Periodic Waveforms - Boise State University
advertisement

Boise State University
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
ECE212 – Circuit Analysis and Design
Periodic Waveforms
Lecture Objectives:
1. To define performance measures of periodic waveforms (zero-to-peak value, peak-to-peak
value, average value, effective or rms value, form factor, and crest factor).
2. To give a physical interpretation of the effective (rms) heating value of a periodic waveform.
3. To compute the above performance measures for common periodic waveforms.
v(t)
3
2
1
t
0
1 2
3
4
5 6
7
8
9
−1
Period: T
= 4 (s)
1
=
= 0.25 (Hz)
4
Frequency: f
Zero-to-Peak or Peak Value:
Vp = max{|Vmax |, |Vmin |} =
max{|3|, | − 1|} = 3 (V)
Peak-to-Peak Value:
Vpp = Vmax − Vmin = 3 − (−1) = 4 (V)
Average Value:
∫
Vavg =
=
1 T
1
v(t) dt =
× Area under v(t) during one period
T 0
T
4
1
[3 × 1 + 2 × 1 + (−1) × 1 + 0 × 1] =
= 1 (V)
4
4
Note:
Vavg =
1
T
∫
∫
T
v(t) dt =⇒ T Vavg
=
T
v(t) dt
0
0
Interpretation: The average value of a periodic waveform is the value of a constant (DC) waveform
that spans the same area as the original waveform over one period.
1
Effective (rms) Value:
√
Vrms
√
∫
1 T 2
1
v (t) dt =
× Area under v 2 (t) during one period
=
T 0
T
√
√
√
1 2
14
2
2
2
=
[3 × 1 + 2 × 1 + (−1) × 1 + 0 × 1] =
=
3.5 = 1.871 (V)
4
4
Note:
√
1
T
Vrms =
∫
T
0
2
v 2 (t) dt =⇒ Vrms
=
1
T
∫
T
v 2 (t) dt
0
Interpretation: The effective value of a periodic waveform is also called the root of the mean of
the squared waveform or rms value for short. The rms value squared is the average value of the
squared waveform.
Idc
i(t)
+
v(t)
R
Vdc
−
R
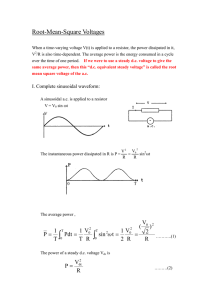
Physical Interpretation of the Effective (Heating) Value of a Periodic Waveform:
Instantaneous Ohm’s Law:
v(t) = Ri(t)
Instantaneous Power:
p(t) = v(t)i(t)
Average Power:
Pavg =
=
1
T
1
T
∫
T
p(t) dt =
0
∫
T
p(t) dt =
0
1
T
1
T
∫
T
0
∫
[
1
v(t)i(t) dt = R
T
[
T
v(t)i(t) dt =
0
1 1
R T
∫
T
]
2
2
= RIrms
i (t) dt
0
∫
T
0
]
v 2 (t) dt
=
2
Vrms
R
The above AC and DC circuits will dissipate the same amount of heat per period if
Vdc = Vrms
and
Idc = Irms
2
|v(t)|
3
2
1
t
