0.3 V to VDD II Input current (any input) ±5 mA IO Output current ±50 mA Total current into VDD+ ±50 mA Total current out of VDD– ±50 mA Duration of short-circuit current at (or below) 25=C (4) Unlimited Continuous total dissipation See Dissipation Rating Table TA Operating free-air temperature range –40°C to 125°C Tstg Storage temperature range –65°C to 150°C Lead temperature 1,6 mm (1/16 inch) from case for 10 seconds (1) (2) (3) (4) 260°C Stresses beyond those listed under absolute maximum ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under recommended operating conditions is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability. All voltage values, except differential voltages, are with respect to the midpoint between VDD+ and VDD–. Differential voltages are at IN+ with respect to IN–. Excessive current will flow if input is brought below VDD– – 0.3 V. The output may be shorted to either supply. Temperature and/or supply voltages must be limited to ensure that the maximum dissipation rating is not exceeded. DISSIPATION RATINGS PACKAGE TA ≤ 25°C POWER RATING DERATING FACTOR ABOVE TA = 25°C TA = 70°C POWER RATING TA = 85°C POWER RATING TA = 125°C POWER RATING D (8 pin) 725 mW 5.8 mW/°C 464 mW 377 mW 145 mW DGK (8 pin) 606 mW 4.847 mW/°C 388 mW 315 mW 121 mW PW (8 pin) 525 mW 4.2 mW/°C 336 mW 273 mW 105 mW PW (14 pin) 720 mW 5.6 mW/°C 634 mW 547 mW 317 mW RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS MIN MAX UNIT VDD Supply voltage 2.7 10 V VI Input voltage VDD– VDD+ – 1 V VIC Common-mode input voltage VDD– VDD+ – 1 V TA Operating free-air temperature –40 125 °C 4 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2003–2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated Product Folder Link(s): TLV2442-Q1 TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 TLV2442-Q1,, TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 www.ti.com........................................................................................................................................... SGLS181C – SEPTEMBER 2003 – REVISED AUGUST 2009 ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS VDD = 3 V, at specified free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted) PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS TLV244x VIO VIC = 1.5 V, VO = 1.5 V, RS = 50 Ω Input offset voltage TLV244xA TA (1) MIN 25°C 25°C 300 Full range Input offset voltage long-term drift (2) VIC = 1.5 V, VO = 1.5 V, RS = 50 Ω IIO Input offset current VIC = 1.5 V, VO = 1.5 V, RS = 50 Ω IIB Input bias current VIC = 1.5 V, VO = 1.5 V, RS = 50 Ω VICR Common-mode input voltage range |VIO| ≤ 8 mV, RS = 50 Ω Low-level output voltage VIC = 1.5 V Large-signal differential voltage amplification AVD 25°C 0.002 µV/mo 25°C 0.5 Full range VO = 1 V to 2 V 150 25°C 1 Full range 260 0 to –0.25 to 2.25 2.5 25°C RL = 600 Ω RL = 1 MΩ pA V 2.98 2.5 Full range IO = 3 mA pA 0.2 to 2 25°C IO = 100 µA VOL µV/°C 25°C IO = –3 mA µV 2 Full range High-level output voltage 950 UNIT 1600 25°C to 85°C VOH 2000 2500 VIC = 1.5 V, VO = 1.5 V, RS = 50 Ω IO = –100 µA MAX 300 Full range Temperature coefficient of input offset voltage αVIO TYP V 2.25 25°C 0.02 25°C 0.63 Full range V 1 25°C 0.7 Full range 0.4 1 V/mV 25°C 750 rid Differential input resistance 25°C 1000 GΩ ri Common-mode input resistance 25°C 1000 GΩ ci Common-mode input capacitance f = 10 kHz 25°C 8 pF zo Closed-loop output impedance f = 1 MHz, AV = 10 25°C 130 Ω CMRR Common-mode rejection ratio VIC = VICR MIN, VO = VDD/2, RS = 50 Ω kSVR Supply-voltage rejection ratio (ΔVDD±/ΔVIO) VDD = 2.7 V to 8 V, VIC = VDD/2, No load IDD Supply current (per channel) VO = 1.5 V, No load (1) (2) 25°C 65 Full range 50 25°C 80 Full range 80 25°C 75 95 725 Full range dB dB 1100 1100 µA Full range is –40°C to 125°C. Typical values are based on the input offset voltage shift observed through 168 hours of operating life test at TA = 150°C extrapolated to TA = 25°C using the Arrhenius equation and assuming an activation energy of 0.96 eV. Copyright © 2003–2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback Product Folder Link(s): TLV2442-Q1 TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 5 TLV2442-Q1,, TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 SGLS181C – SEPTEMBER 2003 – REVISED AUGUST 2009........................................................................................................................................... www.ti.com OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS VDD = 3 V, at specified free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted) PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS VO = 1 V to 2 V, RL = 600 Ω, CL = 100 pF SR Slew rate at unity gain Vn Equivalent input noise voltage Vn(PP) Peak-to-peak equivalent input f = 0.1 Hz to 1 Hz noise voltage f = 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz In Equivalent input noise current f = 10 Hz TA (1) MIN TYP 25°C 0.65 1.3 Full range 0.4 25°C f = 1 kHz 25°C 25°C AV = 1 THD+N Total harmonic distortion plus noise VO = 0.5 V to 2.5 V, RL = 600 Ω, f = 1 kHz AV = 10 170 18 2.6 5.1 0.6 MAX UNIT V/µs nV/√Hz µV fA/√Hz 0.08 25°C AV = 100 0.3 % 2 Gain-bandwidth product f = 10 kHz, RL = 600 Ω, CL = 100 pF 25°C 1.75 MHz BOM Maximum output-swing bandwidth VO(PP) = 1 V, RL = 600 Ω, AV = 1, CL = 100 pF 25°C 0.9 MHz ts Settling time AV = –1, Step = –2.3 V to 2.3 V, RL = 600 Ω, CL = 100 pF 25°C φm Phase margin at unity gain RL = 600 Ω, CL = 100 pF 25°C 65 ° Gain margin RL = 600 Ω, CL = 100 pF 25°C 9 dB (1) 6 To 0.1% To 0.01% 1.5 3.2 µs Full range is –40°C to 125°C. Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2003–2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated Product Folder Link(s): TLV2442-Q1 TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 TLV2442-Q1,, TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 www.ti.com........................................................................................................................................... SGLS181C – SEPTEMBER 2003 – REVISED AUGUST 2009 ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS VDD = 5 V, at specified free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted) PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS TLV244x VIO VDD± = ±2.5 V, VIC = 0, VO = 0, RS = 50 Ω Input offset voltage TLV244xA TA (1) MIN 25°C 25°C 300 Full range Input offset voltage long-term drift (2) VDD± = ±2.5 V, VIC = 0, VO = 0, RS = 50 Ω IIO Input offset current VDD± = ±2.5 V, VIC = 0, VO = 0, RS = 50 Ω IIB Input bias current VDD± = ±2.5 V, VIC = 0, VO = 0, RS = 50 Ω VICR Common-mode input voltage range |VIO| ≤ 5 mV, RS = 50 Ω Low-level output voltage VIC = 2.5 V Large-signal differential voltage amplification AVD 25°C 0.002 µV/mo 25°C 0.5 Full range 150 25°C 1 Full range 260 0 to –0.25 to 4.25 4.5 VIC = 2.5 V, VO = 1 V to 4 V IOL = 5 mA RL = 600 Ω (3) RL = 1 MΩ (3) pA pA V 0 to 4 25°C IOL = 100 µA VOL µV/°C 25°C IOH = –5 mA µV 2 Full range High-level output voltage 950 UNIT 1600 25°C to 85°C VOH 2000 2500 VDD± = ±2.5 V, VIC = 0, VO = 0, RS = 50 Ω IOH = –100 µA MAX 300 Full range Temperature coefficient of input offset voltage αVIO TYP 4.97 25°C 4 Full range 4 4.35 25°C 0.01 25°C 0.8 Full range V V 1.25 25°C 0.9 Full range 0.5 1.3 V/mV 25°C 950 rid Differential input resistance 25°C 1000 GΩ ri Common-mode input resistance 25°C 1000 GΩ ci Common-mode input capacitance f = 10 kHz 25°C 8 pF zo Closed-loop output impedance f = 1 MHz, AV = 10 25°C 140 Ω CMRR Common-mode rejection ratio VIC = VICR MIN, VO = VDD/2, RS = 50 Ω kSVR Supply-voltage rejection ratio (ΔVDD/ΔVIO) VDD = 4.4 V to 8 V, VIC = VDD/2, No load IDD Supply current (per channel) VO = 2.5 V, No load (1) (2) (3) 25°C 70 Full range 70 25°C 80 Full range 80 25°C 75 95 750 Full range dB dB 1100 1100 µA Full range is –40°C to 125°C. Typical values are based on the input offset voltage shift observed through 168 hours of operating life test at TA = 150°C extrapolated to TA = 25°C using the Arrhenius equation and assuming an activation energy of 0.96 eV. Referenced to 2.5 V Copyright © 2003–2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback Product Folder Link(s): TLV2442-Q1 TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 7 TLV2442-Q1,, TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 SGLS181C – SEPTEMBER 2003 – REVISED AUGUST 2009........................................................................................................................................... www.ti.com OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS VDD = 5 V, at specified free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted) PARAMETER TEST CONDITIONS (2) VO = 0.5 V to 2.5 V, RL = 600 Ω , CL = 100 pF (2) SR Slew rate at unity gain Vn Equivalent input noise voltage Vn(PP) Peak-to-peak equivalent input f = 0.1 Hz to 1 Hz noise voltage f = 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz In Equivalent input noise current f = 10 Hz TA (1) MIN TYP 25°C 0.75 1.4 Full range 0.5 25°C f = 1 kHz 25°C 25°C AV = 1 THD+N Total harmonic distortion plus noise VO = 1.5 V to 3.5V, f = 1 kHz, RL = 600 Ω (2) AV = 10 130 16 1.8 3.6 0.6 MAX UNIT V/µs nV/√Hz µV fA/√Hz 0.017 25°C AV = 100 0.17 % 1.5 Gain-bandwidth product f = 10 kHz, RL = 600 Ω (2), CL = 100 pF (2) 25°C 1.81 MHz Maximum output-swing bandwidth VO(PP) = 2 V, AV = 1, RL = 600 Ω (2), CL = 100 pF (2) 25°C 0.5 MHz ts Settling time AV = –1, Step = –0.5 V to 2.5 V, RL = 600 Ω (2), CL = 100 pF (2) φm Phase margin at unity gain RL = 600 Ω (2), CL = 100 pF (2) BOM Gain margin (1) (2) 8 (2) RL = 600 Ω , CL = 100 pF To 0.1% To 0.01% (2) 1.5 25°C 2.6 µs 25°C 68 ° 25°C 8 dB Full range is –40°C to 125°C. Referenced to 2.5 V Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2003–2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated Product Folder Link(s): TLV2442-Q1 TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 TLV2442-Q1,, TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 www.ti.com........................................................................................................................................... SGLS181C – SEPTEMBER 2003 – REVISED AUGUST 2009 TYPICAL CHARACTERISTICS Table of Graphs (1) FIGURE Distribution 2, 3 VIO Input offset voltage vs Common-mode input voltage 4, 5 αVIO Input offset voltage temperature coefficient Distribution 6, 7 IIB/IIO Input bias and input offset currents vs Free-air temperature VOH High-level output voltage vs High-level output current 9, 10 VOL Low-level output voltage vs Low-level output current 11, 12 VO(PP) Maximum peak-to-peak output voltage vs Frequency 13 vs Supply voltage 14 8 IOS Short-circuit output current VO Output voltage vs Differential input voltage Differential voltage amplification vs Load resistance Large-signal differential voltage amplification and phase margin vs Frequency 19, 20 Large-signal differential voltage amplification vs Free-air temperature 21, 22 Output impedance vs Frequency 23, 24 vs Frequency 25 AVD zo CMRR Common-mode rejection ratio kSVR Supply-voltage rejection ratio IDD Supply current SR Slew rate VO Vn THD + N B1 (1) 15 16, 17 18 vs Free-air temperature vs Frequency 26 27, 28 vs Free-air temperature 29 vs Supply voltage 30 vs Load capacitance 31 vs Free-air temperature 32 Inverting large-signal pulse response 