Ampere`s Law - IIS Cremona
advertisement

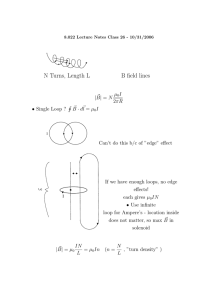
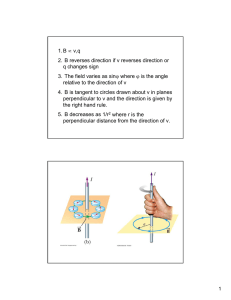
Ampere’s Law Ampere’s Law Level 5 Physics January 2013 Material adapted from MIT 8.02 course notes Ampere’s Law Theory Review Biot-Savart Law Biot-Savart Law ~ The magnetic field contribution, d B, from a current source, Id~s, at a field point P a distance r in the direction of r̂ is given by ~ = dB µ0 Id~s × r̂ 4π r 2 where µ0 is the permeability of free space constant with value µ0 = 4π × 10−7 T · m/A Ampere’s Law Theory Review Magnetic Field for Current-Carrying Wire Infinite Length Wire The magnitude of the magnetic field a distance a away from a wire with current I is B= µ0 I 2πa The magnetic field line direction is given by a right hand rule. Ampere’s Law Theory Ampere Circular Closed Loop Consider a circular closed loop around an infinitely long, straight, current carrying wire as shown below. Ampere’s Law Theory Ampere Circular Closed Loop Consider a circular closed loop around an infinitely long, straight, current carrying wire as shown below. An important H law discovered by Ampere in 1826 results from ~ · d~s along a closed path such as this (called an calculating B Amperian loop). Ampere’s Law Theory Ampere Ampere’s Law - Special Case H ~ · d~s around a circular loop with Calculating the line integral of B radius r yields I I µ0 I ~ · d~s = B ∗ ds 2πr I µ0 I = ds 2πr µ0 I ∗ 2πr = 2πr = µ0 I Ampere’s Law Theory Ampere Ampere’s Law - General Case The more general form of Ampere’s Law involves integrating over an arbitrary closed loop such as the one below. Ampere’s Law Theory Ampere Ampere’s Law - General Case The more general form of Ampere’s Law involves integrating over an arbitrary closed loop such as the one below. It H can be shown with a proof involving cylindrical coordinates that ~ · d~s = µ0 I for this general case as well. B Ampere’s Law Theory Ampere Ampere’s Law Ampere’s Law A closed loop around a current carrying wire relates the surrounding magnetic field to the current by H ~ · d~s = µ0 Ienclosed B where Ienclosed is the current encircled by the loop. Ampere’s Law Theory Ampere Ampere’s Law Ampere’s Law A closed loop around a current carrying wire relates the surrounding magnetic field to the current by H ~ · d~s = µ0 Ienclosed B where Ienclosed is the current encircled by the loop. Ampere’s Law can be used to easily calculate the magnetic field in certain situations when an appropriate Amperian loop is chosen. Typically a good choice allows the magnetic field magnitude to be treated as a constant or for the integral to be evaluated in sections. Biot-Savart’s Law can be used in other situations to find the magnetic field. Ampere’s Law Questions Concept Questions Toroid Central Region What is the best description of the magnetic field in the central circular region of a toroid? 1 Negative 2 Zero 3 Positive Ampere’s Law Questions Concept Questions Toroid Central Region What is the best description of the magnetic field in the central circular region of a toroid? 1 Negative 2 Zero 3 Positive Correct Answer: 2 (There is symmetry so Ampere’s Law can be used. Since Ienclosed = 0, if an Amperian loop is drawn in the central region, B = 0.) Ampere’s Law Questions Concept Questions Toroid Outer Region What is the best description of the magnetic field in the region surrounding a toroid? 1 Negative 2 Zero 3 Positive Ampere’s Law Questions Concept Questions Toroid Outer Region What is the best description of the magnetic field in the region surrounding a toroid? 1 Negative 2 Zero 3 Positive Correct Answer: 2 (Ienclosed = 0 since Ienclosed is the net current encircled by the loop.) Ampere’s Law Questions Concept Questions Coaxial Cable A cross-section of a coaxial cable is shown below. The center of the cable has a 1.0A total current going into the page. The outer region has a uniform current density of 1.0A/m2 pointing out of the page. At what distance in meters from the center of the cable is the magnetic field equal to zero? 3 1/3 4π ) 1 r = (1 + 2 r= 3 r= 4 The magnetic field is never zero 1 2π q +1 1 π +1 Ampere’s Law Questions Concept Questions Coaxial Cable, cont’d. Correct Answer: 3 (The magnetic field is zero if the enclosed current is zero, according to Ampere’s Law. Solving the equation π(r 2 − 1)(1) − 1 = 0 for r yields the answer.) Ampere’s Law Questions Concept Questions One Current Loop Consider a small segment of a circular current loop as shown below. The current flows counterclockwise. What is the direction of the force on this segment? 1 Left 2 Right 3 Into page 4 Out of page Ampere’s Law Questions Concept Questions One Current Loop Consider a small segment of a circular current loop as shown below. The current flows counterclockwise. What is the direction of the force on this segment? 1 Left 2 Right 3 Into page 4 Out of page Correct Answer: 2 (The rest of the loop generates a magnetic field at the segment that points out of the page.)