Reverse Bias characteristic of Zener Diode
advertisement

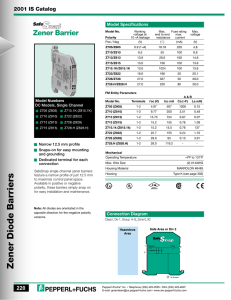
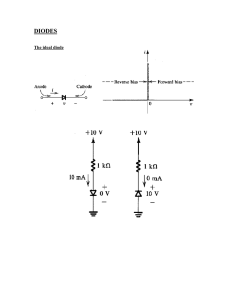
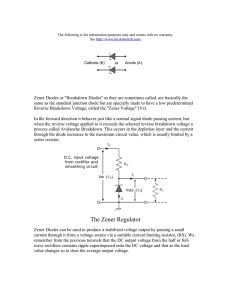
Reverse Bias characteristic of Zener Diode Object: To draw the reverse bias characteristic of Zener diode and to determine Zener breakdown voltage for three Zener diodes. Apparatus used: Zener diode, voltmeter (0-20 volt), mili-ammeter, micro-ammeter, variable D.C. source (0-20 volt). Formula/theory: y Zener diode is a heavily doped PN junction diode. Due to heavily doped, its depletion layer is very thin and is order of micrometer. The forward bias characteristic of Zener diode is same as de the normal PN junction diode but in reverse bias it has different characteristic. Initially, a negligible constant current flow through the zener diode in its reverse bias but at certain voltage, the current becomes abruptly large. This voltage is called as zener voltage. This sudden and sharp increase in zener current is called as zener breakdown. .K .P an The zener breakdown is caused by field emission of charge carriers. i.e. At zener voltage, the field across the junction becomes very large due very thin depletion layer thickness. This sufficiently strong electric field enables tunneling of electrons from the valence to the conduction band of a semiconductor (or directly pulls the electrons form the semiconductor) leading to a large number of free charge carriers. This sudden generation of carriers, rapidly increases the reverse current. D Circuit Diagram: Fig 1: Zener Diode in RB Procedure: 1. First of all, connect the circuit as shown in figure 1 for Zener first. 2. Now increase the voltage (VR) in intervals of 1volt and note the corresponding currents till the current becomes out of scale. At the turning point of curve, measure current for small interval of voltage also. 3. Repeat step 1-2 for other two zener diodes. 4. Plot the graph in VR and IR for all the three zener diodes. 6. Table for VR and IR of third Zener diode Sr. VR IR No. (Volt) (mA) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. .K .P an de y Observation: 1. Least count of voltmeter=……..volt 2. Least count of miliammeter =……..mA 3. Least count of micro-ammeter =…….μA 4. Table for VR and IR of 5. Table for VR and IR of first Zener diode second Zener diode Sr. VR IR Sr. VR IR No. (Volt) (mA) No. (Volt) (mA) 1. 1. 2. 2. 3. 3. 4. 4. 5. 5. 6. 6. 7. 7. 8. 8. 9. 9. 10. 10. Result: The reverse bias characteristic of all the three Zener diodes are in graph1-3. The Zener voltage for them are found as: -6 -5 -4 -3 VR (volt) 0 -2 -1 VZ3=…….volts 0 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 0 -3 -1 -1 0 -2 0 -12 -11 -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 -4 -3 -2 -1 0 -1 -1 IR (mA) -2 -2 VR (volt) IR (mA) VR (volt) VZ2=……..volts, -2 -3 -3 -3 -4 -4 -4 Graph-1 Graph-2 Graph-3 D Precautions: 1. The connection should be tight otherwise fluctuation in voltage and current will happen. 2. At the turning point of curve, more reading should be taken. 3. For plot of Graph, IR should be taken mA. 4. The reading should be in multiple of least count. IR (mA) VZ1=……..volts,