Rectifier Circuits
advertisement

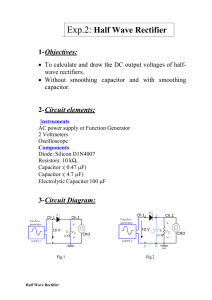
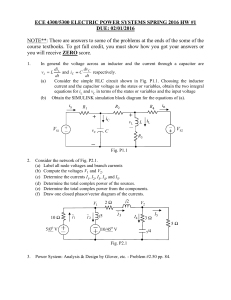
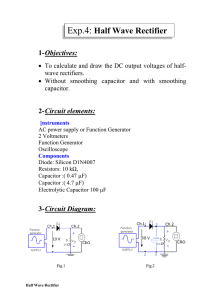
Engineering Tripos Part IIA Paper 3B3 : Switch -mode Electronics Examples Paper 3B3/1 - Rectifier Circuits Diode circuits 1. (a) Find the average value of the current in the 100 Ω load resistor in the bridge rectifier circuit of Fig. 1 assuming ideal diodes. (b) Repeat the calculation assuming a forward voltage drop of 0.8 V (independent of current) in a conducting diode. Fig. 1. 2. (a) Find the average value of the voltage across the resistor R in the three-phase rectifier circuit of Fig. 2 assuming ideal diodes. (b) Find the peak-to-peak value of the ripple voltage across R. (c) A three-phase bridge rectifier circuit uses six diodes and the same (star-connected) voltage source. Find the average and peak-to-peak ripple voltage across the load resistor. (e) What is the diode voltage rating in each case? Fig. 2. Engineering Tripos Part IIA Paper 3B3 : Switch -mode Electronics Capacitor Smoothing - DC power supplies 3. (a) Fig. 3(a) shows a single-phase bridge rectifier with a smoothing capacitor. Estimate the average current in the load resistor and the peak-to-peak ripple voltage across it under the following assumptions: Ideal diodes; The capacitor voltage VC decays almost linearly from its peak value in each half-period; The capacitor discharges for 10 ms in each half-period. Fig. 3(a) (b) Fig. 3(b) shows the angle θ for which each pair of diodes conducts in each half-period. Estimate the value of θ to the nearest 5 degrees. Fig. 3(b) 4.* Fig. 4 shows a regulated power supply delivering 2 A at 13.5 V into a load represented by a resistor R. The bridge rectifier must deliver a voltage to the 4700µF reservoir capacitor which is at least 2 V above the regulator output voltage for the regulator to function properly. Assume that the current I0, from the regulator to the negative power supply line, is very small. Engineering Tripos Part IIA Paper 3B3 : Switch -mode Electronics (a) Assuming a reasonable value for the voltage drop across the conducting diodes, and that their conduction period is small compared to the supply period, estimate the rms voltage which must be specified for the a.c. supply V. (b) What is the peak inverse voltage appearing across each diode ? (c) If the regulator data sheet gives its ripple rejection ratio as typically 65 dB, estimate the peak-to-peak ripple voltage at the load R. Fig. 4. Inductors and Inductor-Capacitor smoothing 5. (a) A half wave rectifier is used to give a simple power reduction in a 240V electric kettle. Explain using a sketch of the voltage and current in the element why the power reduction is likely to be less than 50%. 6. (a) A single phase bridge rectifier supplies a 1kW washing machine motor drive. The smoothing capacitance is 6.8 mF and the smoothing inductance is 5 mH. Estimate the ripple at full load (24Ω equivalent load), when the ac supply is 220 V. (b) What is the dc link voltage under full load? (c) What is the % voltage regulation no load to full load? Engineering Tripos Part IIA Paper 3B3 : Switch -mode Electronics 7.* (a) A single phase bridge rectifier is used to provide the dc supply in a 240V, 11 W compact fluorescent lamp. Give three reasons why this is a good choice. (b) The fluorescent tube is supplied by a resonant inverter as shown in Fig. 5. The inverter operates at 40 kHz and takes sine half cycles of current from the dc link The average current drawn by the load is found to be 44 mA . Estimate the high frequency ripple current in the 2.2µF smoothing capacitor, stating any assumptions. (Hint: Use the half wave Fourier series for current). (c) Give two reasons why the high frequency ripple current in the smoothing capacitor should be minimised. (2008 Q1 Parts a, c and d) Fig. 5 Answers 1. (a) 81 mA (b) 66 mA 2. (a) 281 V (b) 170 V (c) 561 V; 79 V (d) 588 V, 588 V 3. (a) 0.16 A; 1.7 V (b) 4. (a) 15.4 V (b) 20.76 V (c) 2.4 mV 6. (a) 9.84V (b) 198 V (c) 36% 7. (b) 5.5mA 23° 5. P. R. Palmer October, 2010