33, 34 Voltage-follower large-signal pulse response 35, 36 Inverting small-signal pulse response 37, 38 Voltage-follower small-signal pulse response 39, 40 Equivalent input noise voltage vs Frequency Noise voltage Over a 10-second period Total harmonic distortion plus noise vs Frequency Gain-bandwidth product φm vs Free-air temperature 43 44, 45 vs Free-air temperature 46 vs Supply voltage vs Frequency Phase margin 41, 42 47 19, 20 vs Load capacitance 48 Gain margin vs Load capacitance 49 Unity-gain bandwidth vs Load capacitance 50 For all graphs where VDD = 5 V, all loads are referenced to 2.5 V. Copyright © 2003–2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback Product Folder Link(s): TLV2442-Q1 TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 9 TLV2442-Q1,, TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 SGLS181C – SEPTEMBER 2003 – REVISED AUGUST 2009........................................................................................................................................... www.ti.com DISTRIBUTION OF TLV2442 INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE 16 10 8 6 4 12 10 8 6 4 0 600 700 800 900 −700 −600 −500 −400 0 −300 −200 −100 0 100 200 300 400 500 2 −700 2 VIO − Input Offset Voltage − µV VIO − Input Offset Voltage − µV Figure 2. Figure 3. INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE vs COMMON-MODE INPUT VOLTAGE INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE vs COMMON-MODE INPUT VOLTAGE 2 2 VDD = 3 V TA = 25°C 1.5 VIO − Input Offset Voltage − mV VIO − Input Offset Voltage − mV 1.5 1 0.5 0 −0.5 −1 −1.5 −2 −0.5 VDD = 5 V TA = 25°C 1 0.5 0 −0.5 −1 −1.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 VIC − Common-Mode Input Voltage − V 3 −2 −0.5 0 0.5 1 1.5 Submit Documentation Feedback 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 VIC − Common-Mode Input Voltage − V Figure 4. 10 500 600 700 800 900 12 14 −100 0 100 200 300 400 14 −600 −500 −400 Percentage of Amplifiers − % 16 868 Amplifiers From 1 Wafer Lot VDD = ± 2.5 V TA = 25°C 18 −300 −200 18 20 868 Amplifiers From 1 Wafer Lot VDD = ± 1.5 V TA = 25°C Percentage of Amplifiers − % 20 DISTRIBUTION OF TLV2442 INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE Figure 5. Copyright © 2003–2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated Product Folder Link(s): TLV2442-Q1 TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 TLV2442-Q1,, TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 www.ti.com........................................................................................................................................... SGLS181C – SEPTEMBER 2003 – REVISED AUGUST 2009 DISTRIBUTION OF TLV2442 INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE TEMPERATURE COEFFICIENT DISTRIBUTION OF TLV2442 INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE TEMPERATURE COEFFICIENT 15 18 32 Amplifiers From 1 Wafer Lot VDD = ± 1.5 V P Package 25°C to 125°C 15 Percentage of Amplifiers − % Percentage of Amplifiers − % 12 32 Amplifiers From 2 Wafer Lots VDD = ± 2.5 V P Package 25°C to 125°C 9 6 3 12 9 6 3 0 −8 −7 −6 0 −5 −4 −3 −2 −1 0 1 2 3 −8 −7 −6 4 αVIO − Temperature Coefficient − µV/°C −5 −4 −3 −2 −1 2 3 4 Figure 7. 3 VDD = ± 2.5 V VIC = 0 VO = 0 RS = 50 Ω 30 1 HIGH-LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE vs HIGH-LEVEL OUTPUT CURRENT VDD = 3 V 25 20 IIB 15 IIO 10 5 0 VOH − High-Level Output Voltage − V I IO − Input Bias and Input Offset Currents − pA IIIB IB and IIO Figure 6. INPUT BIAS AND INPUT OFFSET CURRENTS vs FREE-AIR TEMPERATURE 35 0 αVIO − Temperature Coefficient − µV/°C 2.5 2 TA = − 40°C 1.5 1 TA = 125°C 0.5 TA = 85°C TA = 25°C 0 25 45 65 85 105 TA − Free-Air Temperature − °C 125 0 2 4 Figure 8. Copyright © 2003–2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated 6 8 10 12 IOH − High-Level Output Current − mA Figure 9. Submit Documentation Feedback Product Folder Link(s): TLV2442-Q1 TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 11 TLV2442-Q1,, TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 SGLS181C – SEPTEMBER 2003 – REVISED AUGUST 2009........................................................................................................................................... www.ti.com HIGH-LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE vs HIGH-LEVEL OUTPUT CURRENT LOW-LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE vs LOW-LEVEL OUTPUT CURRENT 3 5 VDD = 5 V VDD = 3 V 4 2.5 TA = − 40°C 3.5 VOL − Low-Level Output Voltage − V VOH − High-Level Output Voltage − V 4.5 TA = 25°C 3 2.5 2 TA = 125°C 1.5 TA = 85°C 1 0.5 TA = 125°C 2 TA = 85°C 1.5 1 TA = 25°C TA = − 40°C 0.5 0 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 0 IOH − High-Level Output Current − mA 2 4 Figure 10. 2 TA = 125°C 1.5 TA = 85°C 1 TA = 25°C 0.5 TA = − 40°C 0 6 8 IOL − Low-Level Output Current − mA 10 VO(PP) − Maximum Peak-to-Peak Output Voltage − V VOL − Low-Level Output Voltage − V VDD = 5 V 4 5 RL = 600 Ω VDD = 5 V 4 3 VDD = 3 V 2 1 0 100 1k 10 k Submit Documentation Feedback 100 k 1M 10 M f − Frequency − Hz Figure 12. 12 10 Figure 11. 