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
−1
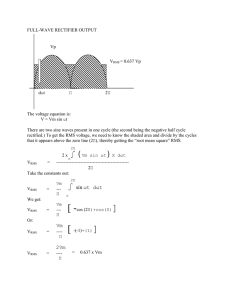
Rectified Waveform:
|V |avg =
=
∫
1 T
|v(t)| dt
T 0
1
[3 × 1 + 2 × 1 + | − 1| × 1 + 0 × 1]
4
=
6
4
Form Factor:
FF =
Vrms
|V |avg
=
√
3.5
1.5
=
1.871
1.5
= 1.247 ≥ 1
Crest Factor:
CF =
Vp
Vrms
=
3
√
3.5
=
3
1.871
= 1.60 ≥ 1
3
= 1.5 (V)
v(t)
Vm
0
T
2T
t
−V m
Sinusoidal Waveform:
Vmax = Vm
Vmin = −Vm
Vp = max{|Vmax |, |Vmin |} =
max{|Vm |, | − Vm |} = Vm
Vpp = Vmax − Vmin = Vm − (−Vm ) = 2Vm
∫
∫
∫ ωT
1 T
1
1 T
Vavg =
v(t) dt =
Vm sin ωt dt =
Vm sin ωt dωt
T 0
T 0
ωT 0
∫ 2π
Vm
1
Vm
[− cos θ]2π
=
[− cos 2π + cos 0] = 0
=
Vm sin θ dθ =
0
2π 0
2π
2π
∫
∫
∫ ωT
1 T 2
1 T 2
1
2
Vrms
=
v (t) dt =
Vm sin2 ωt dt =
Vm2 sin2 ωt dωt
T 0
T 0
ωT 0
[
]
∫
∫
Vm2
1 2π 2
1 2π Vm2
sin 2θ 2π
[1 − cos 2θ] dθ =
=
Vm sin2 θ dθ =
θ−
2π 0
2π 0
2
4π
2
0
[
]
2
2
Vm
sin 4π
Vm
Vm
=
2π −
=
=⇒ Vrms = √
4π
2
2
2
∫ T
∫ T
∫ ωT /2
1
1
2
|V |avg =
|v(t)| dt =
Vm | sin ωt| dt =
Vm sin ωt dωt
T 0
T 0
ωT 0
∫ π
2Vm
2Vm
2
2Vm
[− cos θ]π0 =
[− cos π + cos 0] =
Vm sin θ dθ =
=
2π 0
2π
2π
π
√
√
Vm / 2
π
Vrms
π 2 ∼
√
=
=
FF =
=
= 1.111
|V |avg
2Vm /π
4
2 2
√
Vp
Vm
√
CF =
=
2 ∼
=
= 1.414
Vrms
Vm / 2
4
v(t)
Vm
0
0
T
2T
t
−V m
Sawtooth Waveform:
Vp = max{|Vmax |, |Vmin |} =
max{|Vm |, | − Vm |} = Vm
Vpp = Vmax − Vmin = Vm − (−Vm ) = 2Vm
Vavg =
2
Vrms
=
2
Vrms
=
|V |avg =
FF =
CF =
1
T
1
T
∫
−T /2
∫
T /2
−T /2
Vm3
3
1
T
T /2
∫
v(t) dt =
v 2 (t) dt =
=⇒ Vrms =
T /2
−T /2
Vrms
|V |avg
Vp
Vrms
|v(t)| dt =
√
Vm / 3
=
Vm /2
Vm
√
=
Vm / 3
1
T
∫
1
T
T /2
−T /2
∫
2Vm
t dt =
T
T /2
−T /2
4Vm2 2
t dt =
T2
V
√m
3
∫
[
2Vm t2
T2 2
]T /2
[
4Vm2 t
T3 3
[
4Vm t2
2Vm
t dt =
T
T2 2
0
√
2
2 3 ∼
= √
=
= 1.155
3
3
√
=
3 ∼
= 1.732
2
T
T /2
5
= 0
−T /2
]
3 T /2
=
−T /2
]T /2
=
0
4Vm2
2T 3
×
T3
3×8
4Vm
T2
×
T2
2×4
=
Vm
2
Effective Value of an AC Waveform with a DC Offset
v(t) = Vdc + vac (t)
where
Vavg =
1
T
∫
1
T
v(t) dt =
0
√
Vrms =
√
=
√
=
T
1
T
1
T
∫
0
T
T
0
Vdc dt +
√
T
v 2 (t) dt =
∫
∫
[
0
2
Vdc
+
2 (t)
vac
1
T
∫
0
Vac = Vac,rms =
√
1
T
∫
0
T
vac (t) dt = Vdc + 0 = Vdc
[Vdc + vac (t)]2 dt
]
+ 2vac (t)Vdc dt =
T
0
∫
T
2 +V2
Vdc
ac
where
1
T
2 (t) dt
vac
6
√
1
T
∫
0
T
[
]
2 + v 2 (t) dt
Vdc
ac