MVAR control, integration of wind generation to grid, plausible
advertisement

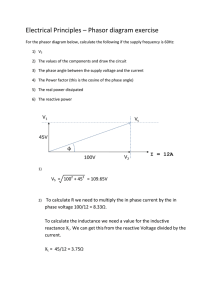
1 MVAR control, integration of wind generation to grid, plausible solutions for supporting quality power and reliable grid in free markets Diran Obadina Principal, Systems Development ERCOT July 29, 2015 Paper Number 15PESGM2585 2 Current Records – July 15, 2015 Peak Demand Record: 68,305 megawatts (MW) 68,305 MW, August 3, 2011 Weekend Record 65,159 MW, Sunday, August 28, 2011 Winter Peak Record: 57,265 MW 57,265 MW, February 10, 2011 June 2015 Demand - 61,732 MW, June 10 June 2014 Demand - 59,786 MW, June 30 Wind Generation Records (instantaneous) • 11,154 MW, February 19, 2015, 10:52 p.m. - Non-Coastal Wind Output = 9,872 MW - Coastal Wind Output = 1,282 MW - Supplying 34.2% of the load - Active Wind Capacity = 13,370 MW 40.58% Wind Penetration, March 29, 2015, 2:12 a.m. - Total Wind Output = 10,308 MW - Total Load = 25,400 MW 3 Wind Generation – June 30, 2015 25,000 MW ERCOT Wind Installations by Year (as of end of June 2015) Cumulative MW Installed IA Signed-Financial Security Posted 23,407 22,607 IA Signed-No Financial Security 3,590 4,390 20,000 MW 16,365 5,593 15,000 MW 5,593 2,941 12,470 11,065 10,407 10,000 MW 9,400 9,604 8,916 8,005 13,424 13,424 13,424 2015 2016 2017 12,470 4,785 5,000 MW 8,916 9,400 9,604 2010 2011 10,407 11,065 8,005 2,875 4,785 1,854 977 1,173 1,385 816 116 816 977 1,173 1,385 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 0,000 MW 2,875 1,854 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2012 2013 2014 The data presented here is based upon the latest registration data provided to ERCOT by the resource owners and can change wi thout notice. Any capacity changes will be reflected in current and subsequent years' totals. Scheduling delays will also be reflected in the planned projects as that information is received. This chart reflects planned units in the calendar year of submission rather than installations by peak of year shown. Financial security posted for funding interconnection facilities does not include CREZ security deposits, which are refunded to the Interconnecting Entity when an IA is signed. 4 Cumulative Installed and Planned Solar Capacity Megawatts 12,000 10,346 10,000 7,756 8,000 6,000 10,153 4,000 7,563 Cumulative MW Under Study Cumulative MW Installed 15 42 82 121 191 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 288 193 2015 95 2,000 193 193 2016 2017 0 5 COMPETITIVE RENEWABLE ENERGY ZONES 6 Challenges of Voltage control • Large wind power farms with little or no local loads served and/or large synchronous machines in the zone affecting system stability • Long, highly compensated 345KV transmission lines to load centers in the north and east; – Critical voltage at voltage collapse point is relatively high which could put the system at risk even when the voltages are within normal ranges • Multiple wind resource and transmission owners – Consideration of fairness in a competitive environment. 7 Wind Power vs 345 KV Voltage 8 Proposed Framework Load Forecast Wind Forecast Current Operating Plan Contingency List Reactive Resource Scheduling Outage Schedules Transmission Operators SCADA EMS Real time Reactive Dispatch 9 Reactive Resource Scheduler • Schedules switchable reactive devices over multiple hours into the future • Objective is to minimize number of switching needed over the scheduling horizon in order to maintain voltage • Maintain adequate reactive reserve in defined reactive areas • Executes in the day-ahead following RUC and then hourly to refine the day-ahead schedules 10 Forecasted Load -Curve Scheduling Horizon; Scheduling Interval; Load Curve … … Scheduling horizon (T) time 11 Reactive Resource Scheduling Objective 12 Reactive Resource Scheduling • • • • Scheduling Horizon: 12-24 hours Scheduling Interval: 30-60 mins Works with the RT Reactive Dispatch Maintains adequate reserve with the voltage control area 13 Reactive Resource Scheduler - Controls • • • • • Shunt Capacitors Shunt reactors Line switching Unit commitment Invokes Reactive Dispatch 14 Real Time Reactive Dispatch • Executes in the Real Time Sequence • Objective – Manage the voltage across the ERCOT grid – – – – Secure base case voltage ranges throughout system Maintain post contingency voltages Restore post-event secure voltage profile Minimum shift/minimum number of controls objective function 15 Real Time Reactive Dispatch - Controls • • • • Generator AVR Target Voltage Synchronous Condenser AVR Target Voltage SVC Target Voltage On-line Transformer Taps – Tap position – Target voltage • Invokes the Reactive Resource Scheduling (RRS) in case of infeasibility 16 Thank You!