2.5 2 8 MAXIMUM PEAK-TO-PEAK OUTPUT VOLTAGE vs FREQUENCY LOW-LEVEL OUTPUT VOLTAGE vs LOW-LEVEL OUTPUT CURRENT 0 6 IOL − Low-Level Output Current − mA Figure 13. Copyright © 2003–2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated Product Folder Link(s): TLV2442-Q1 TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 TLV2442-Q1,, TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 www.ti.com........................................................................................................................................... SGLS181C – SEPTEMBER 2003 – REVISED AUGUST 2009 SHORT-CIRCUIT OUTPUT CURRENT vs FREE-AIR TEMPERATURE SHORT-CIRCUIT OUTPUT CURRENT vs SUPPLY VOLTAGE 25 VO = VDD/2 VIC = VDD/2 TA = 25°C 20 I OS − Short-Circuit Output Current − mA I OS − Short-Circuit Output Current − mA 25 VID = −100 mV 15 10 5 0 −5 −10 −15 VID = 100 mV −20 −25 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 15 VID = −100 mV 10 5 0 −5 −10 −20 −25 0 25 50 75 100 Figure 14. Figure 15. OUTPUT VOLTAGE vs DIFFERENTIAL INPUT VOLTAGE OUTPUT VOLTAGE vs DIFFERENTIAL INPUT VOLTAGE 3 125 5 VDD = 3 V VIC = 1.5 V RL = 600 Ω TA = 25°C 4 VO − Output Voltage − V VO − Output Voltage − V −50 TA − Free-Air Temperature − °C VDD − Supply Voltage − V 2.5 VID = 100 mV −15 −25 −75 10 VDD = 5 V VO = 2.5 V 20 2 1.5 1 VDD = 5 V VIC = 2.5 V RL = 600 Ω TA = 25°C 3 2 1 0.5 0 −1000 −750 −500 −250 0 250 500 750 1000 0 −1000 −750 −500 −250 0 250 500 750 VID − Differential Input Voltage − µV VID − Differential Input Voltage − µV Figure 16. Figure 17. Copyright © 2003–2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback Product Folder Link(s): TLV2442-Q1 TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 1000 13 TLV2442-Q1,, TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 SGLS181C – SEPTEMBER 2003 – REVISED AUGUST 2009........................................................................................................................................... www.ti.com DIFFERENTIAL VOLTAGE AMPLIFICATION vs LOAD RESISTANCE 100 A VD − Differential Voltage Amplification − V/mV VO(PP) = 2 V TA = 25°C VDD = 5 V VDD = 3 V 10 1 0.1 1 10 100 1000 RL − Load Resistance − kΩ Figure 18. LARGE-SIGNAL DIFFERENTIAL VOLTAGE AMPLIFICATION AND PHASE MARGIN vs FREQUENCY VDD = 3 V RL = 600 Ω CL = 600 pF TA = 25°C AVD AVD − Large-Signal Differential Voltage Amplification − dB 60 ÁÁ ÁÁ ÁÁ ÁÁ ÁÁ 180° 135° 40 90° 20 45° 0 0° −20 −40 10 k φ m − Phase Margin 80 −45° 100 k 1M f − Frequency − Hz −90° 10 M Figure 19. 14 Submit Documentation Feedback Copyright © 2003–2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated Product Folder Link(s): TLV2442-Q1 TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 TLV2442-Q1,, TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 www.ti.com........................................................................................................................................... SGLS181C – SEPTEMBER 2003 – REVISED AUGUST 2009 LARGE-SIGNAL DIFFERENTIAL VOLTAGE AMPLIFICATION AND PHASE MARGIN vs FREQUENCY 80 135° 40 90° 20 45° 0 0° −20 φ m − Phase Margin 60 AVD − Large-Signal Differential AVD Voltage Amplification − dB ÁÁ ÁÁ ÁÁ ÁÁ ÁÁ 180° VDD = 5 V RL = 600 Ω CL = 600 pF TA = 25°C −45° −40 10 k 100 k −90° 10 M 1M f − Frequency − Hz Figure 20. LARGE-SIGNAL DIFFERENTIAL VOLTAGE AMPLIFICATION vs FREE-AIR TEMPERATURE LARGE-SIGNAL DIFFERENTIAL VOLTAGE AMPLIFICATION vs FREE-AIR TEMPERATURE 1000 1000 ÁÁ ÁÁ ÁÁ ÁÁ ÁÁ 100 RL = 1 MΩ ÁÁ ÁÁ ÁÁ ÁÁ ÁÁ 10 RL = 600 Ω 1 0.1 −75 −50 −25 0 25 50 75 TA − Free-Air Temperature − °C Figure 21. Copyright © 2003–2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated 100 VDD = 5 V VIC = 2.5 V VO = 1 V to 4 V RL = 1 MΩ AVD AVD − Large-Signal Differential Voltage Amplification − V/mV AVD AVD − Large-Signal Differential Voltage Amplification − V/mV VDD = 3 V VIC = 2.5 V VO = 1 V to 4 V 125 100 10 RL = 600 Ω 1 0.1 −75 −50 −25 0 25 50 75 100 125 TA − Free-Air Temperature − °C Figure 22. Submit Documentation Feedback Product Folder Link(s): TLV2442-Q1 TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 15 TLV2442-Q1,, TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 SGLS181C – SEPTEMBER 2003 – REVISED AUGUST 2009........................................................................................................................................... www.ti.com OUTPUT IMPEDANCE vs FREQUENCY OUTPUT IMPEDANCE vs FREQUENCY 1000 100 AV = 100 zzo Ω o − Output Impedance − O zzo Ω o − Output Impedance − O VDD = 3 V TA = 25°C 100 AV = 100 10 AV = 10 1 AV = 1 10 AV = 10 1 AV = 1 VDD = 5 V TA = 25°C 0.1 100 1k 10 k 100 k 0.1 100 1M 1k 10 k Figure 23. COMMON-MODE REJECTION RATIO vs FREE-AIR TEMPERATURE 100 100 TA = 25°C VDD = 5 V VIC = 2.5 V 80 CMRR − Common-Mode Rejection Ratio − dB CMRR − Common-Mode Rejection Ratio − dB 1M Figure 24. COMMON-MODE REJECTION RATIO vs FREQUENCY VDD = 3 V VIC = 1.5 V 60 40 20 0 10 100 1k 10 k 100 k f − Frequency − Hz 1M 10 M VDD = 5 V 90 VDD = 3 V 80 70 60 −75 −50 −25 0 25 50 75 100 TA − Free-Air Temperature − °C Figure 25. 16 100 k f − Frequency − Hz f − Frequency − Hz Submit Documentation Feedback 125 Figure 26. Copyright © 2003–2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated Product Folder Link(s): TLV2442-Q1 TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 TLV2442-Q1,, TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 www.ti.com........................................................................................................................................... SGLS181C – SEPTEMBER 2003 – REVISED AUGUST 2009 SUPPLY-VOLTAGE REJECTION RATIO vs FREQUENCY SUPPLY-VOLTAGE REJECTION RATIO vs FREQUENCY 100 VDD = 3 V TA = 25°C kSVR k SVR − Supply-Voltage Rejection Ratio − dB kSVR k SVR − Supply-Voltage Rejection Ratio − dB 100 80 60 kSVR+ 40 kSVR − 20 0 10 100 1k 10 k 100 k 1M VDD = 5 V TA = 25°C 80 60 kSVR+ kSVR − 40 20 0 10 10 M 100 1k 100 k f − Frequency − Hz f − Frequency − Hz Figure 27. Figure 28. SUPPLY-VOLTAGE REJECTION RATIO vs FREE-AIR TEMPERATURE 1M 10 M SUPPLY CURRENT vs SUPPLY VOLTAGE 100 2.5 VDD = 2.5 V to 8 V 98 2 IIDD DD − Supply Current − mA kSVR k SVR − Supply-Voltage Rejection Ratio − dB 10 k 96 94 92 90 −75 TA = 25°C TA = 85°C 1.5 TA = − 40°C 1 0.5 0 −50 −25 0 25 50 75 100 TA − Free-Air Temperature − °C 125 0 2 4 6 8 VDD − Supply Voltage − V Figure 29. Copyright © 2003–2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated 10 Figure 30. Submit Documentation Feedback Product Folder Link(s): TLV2442-Q1 TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 17 TLV2442-Q1,, TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 SGLS181C – SEPTEMBER 2003 – REVISED AUGUST 2009........................................................................................................................................... www.ti.com SLEW RATE vs LOAD CAPACITANCE SLEW RATE vs FREE-AIR TEMPERATURE 3 3 VDD = 5 V AV = − 1 TA = 25°C 2.5 VDD = 5 V RL = 600 Ω CL = 100 pF AV = 1 2.5 SR − Slew Rate − V/ µs SR − Slew Rate − V/ µ s SR − 2 SR − SR + 1.5 1 0.5 2 1.5 SR + 1 0.5 0 10 100 1k 10 k CL − Load Capacitance − pF 0 −75 100 k −50 −25 0 Figure 31. 50 75 100 125 Figure 32. INVERTING LARGE-SIGNAL PULSE RESPONSE INVERTING LARGE-SIGNAL PULSE RESPONSE 5 3 VDD = 3 V RL = 2 kΩ CL = 100 pF AV = − 1 TA = 25°C VDD = 5 V RL = 2 kΩ CL = 100 pF AV = − 1 TA = 25°C 4 V VO O − Output Voltage − V V VO O − Output Voltage − V 25 TA − Free-Air Temperature − °C 2 1 3 2 1 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 t − Time − µs 7 8 9 10 0 0 1 2 3 4 Figure 33. 18 Submit Documentation Feedback 5 6 7 8 9 10 t − Time − µs Figure 34. Copyright © 2003–2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated Product Folder Link(s): TLV2442-Q1 TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 TLV2442-Q1,, TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 www.ti.com........................................................................................................................................... SGLS181C – SEPTEMBER 2003 – REVISED AUGUST 2009 VOLTAGE-FOLLOWER LARGE-SIGNAL PULSE RESPONSE VOLTAGE-FOLLOWER LARGE-SIGNAL PULSE RESPONSE 5 VDD = 3 V RL = 600 Ω CL = 100 pF AV = 1 TA = 25°C VDD = 5 V RL = 600 Ω CL = 100 pF AV = 1 TA = 25°C 4 V VO O − Output Voltage − V VO VO − Output Voltage − V 3 2 1 3 2 1 0 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 10 2 2.5 3 Figure 36. 2.58 1.5 1.48 1.46 4 4.5 5 VDD = 5 V RL = 600 Ω CL = 100 pF AV = −1 TA = 25°C 2.56 1.52 3.5 INVERTING SMALL-SIGNAL PULSE RESPONSE V VO O − Output Voltage − V V VO O − Output Voltage − V 1.54 1.5 Figure 35. VDD = 3 V RL = 600 Ω CL = 100 pF AV = −1 TA = 25°C 1.56 1 t − Time − µs INVERTING SMALL-SIGNAL PULSE RESPONSE 1.58 0.5 t − Time − µs 2.54 2.52 2.5 2.48 2.46 1.44 2.44 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 t − Time − µs Figure 37. Copyright © 2003–2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated 8 9 10 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 t − Time − µs Figure 38. Submit Documentation Feedback Product Folder Link(s): TLV2442-Q1 TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 19 TLV2442-Q1,, TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 SGLS181C – SEPTEMBER 2003 – REVISED AUGUST 2009........................................................................................................................................... www.ti.com VOLTAGE-FOLLOWER SMALL-SIGNAL PULSE RESPONSE VOLTAGE-FOLLOWER SMALL-SIGNAL PULSE RESPONSE 1.58 2.58 VDD = 3 V RL = 600 Ω CL = 100 pF AV = −1 TA = 25°C 1.54 2.56 VO VO − Output Voltage − V VO − Output Voltage − V VO 1.56 1.52 1.5 1.48 2.54 2.52 2.5 2.48 2.46 1.46 1.44 VDD = 5 V RL = 600 Ω CL = 100 pF AV = −1 TA = 25°C 2.44 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 0 5 V Vn nV/HzHz n − Equivalent Input Noise Voltage − nV V Vn nV/HzHz n − Equivalent Input Noise Voltage − nV VDD = 3 V RS = 20 Ω TA = 25°C 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 2 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 140 VDD = 5 V RS = 20 Ω TA = 25°C 120 100 80 60 40 20 100 1k f − Frequency − Hz 10 k 10 100 1k f − Frequency − Hz Figure 41. 20 2.5 0 0 10 1.5 EQUIVALENT INPUT NOISE VOLTAGE vs FREQUENCY 200 160 1 Figure 40. EQUIVALENT INPUT NOISE VOLTAGE vs FREQUENCY 180 0.5 t − Time − µs t − Time − µs Figure 39. Submit Documentation Feedback 10 k Figure 42. Copyright © 2003–2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated Product Folder Link(s): TLV2442-Q1 TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 TLV2442-Q1,, TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 www.ti.com........................................................................................................................................... SGLS181C – SEPTEMBER 2003 – REVISED AUGUST 2009 TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE vs FREQUENCY 2000 VDD = 5 V f = 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz TA = 25°C 1500 Noise Voltage − nV 1000 500 0 −500 −1000 −1500 −2000 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 10 9 THD + N − Total Harmonic Distortion Plus Noise − % NOISE VOLTAGE OVER A 10-SECOND PERIOD t − Time − s 10 VDD = 3 V RL = 600 Ω TA = 25°C 1 AV = 100 AV = 10 0.1 AV = 1 0.01 10 10 k 100 k f − Frequency − Hz Figure 44. Figure 43. GAIN-BANDWIDTH PRODUCT vs FREE-AIR TEMPERATURE TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION PLUS NOISE vs FREQUENCY 10 3 RL = 600 Ω CL = 100 pF f = 10 kHz VDD = 5 V RL = 600 Ω TA = 25°C Gain-Bandwidth Product − MHz THD + N − Total Harmonic Distortion Plus Noise − % 1k 100 AV = 100 1 AV = 10 0.1 2.5 2 1.5 AV = 1 0.01 10 100 1k f − Frequency − Hz Figure 45. Copyright © 2003–2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated 10 k 100 k 1 −50 −25 0 25 50 75 100 125 TA − Free-Air Temperature − °C Figure 46. Submit Documentation Feedback Product Folder Link(s): TLV2442-Q1 TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 21 TLV2442-Q1,, TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 SGLS181C – SEPTEMBER 2003 – REVISED AUGUST 2009........................................................................................................................................... www.ti.com PHASE MARGIN vs LOAD CAPACITANCE GAIN-BANDWIDTH PRODUCT vs SUPPLY VOLTAGE 75° RL = 600 Ω CL = 100 pF f = 10 kHz TA = 25°C 1.9 Rnull = 100 Ω 60° φom m − Phase Margin Gain-Bandwidth Product − MHz 2 1.8 1.7 45° Rnull = 50 Ω 30° Rnull = 0 Rnull = 20 Ω 15° 1.6 RL = 600 Ω TA = 25°C 0° 10 1.5 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 |VDD ±| − Supply Voltage − V Figure 47. 