1 PHYS 272 Practice Problems Note: For some problems
advertisement
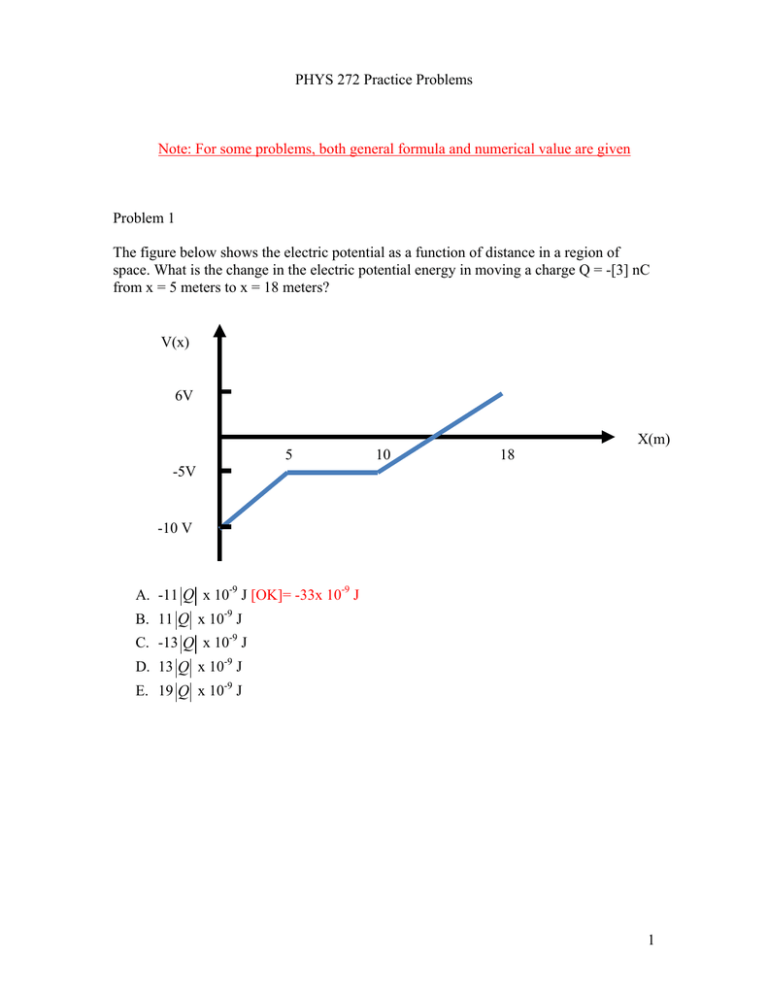
PHYS 272 Practice Problems Note: For some problems, both general formula and numerical value are given Problem 1 The figure below shows the electric potential as a function of distance in a region of space. What is the change in the electric potential energy in moving a charge Q = -[3] nC from x = 5 meters to x = 18 meters? V(x) 6V 5 10 18 X(m) -5V -10 V A. -11 Q x 10-9 J [OK]= -33x 10-9 J B. 11 Q x 10-9 J C. -13 Q x 10-9 J D. 13 Q x 10-9 J E. 19 Q x 10-9 J 1 Problem 2 A capacitor with plates separated by [d] 2 mm has one plate at a potential of 300 Volts and its other plate at a potential of [V2] 250 Volts. What is the magnitude of the electric field between the plates of the capacitor? A. B. C. D. E. (300-V2)x103 /[d] N/C [OK]= 25x103 N/C 2(300-V2)/d N/C (300-V2) N/C (300+V2)x103 /[d]N/C (300+V2)/[d] N/C Problem 3 A fully charged 100 µF (=10-4 F) capacitor has a potential difference across it of 9 Volts. It is then connected to a resistor of [R]10 Ω. How long will it take for the current through the resistor to decrease to 1/10 of its initial value? A. B. C. D. 2.3*[R] x 10-4 seconds [OK]= 2.3 x 10-3 seconds [R]/2.3x10-4 seconds [R] x 10-4 seconds 1/[R] x10-4 seconds Problem 4 A particular alnico (aluminum, cobalt, nickel, and iron bar magnet (magnet A) has a mass of 10 grams. It produces a magnetic field of magnitude [B] 6 x 10-5 T at a location of [d] 0.19 m from the center of the magnet, on the axis of the magnet. If you replaced this magnet with a magnet made of the same material but with a mass of 50 grams (magnet B), approximately what would be the magnetic field at a location [2d] 0.38 m from the center of the magnet, on the axis of the magnet? A. B. C. D. E. 5[B]/8 T [OK]=3.75 x 10-5 T 8[B]/5 T 5[B] T [B]/8 T 5[B]/2 T 2 Problem 5 A capacitor consists of two charged disks of radius R separated by a distance s, where R>>s. The magnitude of the charge on each disk is Q. If Q = [43] C, R = [4.0] m, s = 1.7 mm, s1 = 1.5 mm, and s2 = 0.7 mm, what is the value of V=VC‐VA? A. B. C. D. E. [Q][s1]/(0R2)Volts -[Q][s1]/ (0R2)Volts 0 Volts –[Q][s]/ (0R2)Volts [Q][s]/ (0R2)Volts [OK]=145V Problem 6 Point charges Q1 = [6 nC], Q2 = [-5 nC], Q3 = [8 nC] and Q4 = [-7 nC] are fixed in position in a square pattern that has sides of length L = 4 mm. How much work must an external agent do in order to bring a charge q = 5 nC from far away to the square’s center? 3 A. Wext Q1 Q2 Q4 Q3 1 q 2 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 J 4 0 L [OK]=3.2x10-5J 1 q 2 Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 J 4 0 L 1 q 2 1 Q Q Q Q C. Wext Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q1Q2 Q1Q4 Q2Q3 Q3Q4 1 3 2 4 4 0 L L 2 2 B. Wext D. Wext 1 q 2 1 Q1Q3 Q2Q4 Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q Q 1 2 3 4 1 2 1 4 2 3 3 4 4 0 L L 2 2 Problem 7 Two large conducting disks form a capacitor. The radius, R = 1 cm, of each disk is much larger than the separation between disks, s = .05 cm. Of the answers below, which is the best estimate of force exerted on the right disk by the left disk when the potential difference across the capacitor is [V]100 Volts? 4 [Formula below has R and s in cm] A. 1.39 10 11 R2 2 V N [OK]=5.56x10-5N 2 s B. 2.78 10 11 R2 2 V N s2 C. 2.78 1011 R2 VN s3 D. 2.78 10 11 E. 0 N R2 VN s2 5 Problem 8 Two identical concentric conducting loops are arranged as shown in the figure below. One loop has a steady current flowing through it (provided by the power supply shown.) Will the two loops briefly attract or repel each other when the power is turned off? A. B. C. D. They will attract each other. [OK] They will repel each other. They will neither attract nor repel each other. The answer depends on the direction current was flowing in