Microsoft Word - 12Explore.doc
advertisement
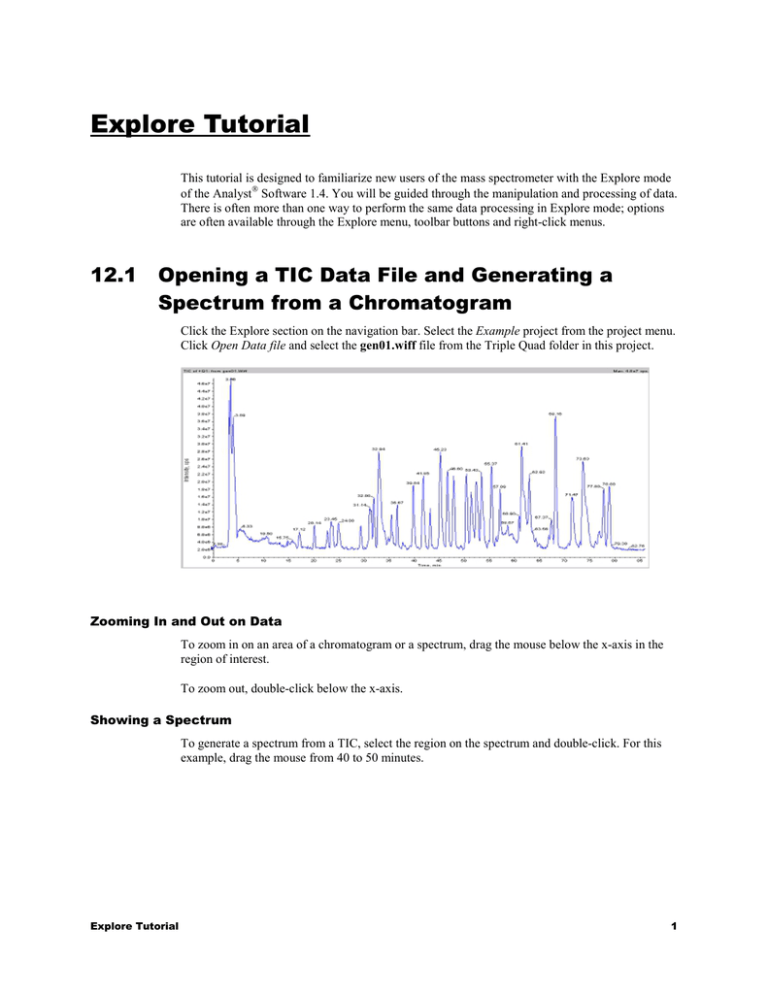
Explore Tutorial This tutorial is designed to familiarize new users of the mass spectrometer with the Explore mode of the Analyst Software 1.4. You will be guided through the manipulation and processing of data. There is often more than one way to perform the same data processing in Explore mode; options are often available through the Explore menu, toolbar buttons and right-click menus. 12.1 Opening a TIC Data File and Generating a Spectrum from a Chromatogram Click the Explore section on the navigation bar. Select the Example project from the project menu. Click Open Data file and select the gen01.wiff file from the Triple Quad folder in this project. Zooming In and Out on Data To zoom in on an area of a chromatogram or a spectrum, drag the mouse below the x-axis in the region of interest. To zoom out, double-click below the x-axis. Showing a Spectrum To generate a spectrum from a TIC, select the region on the spectrum and double-click. For this example, drag the mouse from 40 to 50 minutes. Explore Tutorial 1 Alternatively, you can select a region, right-click and select Show Spectrum from the menu. 12.2 Manipulating Panes Within a Window of Explore Once you have opened a spectrum, there will be two panes in the window. The Pane Toolbar contains the buttons that are used for operations between two (or more) panes in a data window. These operations are Move Pane, Delete Pane, Lock Pane, Hide Pane, Show Pane and Tile Pane. These tools are also all available as menu commands from the Window menu. Explore Tutorial 2 Moving Panes Highlight a second area of the TIC around the peak at 46.6 minutes and double-click to generate a second spectrum. To move panes, click the Move Pane button , it will turn gray. The cursor changes to a cross with arrows when the mouse is moved to the edge of the active pane. Next, select the pane to be moved by clicking on it, it will now have a blue border. Move the mouse to the edge of the active pane. When the cursor change to the cross shape, hold the left mouse button down. As you move the cursor away from the bottom pane, a gray box will appear. Move the mouse to move the gray box to the new location for the pane. Release the mouse button to drop the pane into place. Explore Tutorial 3 Try selecting the middle pane, clicking the cross on the border of the pane, then dragging the gray box to the right hand side of the bottom pane and release. The two panes should be side by side, as shown below: The Move Pane tool can be used to move panes between separate windows as well. Once you are done moving panes, click the truck button again to return to Deleting Panes When multiple panes are open within one window, they can be manipulated with the other Pane toolbar buttons. To delete a pane, select the pane and click the Delete Pane button. You can also right-click and select Delete Pane from the menu. Locking a Pane into Position To lock the position of a pane within a window, select the pane and click the LockPane button: Now this pane cannot be moved until the Lock Pane button is un-clicked. Hiding and Showing Panes To hide a pane, select the pane and click the Hide Pane button: This pane will now be moved to the background and all other panes remain shown. A pane can also be brought to the foreground by clicking on the Maximize Pane button: Explore Tutorial 4 This pane will become the only pane in view. To choose a pane and delete all other panes, select the pane of interest then select DeleteOthers.dll from the Scripts menu. To restore the original view and see all panes open in the window, click the Tile pane button: . Explore Tutorial 5 12.3 Subtracting, Overlaying and Adding Data in a Single Pane Multiple data panes can also be overlaid, subtracted or added. Subtracting Background from a Data Spectrum Delete all open spectral panes. Select a background area of the TIC in the 44.5-minute range. With the shift key depressed, select another background region around 46.0 minutes. Click the right mouse button and select Set Subtract Range. The 44.5 and 46.0-minute ranges selected should now turn green. Highlight another area around the 45.23-minute peak and double-click to bring up this spectrum pane. A spectrum with the 44.5 and 46.0-minute regions subtracted appears. To clear the subtraction ranges, select Clear Subtract Range from the right mouse button menu and the previously selected green subtract ranges disappear. Explore Tutorial 6 An alternative method for subtracting the background away from a data spectrum is to first open the two spectra to be subtracted. Click the blue selected range and drag it over to the peak at 46.5 minutes. An un-subtracted spectrum now appears. Highlight another background area around 46.0minute peak and double-click this region to generate a spectrum pane of the background. Select the bottom pane containing the spectra for the peak at 46.50 minutes and