7 8 GAIN MARGIN vs LOAD CAPACITANCE 2 RL = 600 Ω TA = 25°C Gain Margin − dB Rnull = 20 Ω 0 10 Rnull = 0 100 1K 10 K CL − Load Capacitance − pF Figure 49. Submit Documentation Feedback 1.5 ÁÁ ÁÁ ÁÁ ÁÁ 10 5 22 Rnull = 100 Ω RL = 600 Ω TA = 25°C Rnull = 50 Ω 20 15 100 k UNITY-GAIN BANDWIDTH vs LOAD CAPACITANCE B1 − Unity-Gain Bandwidth − kHz 25 100 1k 10 k CL − Load Capacitance − pF Figure 48. 100 K 1 0.5 0 10 100 1k 10 k CL − Load Capacitance − pF Figure 50. 100 k Copyright © 2003–2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated Product Folder Link(s): TLV2442-Q1 TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 TLV2442-Q1,, TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 www.ti.com........................................................................................................................................... SGLS181C – SEPTEMBER 2003 – REVISED AUGUST 2009 APPLICATION INFORMATION macromodel information Macromodel information provided was derived using PSpice™ Parts™ model generation software. The Boyle macromodel (2) and subcircuit in Figure 51 were generated using the TLV244x typical electrical and operating characteristics at TA = 25°C. Using this information, output simulations of the following key parameters can be generated to a tolerance of 20% (in most cases): (2) • • • • • • G. R. Boyle, B. M. Cohn, D. O. Pederson, and J. E. Solomon, “Macromodeling of Integrated Circuit Operational Amplifiers,” IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, SC-9, 353 (1974). • • • • • • Maximum positive output voltage swing Maximum negative output voltage swing Slew rate Quiescent power dissipation Input bias current Open-loop voltage amplification Unity gain frequency Common-mode rejection ratio Phase margin DC output resistance AC output resistance Short-circuit output current limit 99 3 VCC + 9 RSS 92 FB 10 VC J1 DP J2 IN + 11 RD1 VAD DC 12 C1 R2 − 53 − C2 6 91 + VLP − − + VLN + GCM GA VLIM − 8 RD2 RO1 DE 5 54 4 DLP 7 60 + − + HLIM − + 90 RO2 VB IN − VCC − − + ISS RP 2 1 DLN EGND + − + VE .SUBCKT TLV2442 1 2 3 4 5 C1 11 12 14E−12 C2 6 7 60.00E−12 DC 5 53 DX DE 54 5 DX DLP 90 91 DX DLN 92 90 DX DP 4 3 DX EGND 99 0 POLY (2) (3,0) (4,) 0 .5 .5 FB 7 99 POLY (5) VB VC VE VLP VLN 0 + 984.9E3 −1E6 1E6 1E6 −1E6 GA 6 0 11 12 377.0E−6 GCM 0 6 10 99 134E−9 ISS 3 10 DC 216.0E−6 HLIM 90 0 VLIM 1K J1 11 2 10 JX J2 12 1 10 JX R2 6 9 100.OE3 OUT RD1 60 11 2.653E3 RD2 60 12 2.653E3 R01 8 5 50 R02 7 99 50 RP 3 4 4.310E3 RSS 10 99 925.9E3 VAD 60 4 −.5 VB 9 0 DC 0 VC 3 53 DC .78 VE 54 4 DC .78 VLIM 7 8 DC 0 VLP 91 0 DC 1.9 VLN 0 92 DC 9.4 .MODEL DX D (IS=800.0E−18) .MODEL JX PJF (IS=1.500E−12BETA=1.316E-3 + VTO=−.270) .ENDS Figure 51. Boyle Macromodel and Subcircuit Copyright © 2003–2009, Texas Instruments Incorporated Submit Documentation Feedback Product Folder Link(s): TLV2442-Q1 TLV2442A-Q1 TLV2444A-Q1 23 PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM www.ti.com 11-Jul-2015 PACKAGING INFORMATION Orderable Device Status (1) Package Type Package Pins Package Drawing Qty Eco Plan Lead/Ball Finish MSL Peak Temp (2) (6) (3) Op Temp (°C) Device Marking (4/5) TLV2442AQDRG4Q1 ACTIVE SOIC D 8 2500 Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM -40 to 125 2442AQ TLV2442AQDRQ1 ACTIVE SOIC D 8 2500 Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM -40 to 125 2442AQ TLV2442AQPWRG4Q1 ACTIVE TSSOP PW 8 2000 Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM -40 to 125 2442AQ TLV2442AQPWRQ1 OBSOLETE TSSOP PW 8 TBD Call TI Call TI -40 to 125 TLV2442QDGKRQ1 ACTIVE VSSOP DGK 8 2500 Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) CU NIPDAU | CU NIPDAUAG Level-2-260C-1 YEAR -40 to 125 TBD Call TI Call TI -40 to 125 2000 Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM -40 to 125 TBD Call TI Call TI -40 to 125 Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) CU NIPDAU Level-1-260C-UNLIM -40 to 125 TLV2442QDRQ1 OBSOLETE SOIC D 8 TLV2442QPWRG4Q1 ACTIVE TSSOP PW 8 TLV2442QPWRQ1 OBSOLETE TSSOP PW 8 TLV2444AQPWRQ1 ACTIVE TSSOP PW 14 2000 OBR 2442Q1 2444AQ (1) The marketing status values are defined as follows: ACTIVE: Product device recommended for new designs. LIFEBUY: TI has announced that the device will be discontinued, and a lifetime-buy period is in effect. NRND: Not recommended for new designs. Device is in production to support existing customers, but TI does not recommend using this part in a new design. PREVIEW: Device has been announced but is not in production. Samples may or may not be available. OBSOLETE: TI has discontinued the production of the device. (2) Eco Plan - The planned eco-friendly classification: Pb-Free (RoHS), Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt), or Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br) - please check http://www.ti.com/productcontent for the latest availability information and additional product content details. TBD: The Pb-Free/Green conversion plan