loop 1. Problem 9 Consider the circuit shown below. If you were to unscrew bulb B from its socket (effectively removing it from the circuit), bulb A would 6 A. Get dimmer [OK] B. Get brighter C. Remain the same D. Go out 7 Problem 10 Answer: 2 Problem 11 An ion whose charge is q = +2e and whose mass is M enters a velocity selector, a region of space in which there is a magnetic field directed out of thepage and an electric field perpendicular to the magnetic field as shown in the figure. If B = [0.3] T, what electric field strength will allow only those ions traveling with speed 0.01 c (= 3 x 106 m/s) through the small slit. 8 A. B. C. D. E. B*3 x 106 N/C [OK]= 0.9 x 106 N/C B/(3 x 106) N/C 2*B*3 x 106 N/C 2*B/(3 x 106) N/C Not enough information Problem 12 You are presented with a length of wire L and told its resistance is R. If this wire is stretched until its length is 2L, its new resistance R’ would be [Hint: Assume the density of the wire remains constant.] A. B. C. D. E. 4R [OK] 2R R 8R R/2 Problem 13 A circular wire loop moving at constant velocity enters a long region of uniform magnetic field B that is perpendicular to the plane determined by the loop. Which one of the graphs best describes the emf in the loop as a function of time t? 9 A. B. C. D. E. A [OK] B C D E 10 Problem 14 A proton enters a magnetic field and follows trajectory 2. An alpha particle (twice the charge and 4 times the mass) enters the same magnetic field in the same way and with the same velocity as the proton. Which of the following is the correct trajectory for the alpha? A. B. C. D. E. 3 2 1 4 5 [OK] 11 Problem 15 The following are two-dimensional cross sections through 4 spherical shells and one cube. Rank in order, from largest to smallest, the electric fluxes a to b through surfaces a to e. A. B. C. D. E. Φb = Φe > Φa = Φc = Φd [OK] Φa > Φc > Φb > Φd > Φe Φe > Φd > Φb > Φc > Φa Φb > Φa > Φc > Φe > Φd Φd = Φe > Φc > Φa = Φb Problem 16 A positive charge undergoes a brief acceleration at time t = 0 in the –y direction. At the instant shown, the charge lies along the x-axis. Detectors are arranged in a circle of radius R in the x-y plane so that at time t = R/c the radiation reaches the detectors. At what angle as measured from the positive x-axis will the intensity of the radiated field (radiation) as measured by the detectors be ½ of its maximum value (for the same distance from the charge)? 12 A. 45, 135, 225, 315 degrees from the x-axis [OK] (note: intensity of radiation goes as E2) B. 0 and 180 degrees from the x-axis C. 90 and 270 degrees D. 60, 120, 240, 300 E. 30, 150, 210, 330 13 Problem 17 A wire carrying a current of circular cross section I has two segments which have equal diameters. If the conductivities for the two segments have the ratio σ1:σ2=2:1, what is the ratio E1:E2 of the electric field strengths in the two segments of the wire. A. B. C. D. E. E1/E2 = 1/2 E1/E2 = 1/4 E1/E2 = 1/1 E1/E2 = 2/1 E1/E2 = 4/1 [OK] Problem 18 A thick wire of radius R carries a current I1. The magnetic field inside the wire a distance r from the center of the wire where r < R is 0 I1r 2 R 2 IR B. B 0 1 2 2 r I C. B 0 1 2 R A. B [OK] 14 D. B 0 I1 2 r Problem 19 A long straight wire suspended in the air carries a conventional current of [I=8.2] amperes in the –x direction as shown in the figure below. The wire runs along the x-axis. At a particular instant, an electron at location <0, -0.003, 0> m has a velocity of <1.5 x 105, -1.8 x 105, 0> m/s. The magnetic force on the electron due to the current in the wire is A. 1.92I,1.6I,0 10 18 N B. 1.92I,1.6I,0 10 [OK] 18 N C. 1.92I,1.6I,0 10 18 N D. 1.92I,1.6I,0 10 18 N Problem 20 Which figure below correctly displays the polarization of an initially uncharged plastic sphere by an electric field that points to the left? A. B [OK] 15 B. C. D. E. F. A C D E F 16