Wizard Test Maker
advertisement

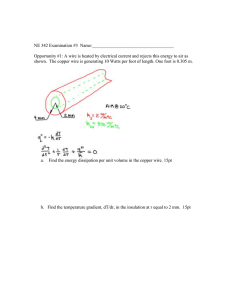
RESISTANCE IN WIRES NAME:____________________ 1. A copper wire of length L and cross-sectional area A has resistance R. A second copper wire at the same temperature has a length of 2L and a cross-sectional area of 12A. What is the resistance of the second copper wire? 1) R 2) 2R 3) 1 R 2 4) 4R 2. If the length of a copper wire is reduced by half, then the resistance of the wire will be 1) halved 3) quartered 2) doubled 4) quadrupled 3. A uniform copper wire has a resistance of 100 ohms. If the wire is cut into 10 equal lengths, the resistance of each piece will be 1) 1 Ω 3) 100 Ω 2) 10 Ω 4) 1,000 Ω 4. The graph below shows the relationship between the potential difference across a metallic conductor and the electric current through the conductor at constant temperature T1. Which graph best represents the relationship between potential difference and current for the same conductor maintained at a higher constant temperature, T2? 1) 3) 2) 4) 5. As the temperature of a metal conductor is reduced, the resistance of the conductor will 1) decrease 3) remain the same 2) increase 6. The diagram below represents a lamp, a 10-volt battery, and a length of nichrome wire connected in series. 10. If the diameter of a wire were decreased, its electrical resistance would 1) decrease 3) remain the same 2) increase 11. Plastic insulation surrounds a wire having diameter d and length … as shown below. As the temperature of the nichrome is decreased, the brightness of the lamp will 1) decrease 3) remain the same 2) increase 7. To reduce the resistance of a metal conductor one should 1) cool the conductor to a low temperature 2) heat the conductor to a high temperature 3) coat the conductor with an insulator 4) wire the conductor in series with another resistor 8. As the temperature of a coil of copper wire increases, its electrical resistance 1) decreases 3) remains the same 2) increases 9. The diagram below shows a circuit in which a copper wire connects points A and B. The electrical resistance between points A and B can be decreased by 1) replacing the wire with a thicker copper wire of the same length 2) replacing the wire with a longer copper wire of the same thickness 3) increasing the temperature of the copper wire 4) increasing the potential difference supplied by the battery A decrease in the resistance of the wire would be produced by an increase in the 1) thickness of the plastic insolation 2) length of the wire 3) diameter d of the wire 4) temperature of the wire 12. Two copper wires have the same length, but the crosssectional area of wire A is twice that of wire B. Compared to the resistance of wire B. the resistance of wire A is 1) one-quarter as great 3) twice as great 2) one-half as great 4) four times as great 13. A 12.0-meter length of copper wire has a resistance of 1.50 ohms. How long must an aluminum wire with the same cross-sectional area be to have the same resistance? 1) 7.32 m 3) 12.0 m 2) 8.00 m 4) 19.7 m 14. What is the resistance at 20°C of a 1.50-meter-long aluminum conductor that has a cross-sectional area of 1.13 × 10–6 meter2? 1) 1.87 × 10–3 Þ 2) 2.28 × 10–2 Þ 3) 3.74 × 10–2 Þ 4) 1.33 × 106 Þ 15. A 10.-meter length of wire with a cross-sectional area of 3.0 × 10–6 square meter has a resistance of 9.4 × 10–2 ohm at 20° Celsius. The wire is most likely made of 1) silver 3) aluminum 2) copper 4) tungsten 16. A 0.500-meter length of wire with a cross-sectional area of 3.14 × 10–6 meters squared is found to have a resistance of 2.53 × 10–3 ohms. According to the resistivity chart, the wire could be made of 1) aluminum 3) nichrome 2) copper 4) silver 17. The graph below represents the relationship between potential difference and current for four different resistors. Which resistor has the greatest resistance? 19. In the diagrams below, l represents a unit length of copper wire and A represents a unit cross-sectional area. Which copper wire has the smallest resistance at room temperature? 1) 2) 3) 1) 2) A B 3) 4) C D 18. A student needs to increase the resistance in a circuit. All that is available for this task is a wide variety of wires of different lengths and thicknesses. To obtain the maximum resistance, the student should replace the wire with one that is 1) shortest and thickest 3) longest and thickest 2) shortest and thinnest 4) longest and thinnest 4) 20. What is the resistance at 20.ºC of a 2.0-meter length of tungsten wire with a cross-sectional area of 7.9 × 10–7 meter2? 1) 5.7 × 10–1 Þ 2) 1.4 × 10–1 Þ 3) 7.1 × 10–2 Þ 4) 4.0 × 10–2 Þ 21. A metal wire has length L and cross-sectional area A. The resistance of the wire is directly proportional to 1) L A 2) L × A 3) A L 4) L + A 22. Aluminum, copper, gold, and nichrome wires of equal lengths of 1.0 × 10–1 meter and equal cross-sectional areas of 2.5 × 10–6 meter2 are at 20. °C. Which wire has the greatest electrical resistance? 1) aluminum 3) gold 2) copper 4) nichrome RESISTANCE IN WIRES NAME:____________________ Reference Tables RESISTANCE IN WIRES NAME:____________________ Reference Tables Answer Key [New Exam] 1. 4 2. 1 3. 2 4. 1 5. 1 6. 2 7. 1 8. 2 9. 1 10. 2 11. 3 12. 2 13. 1 14. 3 15. 3 16. 4 17. 4 18. 4 19. 3 20. 2 21. 1 22. 4