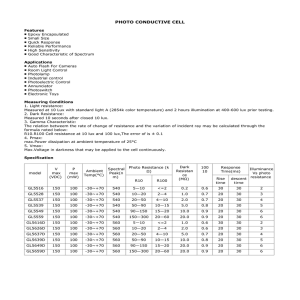
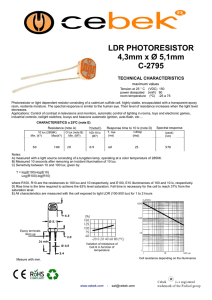
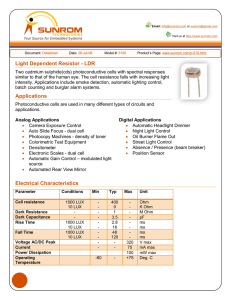
Common Electrical Terms, Abbreviations and Definitions lumen (lm
advertisement

Common Electrical Terms, Abbreviations and Definitions lumen (lm) Practical Definition: This is a measurement of how bright a light source is rated. Really not a good practical measurement. An example is when you purchase a 100-watt light bulb. Watt is the power consumed, not a measurement of light, but we all know that a 100-watt light bulb is pretty bright. Used to compare two light sources to one another. See Lux definition below. Technical Definition: The lumen (symbolized lm) is the International Unit of luminous flux. A unit of luminous flux equal to the light emitted in a unit solid angle by a uniform point source of one candela (see definition below) intensity. lux (lx) Practical Definition: Lux is the amount of light you actually see. One lux is equal to one lumen per square meter. It is the amount of light cast on a surface. This is the most practical measurement of light. See the chart below for examples: Illuminance 0.00005 lux 0.0001 lux 0.001 lux 0.01 lux 0.25 lux 1 lux 10 lux 50 lux 80 lux 400 lux 400 lux 1000 lux 32000 lux 100000 lux Abbreviation 50 µlx 100 µlx 1 mlx 10 mlx 250 mlx 1 lx 10 lx 50 lx 80 lx 400 lx 400 lx 1 klx 32 klx 100 klx Pronunciation 50 micro-lux 100 micro-lux 1 milli-lux 10 milli-lux 250 milli-lux 1 lux 10 lux 50 lux 80 lux 400 lux 400 lux 1 kilo-lux 32 kilo-lux 100 kilo-lux Example Starlight Moonless overcast night sky Moonless clear night sky Quarter Moon Full Moon on a clear night Moonlight at high altitude at tropical latitudes Candle at a distance of 1 ft Family living room Hallway/Toilet A brightly lit office Sunrise or sunset on a clear day Typical TV studio lighting Sunlight on an average day (min.) Sunlight on an average day (max.) Engineering Definition: The lux (symbol: lx) is the unit of illuminance and luminous emittance. It is used in photometry as a measure of the intensity of light, with wavelengths weighted according to the luminosity function, a standardized model of human brightness perception. It is used as a measure of the intensity of light. In English, "lux" is used in both singular and plural. 1 lux = 1 lumen/sq. meter. foot-candle (fc) Practical Definition: In practical applications, as when measuring room illumination, it is very difficult to measure illuminance more accurately than ±10%, and for many purposes it is quite sufficient to think of one foot-candle as about ten lux. Therefore, it is commonplace to simply state 1 fc = 10 lux. Technical Definition: One foot-candle ≈ 10.764 lux. The foot-candle (or lumen per square foot) is a non-SI unit of illuminance. It is obsolete but it is still in fairly common use in the United States, particularly in construction-related engineering and in building codes. Because lux and foot-candles are different units of the same quantity, it is perfectly valid to convert foot-candles to lux and vice versa. Common Electrical Terms, Abbreviations and Definitions…pg 2 The name "foot-candle" conveys "the illuminance cast on a surface by a one-candela source one foot away.” As natural as this sounds, this style of name is now frowned upon, because the dimensional formula for the unit is not foot · candela, but lumen/sq ft. Some sources do however note that the "lux" can be thought of as a "meter-candle" (i.e. the illuminance cast on a surface by a one-candela source one meter away). A source that is farther away provides less illumination than one that is close, so one lux is less illuminance than one foot-candle. Since illuminance follows the inverse-square law, and since one foot = 0.3048 m, one lux = 0.30482 foot-candle ≈ 1/10.764 footcandle. ampere (amp or A) Practical Definition: The ampere, in practice often shortened to amp, is a unit of electric current, or amount of electric charge per second. Technical Definition: The base unit of electric current in the International System of Units that is equal to a constant current which when maintained in two straight parallel conductors of infinite length and negligible circular sections one meter apart in a vacuum produces between the conductors a force equal to 2 × 10−7 newton per meter of length. ampere–hour (Amp-Hours or Ah) Practical Definition: A unit of measure to describe how long a battery will run. For example, a 12 Ah battery will run for 12 hours with a 1 amp load on it, or 6 hours with a 2 amp load on it, or 3 hours with a 4 amp load on it, and so on. Technical Definition: A unit quantity of electricity equal to the quantity carried past any point of a circuit in one hour by a steady current of one ampere. Light Emitting Diode (LED) Practical Definition: A very small light source used in electronics. Technical Definition: A semiconductor diode that emits light when a voltage is applied to it and that is used especially in electronic devices (as for an indicator light). watt (W) Practical Definition: A unit of power, often incorrectly associated with light output. 1 Watt = 1 Volt x 1 Amp Technical Definition: The watt (symbol: W) is the SI derived unit of power, equal to one joule of energy per second. That is, if 1 volt of potential difference is applied to a resistive load, and a current of 1 ampere flows, then 1 watt of power is dissipated. Common Electrical Terms, Abbreviations and Definitions…pg 3 volt (V) Practical Definition: Volt is used to quantify the electrical potential of an electrical source. See list below for common examples: Nominal voltages of familiar sources: • Nerve cell action potential: around 75 mV • Single-cell, rechargeable NiMH or NiCd battery: 1.2 V • Mercury battery: 1.355 V • Single-cell, non-rechargeable alkaline battery (e.g. AAA, AA, C and D cells): 1.5 V • Lithium polymer rechargeable battery: 3.75 V • Automobile electrical system: "12 V", about 11.8 V discharged, 12.8 V charged, and 13.814.4 V while charging (vehicle running). • Household mains electricity: 120 V in North America • Rapid transit third rail: 600 to 750 V • High speed train overhead power lines: 25 kV (kilo-volt) • High voltage electric power transmission lines: 110 kV (kilo-volt) • Lightning: Varies greatly, often around 100 MV (mega-volt) Technical Definition: The unit of electrical potential difference and electromotive force equal to the difference of potential between two points in a conducting wire carrying a constant current of one ampere when the power dissipated between these two points is equal to one watt and equivalent to the potential difference across a resistance of one ohm when one ampere is flowing through it Rated Power: the maximum amount of wattage (W) the solar panel is rated for Peak Power: the maximum amount of power in watts (W) the solar panel will produce Peak Power Voltage: the maximum amount of voltage (V) or power the solar panel will produce Peak Power Current: the maximum amount of current in amps (A) that the solar panel will produce Open Circuit Voltage: a short spike in voltage (V) that is not sustained over a period of time Short Circuit Current: a short spike in amps (A) that is not sustained over a period of time UV: (Ultra Violet) beyond the visible spectrum at its violet end -- used of radiation having a wavelength shorter than wavelengths of visible light and longer than those of X-rays