has not been defined. Pb-Free (RoHS): TI's terms "Lead-Free" or "Pb-Free" mean semiconductor products that are compatible with the current RoHS requirements for all 6 substances, including the requirement that lead not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous materials. Where designed to be soldered at high temperatures, TI Pb-Free products are suitable for use in specified lead-free processes. Pb-Free (RoHS Exempt): This component has a RoHS exemption for either 1) lead-based flip-chip solder bumps used between the die and package, or 2) lead-based die adhesive used between the die and leadframe. The component is otherwise considered Pb-Free (RoHS compatible) as defined above. Green (RoHS & no Sb/Br): TI defines "Green" to mean Pb-Free (RoHS compatible), and free of Bromine (Br) and Antimony (Sb) based flame retardants (Br or Sb do not exceed 0.1% by weight in homogeneous material) (3) MSL, Peak Temp. - The Moisture Sensitivity Level rating according to the JEDEC industry standard classifications, and peak solder temperature. (4) There may be additional marking, which relates to the logo, the lot trace code information, or the environmental category on the device. Addendum-Page 1 Samples PACKAGE OPTION ADDENDUM www.ti.com 11-Jul-2015 (5) Multiple Device Markings will be inside parentheses. Only one Device Marking contained in parentheses and separated by a "~" will appear on a device. If a line is indented then it is a continuation of the previous line and the two combined represent the entire Device Marking for that device. (6) Lead/Ball Finish - Orderable Devices may have multiple material finish options. Finish options are separated by a vertical ruled line. Lead/Ball Finish values may wrap to two lines if the finish value exceeds the maximum column width. Important Information and Disclaimer:The information provided on this page represents TI's knowledge and belief as of the date that it is provided. TI bases its knowledge and belief on information provided by third parties, and makes no representation or warranty as to the accuracy of such information. Efforts are underway to better integrate information from third parties. TI has taken and continues to take reasonable steps to provide representative and accurate information but may not have conducted destructive testing or chemical analysis on incoming materials and chemicals. TI and TI suppliers consider certain information to be proprietary, and thus CAS numbers and other limited information may not be available for release. In no event shall TI's liability arising out of such information exceed the total purchase price of the TI part(s) at issue in this document sold by TI to Customer on an annual basis. OTHER QUALIFIED VERSIONS OF TLV2442-Q1, TLV2442A-Q1, TLV2444A-Q1 : • Catalog: TLV2442, TLV2442A, TLV2444A • Military: TLV2442M, TLV2442AM NOTE: Qualified Version Definitions: • Catalog - TI's standard catalog product • Military - QML certified for Military and Defense Applications Addendum-Page 2 PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION www.ti.com 14-Mar-2013 TAPE AND REEL INFORMATION *All dimensions are nominal Device Package Package Pins Type Drawing TLV2442QDGKRQ1 VSSOP DGK TLV2442QPWRG4Q1 TSSOP TLV2444AQPWRQ1 TSSOP SPQ Reel Reel A0 Diameter Width (mm) (mm) W1 (mm) B0 (mm) K0 (mm) P1 (mm) W Pin1 (mm) Quadrant 8 2500 330.0 12.4 5.3 3.4 1.4 8.0 12.0 Q1 PW 8 2000 330.0 12.4 7.0 3.6 1.6 8.0 12.0 Q1 PW 14 2000 330.0 12.4 6.9 5.6 1.6 8.0 12.0 Q1 Pack Materials-Page 1 PACKAGE MATERIALS INFORMATION www.ti.com 14-Mar-2013 *All dimensions are nominal Device Package Type Package Drawing Pins SPQ Length (mm) Width (mm) Height (mm) TLV2442QDGKRQ1 VSSOP DGK 8 2500 367.0 367.0 35.0 TLV2442QPWRG4Q1 TSSOP PW 8 2000 367.0 367.0 35.0 TLV2444AQPWRQ1 TSSOP PW 14 2000 367.0 367.0 35.0 Pack Materials-Page 2 PACKAGE OUTLINE PW0008A TSSOP - 1.2 mm max height SCALE 2.800 SMALL OUTLINE PACKAGE C 6.6 TYP 6.2 SEATING PLANE PIN 1 ID AREA A 0.1 C 6X 0.65 8 1 3.1 2.9 NOTE 3 2X 1.95 4 5 B 4.5 4.3 NOTE 4 SEE DETAIL A 8X 0.30 0.19 0.1 C A 1.2 MAX B (0.15) TYP 0.25 GAGE PLANE 0 -8 0.15 0.05 0.75 0.50 DETAIL A TYPICAL 4221848/A 02/2015 NOTES: 1. All linear dimensions are in millimeters. Any dimensions in parenthesis are for reference only. Dimensioning and tolerancing per ASME Y14.5M. 2. This drawing is subject to change without notice. 3. This dimension does not include mold flash, protrusions, or gate burrs. Mold flash, protrusions, or gate burrs shall not exceed 0.15 mm per side. 4. This dimension does not include interlead flash. Interlead flash shall not exceed 0.25 mm per side. 5. Reference JEDEC registration MO-153, variation AA. www.ti.com EXAMPLE BOARD LAYOUT PW0008A TSSOP - 1.2 mm max height SMALL OUTLINE PACKAGE 8X (1.5) 8X (0.45) SYMM 1 8 (R0.05) TYP SYMM 6X (0.65) 5 4 (5.8) LAND PATTERN EXAMPLE SCALE:10X SOLDER MASK OPENING METAL SOLDER MASK OPENING METAL UNDER SOLDER MASK 0.05 MAX ALL AROUND 0.05 MIN ALL AROUND SOLDER MASK DEFINED NON SOLDER MASK DEFINED SOLDER MASK DETAILS NOT TO SCALE 4221848/A 02/2015 NOTES: (continued) 6. Publication IPC-7351 may have alternate designs. 7. Solder mask tolerances between and around signal pads can vary based on board fabrication site. www.ti.com EXAMPLE STENCIL DESIGN PW0008A TSSOP - 1.2 mm max height SMALL OUTLINE PACKAGE 8X (1.5) 8X (0.45) SYMM (R0.05) TYP 1 8 SYMM 6X (0.65) 5 4 (5.8) SOLDER PASTE EXAMPLE BASED ON 0.125 mm THICK STENCIL SCALE:10X 4221848/A 02/2015 NOTES: (continued) 8. Laser cutting apertures with trapezoidal walls and rounded corners may offer better paste release. IPC-7525 may have alternate design recommendations. 