click the Subtract button. Select the middle pane containing the spectra for the background. The spectrum for the background is now subtracted from the bottom pane containing the spectrum for the 46.50-minute peak. Under the Edit menu, select Undo to undo the subtraction. Move the background blue selected region over to the peak at 43 minutes to produce two data spectra. For more information about background subtraction, please refer to the online help. Overlaying Two Data Panes Highlight the bottom pane in the window. Click the Overlay pane button then click the middle pane (with the spectrum). Explore Tutorial 7 The middle pane’s spectrum is now overlaid on the bottom pane, with the overlaid data displayed in red. The result of the operation is a single pane containing two sets of data with one data set active (The program labels the active set with the peak masses). To switch between the overlaid spectra, click the Cycle Overlays button. This will change which set of peaks are active and labeled. Click Remove Overlays to delete the inactive overlay. Remove the overlay with the 823 spectrum active and labeled. Summing Two Data Panes To sum the two data panes, click one spectrum, click the Add Data button, then click the other data pane. The result is a data pane containing the sum of both spectra. Select Undo from the Edit menu to undo this operation. Explore Tutorial 8 12.4 Linking Two Spectrum Panes Together Two panes can be linked together such that the scale of the x-axis in both is the same (but only if the panes contain the same type of data). When two panes are linked, zooming in on a region of one spectrum will simultaneously zoom the same region in the other spectrum. This is useful when comparing two spectra. Click one of the data panes, click the Link Panes button and click the second data pane. These panes are now linked. Try zooming in on one pane by dragging below the x-axis. The second pane should also zoom. To link more than two panes together, link the first two panes. Then click Link Panes button again and click on the third pane, and so on. Removing a Link To remove links, select the Remove Pane Linking button and click any linked pane. Deleting a linked pane will also remove the link. Explore Tutorial 9 12.5 Extracting Ions from a Chromatogram When looking for specific ions in a chromatogram, it is useful to generate Extracted Ion Chromatograms (XICs) of the ions of interest. In an XIC, the intensity of an ion is plotted as a function of time. With the gen01.wiff data file opened, right-click and select Extract Ions. (Alternatively, click the Extract Using Dialog button.) Type in the Start and Stop mass of the ion of interest. This range should reflect the mass accuracy of mass spectrometer. In this example, type in two ranges, 514-515 and 1035-1037 and click OK. Two new panes in the window appear showing the extracted ion chromatograms for the two ranges. Note: An XIC can also be generated from a spectrum. To obtain an XIC of an ion appearing in a single scan of a TIC, select the ion and right-click. If Extract Ions (Use Range) is chosen, an XIC will be generated using the mass range of the selection. If Extract Ions (Use Maximum) is selected, an XIC will be generated using the mass at the maximum of the selection. Explore Tutorial 10 12.6 Generating a Base Peak Chromatogram A base peak chromatogram is a useful tool to view the TIC of the MS data, to get an idea of the width of your chromatographic peaks. A Base Peak Chromatogram (BPC) depicts the intensity of the largest peak in a scan as a function of time or scan number. The display uses two colors, alternating each time the mass of the base peak changes. BPC is useful in instances where the total ion chromatogram (TIC) is dominated by noise so that there is a large offset and chromatographic peaks are hard to distinguish. Right-click the TIC of the MS data and select Show Base Peak Chromatogram. Alternatively, select the Base Peak Chromatogram button. The Base Peak Chromatogram Options box appears. Enter the mass range of the ions to be considered for the calculation and select OK. A base peak chromatogram now appears in a new pane at the bottom of the window. Explore Tutorial 11 Changing the Colors in a BPC To change the Alternative Colour, select Appearance Options under Settings in the Tools menu. The color of the alternative base peak can be changed in the Graph Colours and Fonts tab. The first color under Trace Color is the default color used for drawing your spectrum. To make the base peak all the same color, change the alternate color to be the same as the first color in the trace, in this case blue. Delete the Base Peak Chromatogram. Explore Tutorial 12 12.7 Scaling a Pane in the Y axis To expand a specific region of a TIC in the y dimension, click the Set Selection button and enter the time range to be expanded. In this example, enter the time window from 15-25 minutes. Click OK to close the dialog and make