Experiment- Objective : To study I-V Characteristics of Zener Diode
advertisement

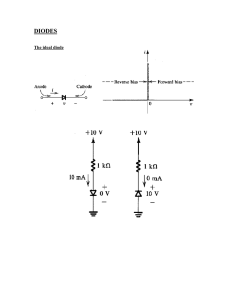
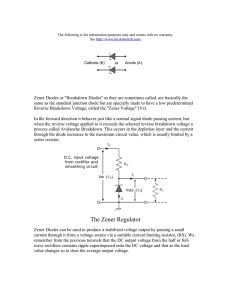
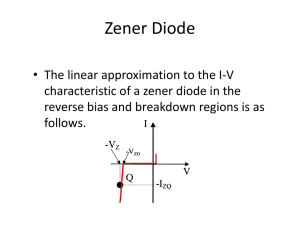
ExperimentObjective : To study I-V Characteristics of Zener Diode Instrument Used : Diode Characteristics Trainer (NV6501) Items Required: 1. Zener Diode, Regulated Power Supply 2. Multi meters and Connecting wire Procedure: To plot Reverse Characteristics proceed as follows 1. Rotate potentiometer P1 fully in CCW (counter clockwise direction). 2. Connect Ammeter between TP9 and TP10, to measure diode current ID (mA) & set Ammeter at 200mA range. 3. Connect Voltmeter across TP3 and TP11, to measure diode voltage VD & set Voltmeter at 20V range. 4. Switch ‘On’ the power supply. 5. Vary the potentiometer P1 so as to increase the value of diode voltage VD from zero to 6.8V in steps and measure the corresponding values of diode current Iz in mA & note down in the Observation Table. 6. Plot a curve between diode voltage Vz and diode current Iz as shown in figure 2 (third quadrant) using suitable scale, with the help of Observation Table . This curve is the required Reverse Characteristics of Zener diode. 7. Switch ‘Off’ the supply. Graph: I vs. V graph is shown in graph page no_____. Result: Zener breakdown voltage for Zener diode is ___________Volt. Circuit Diagram: Figure 1 Circuit of Reverse bias Characteristics of Zener diode Figure 2 I- V characteristics of forward and reverse bias Observation Table: Sr. No. Reverse Bias Voltage (V) Reverse Bias Current (µA) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Calculation: From the value of potential difference and current find Zener breakdown voltage of the Zener diode for a reverse bias. Questions: 1. What do you means by Zener break down voltage? 2. Zener diode reverse bias current increases suddenly, why? 3. List out few differences between P N Junction Diode and Zener Diode. 4. Explain use of Zener diode as a voltage regulator with appropriate circuit diagram.