9. Board assembly site may have different recommendations for stencil design. www.ti.com IMPORTANT NOTICE Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, enhancements, improvements and other changes to its semiconductor products and services per JESD46, latest issue, and to discontinue any product or service per JESD48, latest issue. Buyers should obtain the latest relevant information before placing orders and should verify that such information is current and complete. All semiconductor products (also referred to herein as “components”) are sold subject to TI’s terms and conditions of sale supplied at the time of order acknowledgment. TI warrants performance of its components to the specifications applicable at the time of sale, in accordance with the warranty in TI’s terms and conditions of sale of semiconductor products. Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI deems necessary to support this warranty. Except where mandated by applicable law, testing of all parameters of each component is not necessarily performed. TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or the design of Buyers’ products. Buyers are responsible for their products and applications using TI components. To minimize the risks associated with Buyers’ products and applications, Buyers should provide adequate design and operating safeguards. TI does not warrant or represent that any license, either express or implied, is granted under any patent right, copyright, mask work right, or other intellectual property right relating to any combination, machine, or process in which TI components or services are used. Information published by TI regarding third-party products or services does not constitute a license to use such products or services or a warranty or endorsement thereof. Use of such information may require a license from a third party under the patents or other intellectual property of the third party, or a license from TI under the patents or other intellectual property of TI. Reproduction of significant portions of TI information in TI data books or data sheets is permissible only if reproduction is without alteration and is accompanied by all associated warranties, conditions, limitations, and notices. TI is not responsible or liable for such altered documentation. Information of third parties may be subject to additional restrictions. Resale of TI components or services with statements different from or beyond the parameters stated by TI for that component or service voids all express and any implied warranties for the associated TI component or service and is an unfair and deceptive business practice. TI is not responsible or liable for any such statements. Buyer acknowledges and agrees that it is solely responsible for compliance with all legal, regulatory and safety-related requirements concerning its products, and any use of TI components in its applications, notwithstanding any applications-related information or support that may be provided by TI. Buyer represents and agrees that it has all the necessary expertise to create and implement safeguards which anticipate dangerous consequences of failures, monitor failures and their consequences, lessen the likelihood of failures that might cause harm and take appropriate remedial actions. Buyer will fully indemnify TI and its representatives against any damages arising out of the use of any TI components in safety-critical applications. In some cases, TI components may be promoted specifically to facilitate safety-related applications. With such components, TI’s goal is to help enable customers to design and create their own end-product solutions that meet applicable functional safety standards and requirements. Nonetheless, such components are subject to these terms. No TI components are authorized for use in FDA Class III (or similar life-critical medical equipment) unless authorized officers of the parties have executed a special agreement specifically governing such use. Only those TI components which TI has specifically designated as military grade or “enhanced plastic” are designed and intended for use in military/aerospace applications or environments. Buyer acknowledges and agrees that any military or aerospace use of TI components which have not been so designated is solely at the Buyer's risk, and that Buyer is solely responsible for compliance with all legal and regulatory requirements in connection with such use. TI has specifically designated certain components as meeting ISO/TS16949 requirements, mainly for automotive use. In any case of use of non-designated products, TI will not be responsible for any failure to meet ISO/TS16949. Products Applications Audio www.ti.com/audio Automotive and Transportation www.ti.com/automotive Amplifiers amplifier.ti.com Communications and Telecom www.ti.com/communications Data Converters dataconverter.ti.com Computers and Peripherals www.ti.com/computers DLP® Products www.dlp.com Consumer Electronics www.ti.com/consumer-apps DSP dsp.ti.com Energy and Lighting www.ti.com/energy Clocks and Timers www.ti.com/clocks Industrial www.ti.com/industrial Interface interface.ti.com Medical www.ti.com/medical Logic logic.ti.com Security www.ti.com/security Power Mgmt power.ti.com Space, Avionics and Defense www.ti.com/space-avionics-defense Microcontrollers microcontroller.ti.com Video and Imaging www.ti.com/video RFID www.ti-rfid.com OMAP Applications Processors www.ti.com/omap TI E2E Community e2e.ti.com Wireless Connectivity www.ti.com/wirelessconnectivity Mailing Address: Texas Instruments, Post Office Box 655303, Dallas, Texas 75265 Copyright © 2015, Texas Instruments Incorporated