the selection in the TIC/ Next, click the Expand Selection By button and enter an expansion factor. Use a factor of 4 in this example. Click OK to expand the data. Only the selected region is expanded. A double-headed arrow is shown in the plot, at the location of the expansion. Removing an Expansion Click the Clear Ranges button to return the expanded region to normal. Explore Tutorial 13 12.8 Adding Captions and User Text to a Pane There are two types of text you may add to a pane, captions and user text. • Use a caption when you want to label a peak. The caption maintains its position relative to the peak. • Use User text when you want to annotate a spectrum. User text maintains its position relative to the pane. On the TIC of the gen01.wiff data file and zoom in on the region between 15-20 minutes. With the mouse cursor on the graph near the peak at 17 minutes, right-click and select Add Caption. Enter the words “Caption Text”. Next, with the mouse cursor in the top left corner of the pane, rightclick and select Add User Text and type in “User Text”. Double-click the X and Y-axes of the window to rescale the chromatogram. The “User Text” remains in the same position in the window and the “Caption Text” remains in the same position relative to the peak. Both captions and user text can be moved by clicking and dragging to a new location. Editing Text in a Pane If you right-click exactly on the user text or a caption, a right-click menu appears where you can choose to edit or delete the text. If you choose Edit, it will open up an editor and you can change the text as desired. Explore Tutorial 14 If you click Font in the editor, the program will open up a Font editor where you can change the size and color of the text. Default fonts for User Text and Captions can be set on the Graph Colors and Fonts tab of Appearance Option window (Tools > Settings > Appearance Options). Explore Tutorial 15 12.9 Showing File Information for a Data File Information about the acquisition method for every data file can be viewed using the File Information options. To control what is displayed in File Information, access the File Information Options; select the Appearance Options from the Tools > Settings menu. Click the TIC of the open data file, right-click and select Show File Information. Alternatively, you can click the Show File Info button. Explore Tutorial 16 The program will display the file information in a pane below the data. Creating an Acquisition Method from an Acquired Data file You can create an acquisition method from the file information for a data file. Once the file information is shown, right-click the pane and select Save Acquisition Method… This will automatically build a new acquisition method, similar to what was used to collect the original data file. This new acquisition method can now be named and saved. Explore Tutorial 17 12.10 Contour Plots A Contour Plot graph is a color-coded plot of a complete data set. Contour Plot is a postacquisition tool that does not function in a real-time scan acquisition. In a Contour Plot of a Total Ion Chromatogram (TIC), the x-axis represents retention time or scan, the y-axis represents mass, and the color represents the intensity of the data at that point. In a Contour Plot of a Total Wavelength Chromatogram (TWC), the y-axis represents wavelength, and the color represents absorbance. For both types of displays, and for immediate comparison, the x-axis spacing initially is the same as the graph pane. You can define colors to provide a contrast that is most useful to you. Contour Plot supports the following WIFF scan types: Q1 Scan, Q3 Scan, Product Ion, Precursor Ion, Neutral Loss, TOF MS, TOF Product, EMS Scan, EMC Scan, EPI Scan, ER Scan, and Agilent DAD. Displaying the Contour Plot Pane Click the TIC of the gen01.wiff data file and zoom in on the region of the spectrum you wish to examine. Right-click and select Show Contour Plot or click the Show Contour Plot button. The program displays the contour plot below the TIC. Contour Plot’s cross-hair pointer displays the x-axis and y-axis values for the current position of the pointer. The display of this information allows you to accurately select an area of the Contour Plot for closer examination. Right-click the contour plot and select Show Cross-Hair. The crosshair pointer appears only when the mouse is within the boundaries of the Contour Plot graph. Right-click and select Hide Cross-Hair to remove. Explore Tutorial 18 The third axis in Contour Plot, color, represents either intensity or wavelength. You can change the high and low intensity or wavelength values in Contour Plot using the control triangles on the color bar above the Contour Plot. The actual values are based on a percentage of the maximum intensity or wavelength within the selected area displayed in the Contour Plot. The value is displayed in the top right corner of the Contour Plot pane. Slide the left and right triangles to automatically