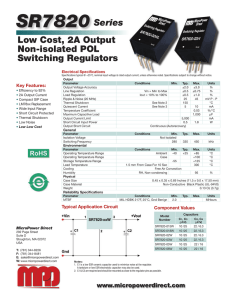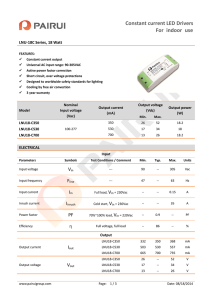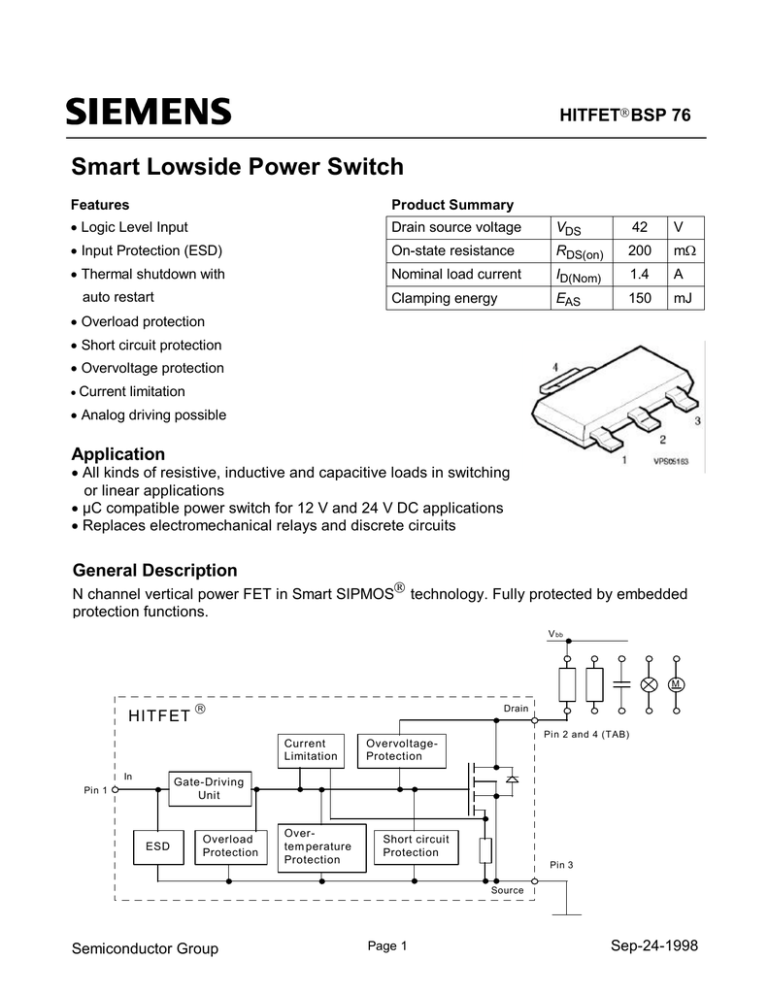
HITFET BSP 76
Smart Lowside Power Switch
Features
Product Summary
•Logic Level Input
Drain source voltage
VDS
42
V
•Input Protection (ESD)
On-state resistance
RDS(on)
200
mΩ
•Thermal shutdown with
Nominal load current
ID(Nom)
1.4
A
Clamping energy
EAS
150
mJ
auto restart
•Overload protection
•Short circuit protection
•Overvoltage protection
•Current limitation
•Analog driving possible
Application
•All kinds of resistive, inductive and capacitive loads in switching
or linear applications
•µC compatible power switch for 12 V and 24 V DC applications
•Replaces electromechanical relays and discrete circuits
General Description
N channel vertical power FET in Smart SIPMOS technology. Fully protected by embedded
protection functions.
V bb
M
HITFET
Drain
Current
Limitation
In
Pin 2 and 4 (TAB)
OvervoltageProtection
Gate-Driving
Unit
Pin 1
ESD
Overload
Protection
Overtem perature
Protection
Short circuit
Protection
Pin 3
Source
Semiconductor Group
Page 1
Sep-24-1998
Maximum Ratings at Tj = 25°C, unless otherwise specified
Parameter
Symbol
Drain source voltage
VDS
42
Drain source voltage for short circuit protection
Continuous input voltage
VDS(SC)
42
VIN
-0.2 ... +10
Peak input voltage (IIN ≤2 mA)
VIN(peak)
-0.2 ... VDS
Operating temperature
Tj
-40 ...+150
Storage temperature
Tstg
-55 ... +150
Power dissipation
Ptot
3.8
W
TC = 85 °C
Unclamped single pulse inductive energy 1)
EAS
150
mJ
VLD
50
V
VESD
2
kV
Load dump protection VLoadDump2) = VA + VS
VIN = 0 and 10 V, td = 400 ms, RI = 2 Ω,
RL = 9 Ω, VA = 13.5 V
Electrostatic discharge voltage (Human Body Model)
Value
Unit
V
°C
according to MIL STD 883D, method 3015.7 and
EOS/ESD assn. standard S5.1 - 1993
DIN humidity category, DIN 40 040
E
IEC climatic category; DIN IEC 68-1
40/150/56
Thermal resistance
junction - ambient:
RthJA
K/W
@ min. footprint
125
@ 6 cm2 cooling area 3)
junction-soldering point:
