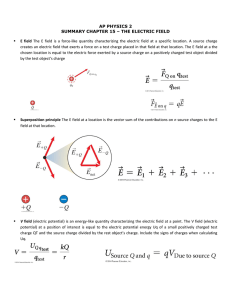
Electric Potential Energy
advertisement
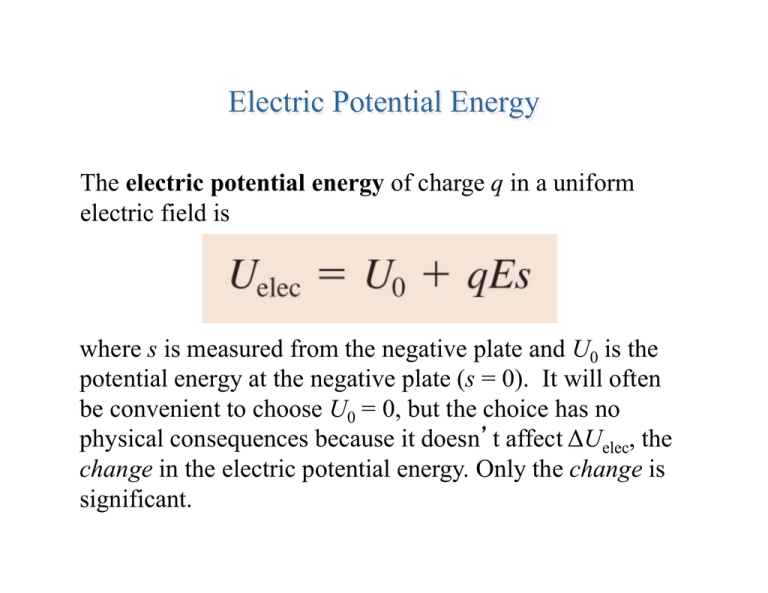
Electric Potential Energy The electric potential energy of charge q in a uniform electric field is where s is measured from the negative plate and U0 is the potential energy at the negative plate (s = 0). It will often be convenient to choose U0 = 0, but the choice has no physical consequences because it doesn t affect ΔUelec, the change in the electric potential energy. Only the change is significant. Analogy to Gravitational PE Gravitation PE depends on mass General Physics 2 Electric potential energy depends on charge Electric Potential 2 The Potential Energy of Point Charges Consider two point charges, q1 and q2, separated by a distance r. The electric potential energy is This is explicitly the energy of the system, not the energy of just q1 or q2. Note that the potential energy of two charged particles approaches zero as r → ∞. Which set has a positive potential energy? Which set has a negative potential energy? EXAMPLE 29.2 Approaching a charged sphere EXAMPLE 29.2 Approaching a charged sphere The Potential Energy of a Dipole The potential energy of an electric dipole p in a uniform electric field E is The potential energy is minimum at ø = 0° where the dipole is aligned with the electric field. Remember p = qs Electrical Potential Energy • For a charge in a uniform electric field • For point charges Think-Pair-Share • What is the potential energy of this system, taking U = 0 at a great distance? +4Q General Physics 2 Electric Potential 12 Think-Pair-Share • What is the potential energy of this system, taking U = 0 at a great distance? General Physics 2 Electric Potential 13 Workbook Problems on Electric Potential Energy • P. 29-1 #1 • P.29-3 #5, 6 • P29-4 #7, 8 General Physics 2 Electric Potential 14 The Electric Potential We define the electric potential V (or, for brevity, just the potential) as Charge q is used as a probe to determine the electric potential, but the value of V is independent of q. The electric potential, like the electric field, is a property of the source charges. The unit of electric potential is the joule per coulomb, which is called the volt V: The Electric Potential of a Point Charge Let q be the source charge, and let a second charge q', a distance r away, probe the electric potential of q. The potential energy of the two point charges is By definition, the electric potential of charge q is The potential extends through all of space, showing the influence of charge q, but it weakens with distance as 1/r. This expression for V assumes that we have chosen V = 0 to be at r = ∞. Equipotential Lines • connect points in space at same potential • equipotential surface is perpendicular to electric field lines General Physics 2 Electric Potential 18 Electric Field & Equipotential Lines • Draw field lines and equipotential lines for the following charge distributions - General Physics 2 Electric Potential 19 Electric Field & Equipotential Lines • Draw field lines and equipotential lines for the following charge distributions + General Physics 2 Electric Potential 20 EXAMPLE 29.8 Calculating the potential of a point charge QUESTIONS: EXAMPLE 29.8 Calculating the potential of a point charge Plug & Chug • What is the electric potential 15.0 cm from a 4.00 x 10-6 C point charge? General Physics 2 Electric Potential 23 The Electric Potential of a Charged Sphere In prac(ce, you are more likely to work with a charged sphere, of radius R and total charge Q, than with a point charge. Outside a uniformly charged sphere, the electric poten(al is iden(cal to that of a point charge Q at the center. That is, Or, in a more useful form, the poten(al outside a sphere that is charged to poten(al V0 is Plug & Chug • What is the electric potential 15.0 cm from a charged sphere with a charge of 4.00 x 10-6 C and a radius of 1.0 cm? • What is the electric potential 20.0 cm from a 1.0 cm diameter charged sphere that has been charged to 1000V? General Physics 2 Electric Potential 25 The Electric Potential of Many Charges The electric poten(al V at a point in space is the sum of the poten(als due to each charge: where ri is the distance from charge qi to the point in space where the poten(al is being calculated. In other words, the electric poten5al, like the electric field, obeys the principle of superposi5on. EXAMPLE 29.10 The potential of two charges QUESTION: EXAMPLE 29.10 The potential of two charges The Electric Potential Inside a Parallel-Plate Capacitor The electric potential inside a parallel-plate capacitor is where s is the distance from the negative electrode. The electric potential, like the electric field, exists at all points inside the capacitor. The electric potential is created by the source charges on the capacitor plates and exists whether or not charge q is inside the capacitor. Electric Potential Think of analogy with gravitational PE, where object with positive PE will fall if released. Here, p+ has high PE when near + plate and will fall toward negative plate when released Think of + charge when wondering if something is high or low potential + charges move from high to low potential Electric Potential low PE High PE - - Unlike mass, charge can be + or -. Thus, PE depends on the sign of the charge. For example, an e- will have high PE when near the - plate and will fall toward the + plate when released - charges move from low to high potential EXAMPLE 29.7 A proton in a capacitor QUESTIONS: EXAMPLE 29.7 A proton in a capacitor EXAMPLE 29.7 A proton in a capacitor EXAMPLE 29.7 A proton in a capacitor EXAMPLE 29.7 A proton in a capacitor EXAMPLE 29.7 A proton in a capacitor ! Electrostatic Potential & PE • When dealing with discrete point charges: ! kq1q2 F = 2 rˆ r ! kq E = 2 rˆ r kq1q2 U= r kq V= r ! U and V are scalars General Physics 2 F and E are vectors Electric Potential ! 38 Workbook • • • • • P29-6 #11, 13 P29-7 #15 P29-9 #17, 18 P29-10 #20 P29-11 #22 General Physics 2 Electric Potential 39