adjust the color range. You can zoom in on part of a Contour Plot graph to view a particular peak or area in greater detail. You can zoom repeatedly to view smaller areas. Using the pointer, drag a box around the area of the Contour Plot graph you want to examine more closely. Right-click in the Contour Plot pane and select Zoom to selection. To zoom in on the x or y-axis: Position the pointer to the left of the y-axis or under the x-axis. Drag away horizontally or vertically to expand area of interest. Displaying Other Graphs from Contour Plots A data spectrum or an XIC can be generated from a Contour Plot. Using the mouse, drag a region of the contour plot that you wish to display. Right-click and select Show Spectrum. If you want to generate an XIC of a specific ion, select the peak by dragging and right-click to select Show XIC. If the Contour Plot is generated from data acquired by a diode array detector (DAD), then a spectrum of a selected region can be displayed by selecting Show DAD Spectrum. As with MS data, an XWC (extracted wavelength chromatogram) can also be generated by selecting a peak and choosing Extract Wavelengths (Use Range) or Extract Wavelengths (Use Maximum) from the right-click menu. Changing Contour Plot Colors Changing Contour Plot colors can provide better contrast and display data specifications according to your precise needs. For example, setting the intensity/wavelength and changing the color of the values for Below Low Data and Above High Data eliminates background noise in Contour Plot. Note: There are five buttons that control color in Contour Plot. Each displays its name when the cursor remains over the button. This way you can be sure you are changing the correct feature. In addition, the Below Low Data and Above High Data buttons shrink and expand on the color bar if you move the slider controls. Once you have changed the contour plot colors, these now become the default colors for all subsequent graphs. Above the graph in the Contour Plot pane, click the No Data button. The Color dialog box is now shown. On the Color palette, click the desired color, and then click OK. By using the Define Custom Colors palette, you can create customized colors for use in the Contour Plot. The no data section of the graph displays the new color. Above the graph in the Contour Plot pane (in the color bar), click the Low (or High) Data button above the slider. Low value is on the left; high value is on the right. The Color dialog box appears. Click the desired color, and then click OK. The low or high value you selected displays in the new color. Contour Plot, and the Contour Plot graph color bar, automatically shade between the low and high colors. Explore Tutorial 19 12.11 The IDA Explorer The Information Dependent Acquisition (IDA) viewer is used to display data acquired through an IDA method. (The IDA Explorer can be turned off and on by going to the IDA Explorer tab in the Appearance Options, under Tools > Settings. Columns present in the List View can be defined under this tab as well.) Click Open Data file and select the nanoflow 100fmol BSA IDA.wiff file from the Tutorial Data project. The leftmost portion of the viewer displays the masses on which a product ion scan was performed. This area allows you to examine the mass, intensity, time and collision energy of ions on which product ion scans were performed. You can view these in either list view or tree view. In list view, the list can be sorted by double-clicking on any column header. You can customize what columns you want to view in list view in Tools > Settings > Appearance Options > IDA Explorer. On the right, the viewer is split into four panes. The top left pane displays the survey TIC data. The bottom left pane shows the XIC of the mass. The top and bottom right panes show the survey and product scans, respectively. The IDA viewer lists all the masses on which Enhanced Product Ion spectra or Enhanced Resolution spectra were performed. Clicking on a mass in the list or tree view displays plots relevant to that mass. You can view the survey spectrum from which the mass was identified and the product spectrum of that mass. It also displays the TIC of the survey scan and the XIC for each mass. Explore Tutorial 20 Note: Brackets around a mass indicate that the mass is “merged”. A merged mass is contiguous across a number of cycles. When a merged mass is displayed, it indicates an averaged spectrum, containing the average of all contiguous spectra. To revert to the normal TIC view, click the Tile Panes button at the top of the IDA viewer. A single active pane can be opened into a separate window by clicking on the Maximize Pane button. For example, when a nice MS/MS spectrum is found, you can open it in a new pane and use it with BioAnalyst™ Software’s Sequence Peptide window. The other buttons on this pane – Maximize Pane and Tile Panes -- can be used to change the appearance of the IDA viewer. Explore Tutorial 21