72
17
RthJS
K/W
1 Not tested, specified by design.
2V
Loaddump is setup without the DUT connected to the generator per ISO 7637-1 and DIN 40839
3 Device on 50mm*50mm*1.5mm epoxy PCB FR4 with 6cm2 (one layer, 70µm thick) copper area for drain
connection. PCB mounted vertical without blown air.
Semiconductor Group
Page 2
Sep-24-1998
Electrical Characteristics
Parameter
Symbol
at Tj = 25°C, unless otherwise specified
Values
Unit
min.
typ.
max.
42
-
55
V
-
1.5
10
µA
Characteristics
Drain source clamp voltage
VDS(AZ)
Tj = - 40 ...+ 150, ID = 10 mA
Off-state drain current Tj = -40 ... +150°C
IDSS
VDS = 32 V, VIN = 0 V
Input threshold voltage
VIN(th)
V
ID = 0.15 mA, Tj = 25 °C
1.3
1.7
2.2
ID = 0.15 mA, Tj = 150 °C
On state input current
IIN(on)
0.9
-
10
30
On-state resistance
RDS(on)
µA
mΩ
ID = 1.4 A, VIN = 5 V, Tj = 25 °C
-
190
240
ID = 1.4 A, VIN = 5 V, Tj = 150 °C
-
350
480
ID = 1.4 A, VIN = 10 V, Tj = 25 °C
-
150
200
ID = 1.4 A, VIN = 10 V, Tj = 150 °C
Nominal load current
1.4
280
-
400
-
A
5
7.5
10
A
On-state resistance
RDS(on)
ID(Nom)
VDS = 0.5 V, Tj < 150°C, VIN = 10 V,
TA = 85 °C
Current limit (active if VDS>2.5 V)1)
ID(lim)
VIN = 10 V, VDS = 12 V, tm = 200 µs
1Device switched on into existing short circuit (see diagram Determination of I
D(lim) . Dependant on the
application, these values might be exceeded for max. 50 µs in case of short circuit occurs while the
device is on condition
Semiconductor Group
Page 3
Sep-24-1998
Electrical Characteristics
Parameter
Symbol
at Tj = 25°C, unless otherwise specified
Values
Unit
min.
typ.
max.
ton
-
45
150
toff
-
60
150
-dVDS/dt on
-
0.4
1
dVDS/dt off
-
0.6
1
Dynamic Characteristics
Turn-on time
V IN to 90% I D:
µs
RL = 4.7 Ω, VIN = 0 to 10 V, V bb = 12 V
Turn-off time
V IN to 10% I D:
RL = 4.7 Ω, VIN = 10 to 0 V, V bb = 12 V
Slew rate on
70 to 50% V bb:
V/µs
RL = 4.7 Ω, VIN = 0 to 10 V, V bb = 12 V
Slew rate off
50 to 70% V bb:
RL = 4.7 Ω, VIN = 10 to 0 V, V bb = 12 V
Protection Functions
Thermal overload trip temperature
Tjt
150
165
-
°C
Thermal hysteresis
∆Tjt
-
10
-
K
Input current protection mode
IIN(Prot)
-
140
300
µA
Unclamped single pulse inductive energy 1)
EAS
150
-
-
mJ
VSD
-
1
-
V
ID = 1.4 A, Tj = 25 °C, Vbb = 12 V
Inverse Diode
Inverse diode forward voltage
IF = 7 A, tm = 250 µs, VIN = 0 V,
tP = 300 µs
1 Not tested, specified by design.
Semiconductor Group
Page 4
Sep-24-1998
Block diagram
Inductive and overvoltage
output clamp
Terms
RL
D
V
Z
2
IIN
1
D
IN
ID
VDS Vbb
HITFET
S
S
3
VIN
HITFET
Short circuit behaviour
Input circuit (ESD protection)
V
IN
Gate Drive
Input
I
I
IN
t
t
D
Source/
Ground
T
t
j
Thermal
hysteresis
t
Semiconductor Group
Page 5
Sep-24-1998
Maximum allowable power dissipation
On-state resistance
Ptot = f(TS ) resp.
