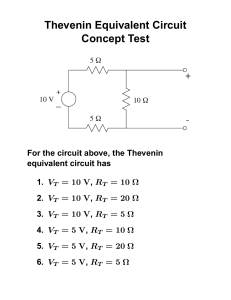
Thevenin`s Theorem For the following Circuit, determine the
advertisement

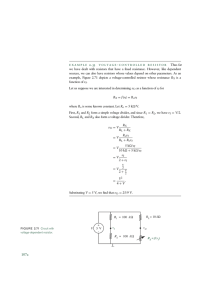
Thevenin’s Theorem For the following Circuit, determine the Thevenin Voltage and the Thevenin Resistance. Create a Thevenin Model then test three resistors for a load resistor to determine which one transfers maximum power from the source to the load. Thevenize the circuit at points A and B. Step 1: Remove the load resistor and determine the open circuit voltage at those nodes. [No current flows through the two 2K ohm resistors so they are not part of the voltage solution. The 1K ohm resistor in parallel with the source does not reduce the voltage at the output terminals and is therefore not involved in the solution. The remaining three resistors form a voltage divider across the source. The voltage of interest, is the voltage across the 4K ohm resistor.] V AB = 4K xV T 1K + 4K + 3K V AB = 4K 1 x16 = x16 = 8Volts 8K 2 The Thevenin Voltage is 8 volts. Step 2 is to determine the resistance looking into the circuit from the point of view of terminals A and B. The Sources will be replaced with their internal resistance for this C:\_ghw\Courses\ElecCir\Thevenin_revisit.doc gwalsh@northshore.edu step. The voltage source with therefore be replaced with a short circuit, a wire. The resulting resistor network can be reduced as shown: The three series resistors add up to 6K ohms and is the Thevenin resistor. The model is complete as shown: Trial and error exercises can now be calculated using the model in place the original circuit. The results for the load with be the same for the Thevenin Circuits as they would for the original circuit. of Test three load resistors and determine which one results in the maximum power delivered to the load. Connect the first to the model, determine total resistance, and total current, then calculate power dissipated by the load resistor. Repeat for the other two resistors. C:\_ghw\Courses\ElecCir\Thevenin_revisit.doc gwalsh@northshore.edu RT = RTH + RL IT = VTH RT PRL = I T RL 2 The table shows the results of calculations. The maximum power delivered to the load is when the load resistor is 6K ohms. The value matches the Thevenin resistor and proves the maximum power transfer theorem. The maximum power is transferred to the load when the load resistor is equal to the source resistance. RL 5K 6K 7K RT 11K 12K 13K IT .727mA .666mA .615mA PRL 2.64mW 2.66mW 2.65mW The curve for this data show the power peaking when RL=6K ohms: C:\_ghw\Courses\ElecCir\Thevenin_revisit.doc gwalsh@northshore.edu