RON = f(Tj ); ID=1.4A; VIN =10V
Ptot = f(TA ) @ RthJA =72 K/W
10
500
mΩ
W
8
Ptot
RDS(on)
7
350
6
300
5
250
4
200
3
150
2
max.
400
max.
100
6cm2
1
0
-75
typ.
50
-50
-25
0
25
50
75
100
°C
0
-50
150
-25
0
25
50
75
100
125
T S ;TA
°C
On-state resistance
Typ. input threshold voltage
RON = f(Tj ); ID= 1.4A; VIN=5V
VIN(th) = f(Tj); ID = 0.15 mA; VDS = 12V
500
175
Tj
2.0
max.
mΩ
V
400
1.6
RDS(on)
VIN(th)
typ.
350
1.4
300
1.2
250
1.0
200
0.8
150
0.6
100
0.4
50
0.2
0
-50
-25
0
25
50
75
100
125
°C
0.0
-50
175
Tj
Semiconductor Group
-25
0
25
50
75
100
°C
150
Tj
Page 6
Sep-24-1998
Typ. transfer characteristics
Typ. short circuit current
ID=f(VIN ); VDS=12V; TJstart=25°C
ID(lim) = f(Tj); VDS =12V
Parameter: VIN
10
8
A
A
8
ID
ID(lim)
6
7
5
6
Vin=10V
5
4
5V
4
3
3
2
2
1
0
0
1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
V
0
-50
10
-25
0
25
50
75
100
125
VIN
°C
175
Tj
Typ. output characteristics
Typ. off-state drain current
ID=f(VDS ); TJstart=25°C
IDSS = f(Tj)
Parameter: VIN
10
11
Vin=10V
A
µA
7V
9
8
ID
max.
6V
7
IDSS
5V
8
7
6
4V
6
5
5
4
4
3
3
3V
2
2
1
0
0.0
typ.
1
1.0
2.0
3.0
4.0
V
0
-50
6.0
VDS
Semiconductor Group
-25
0
25
50
75
100
125
°C
175
Tj
Page 7
Sep-24-1998
Typ. overload current
Typ. transient thermal impedance
ID(lim) = f(t), Vbb =12 V, no heatsink
ZthJC =f(tp) @ 6 cm2 cooling area
Parameter: Tjstart
Parameter: D=tp /T
10 2
12
K/W
D=0.5
A
-40°C
ID(lim)
ZthJA
8
0.2
10 1
0.1
25°C
0.05
85°C
10 0
6
0.02
0.01
150°C
4
10
-1
10
-2
2
Single pulse
0
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
ms
4.0
10
t
-7
10
-6
10
-5
10
-4
10
-3
10
-2
10
-1
10
0
10
1
10
2
s 10
4
tp
Determination of ID(lim)
ID(lim) = f(t); tm = 200µs
Parameter: TJstart
12
A
ID(lim)
-40°C
8
25°C
85°C
6
4
150°C
2
0
0.00
0.10
0.20
0.30
0.40
ms
0.55
t
Semiconductor Group
Page 8
Sep-24-1998
Package and ordering code
all dimensions in mm
Ordering code: Q67060-S7201-A2
Edition 7.97
Published by Siemens AG,
Bereich Halbleiter Vetrieb,
Werbung, Balanstraße 73,
81541 München
© Siemens AG 1997
All Rights Reserved.
Attention please!
As far as patents or other rights of third parties are concerned, liability is only assumed for components,
not for applications, processes and circuits implemented within components or assemblies.
The information describes a type of component and shall not be considered as warranted characteristics.
Terms of delivery and rights to change design reserved.
For questions on technology, delivery and prices please contact the Semiconductor Group Offices in Germany
or the Siemens Companies and Representatives worldwide (see address list).
Due to technical requirements components may contain dangerous substances. For information on the types
in question please contact your nearest Siemens Office, Semiconductor Group.
Siemens AG is an approved CECC manufacturer.
Packing
Please use the recycling operators known to you. We can also help you - get in touch with your nearest sales
office. By agreement we will take packing material back, if it is sorted. You must bear the costs of transport.
For packing material that is returned to us unsorted or which we are not obliged to accept, we shall have to
invoice you for any costs incurred.
Components used in life-support devices or systems must be expressly authorized for such purpose!
Critical components1 of the Semiconductor Group of Siemens AG, may only be used in life-support devices or
systems2 with the express written approval of the Semiconductor Group of Siemens AG.
1)A critical component is a component used in a life-support device or system whose failure can reasonably be
expected to cause the failure of that life-support device or system, or to affect its safety or effectiveness of
that device or system.
2)Life support devices or systems are intended (a) to be implanted in the human body, or (b) to support and/or
maintain and sustain and/or protecf human life. If they fail, it is reasonable to assume that the health of the
Page 9
Sep-24-1998
Semiconductor Group