S3 Electricity Hwks
advertisement

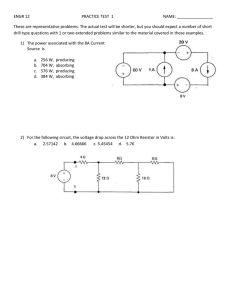
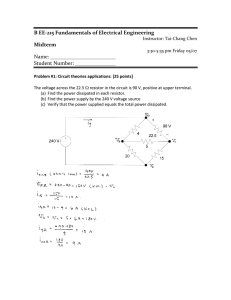
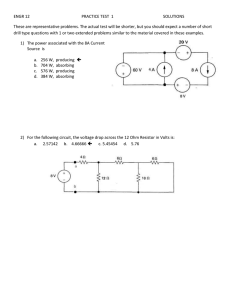
Name Tips for homework You will be given at least a week before homework is to be submitted which gives you a chance to ask in class if you stuck with any questions. Therefore always try the homework before the next class so you can ask. If you are unable to answer a question at first it is worth repeating it as a similar question may come up in the test or be needed for further learning. You can ask friends or other teachers for help but don’t copy someone else’s answers. Millburn Academy S3 Physics page 1 Electricity and Electronics Homeworks S3 Physics Electricity and Electronics Study Guide At the end of this unit you should be able to draw circuit diagrams using a variety of common components use a multimeter to measure voltage, current, and resistance investigate Ohm’s law for a single resistor. plot a graph of voltage and current for a resistor carry out calculations using the Ohm’s Law formula (V= I R) know the rules for switching, current and voltage in series and parallel circuits: Current is same at any point in a series circuit Current in parallel circuit adds up to the supply current Voltages across components in a series circuit adds up to the supply voltage Voltages across components in parallel are all equal to the supply voltage be able to predict unknown currents and voltages in series and parallel circuits be able to calculate electrical power using the formula P = IV know the diagram symbols and truth tables for basic logic gates and combinations to make up systems use magnet and electromagnets to induce voltages in coils know how we use alternators to generate electricity. You will have carried out the following Fourth level Experiences and Outcomes By contributing to investigations into the properties of a range of electronic components, I can select and use them as input and output devices in practical electronic circuits. SCN 4-09b Through investigation, I understand the relationship between current, voltage and resistance. I can apply this knowledge to solve practical problems. SCN 4-09a Using my knowledge of electronic components and switching devices, I can help to engineer an electronic system to provide a practical solution to a real-life situation. SCN 4-09c I can help to design and carry out investigations into the strength of magnets and electromagnets. From investigations, I can compare the properties, uses and commercial applications of electromagnets and supermagnets. SCN 4-08a (More applications in N4) By contributing to an investigation on different ways of meeting society’s energy needs, I can express an informed view on the risks and benefits of different energy sources, including those produced from plants. SCN 4-04a Millburn Academy S3 Physics page 2 Electricity and Electronics Homeworks S3 Electricity Homework 1 Due in / / - Symbols and circuits 1. Copy and complete the following table, filling in the blanks, you may need to research some symbols from the internet. Component Lamp Circuit Symbol Description Changes electrical energy to light energy Resistor Open: breaks a circuit Closed: completes a circuit Ammeter A A resistor whose resistance can be changed A protection device. It melts when the current gets too high Fuse Converts electrical energy into kinetic energy M Battery Converts electrical energy into heat energy Heater Draw neat circuit diagrams of the following using a ruler: 1. A battery connected in series to a bulb and a switch. (2) 2. A cell connected to two bulbs and a resistor in series. (2) 3. A battery connected in series to a variable resistor a bulb and an ammeter. (2) 4. A battery, a switch, two bulbs and a resistor with a voltmeter connected to measure the voltage across the resistor. (2) 5. (Bonus) Search for a circuit diagram of one the following: phone car computer or ipod, by using the search term ipod circuit diagram or similar. If you have access to a printer print out the circuit diagram (don’t try to copy it out!!) Millburn Academy S3 Physics page 3 Electricity and Electronics Homeworks S3 Electricity Homework 2 Due in / / - Resistance 1. Copy and complete the following passage filling in the blank spaces with words from the word bank. Some words may be used more than once. Word bank: current, amps, resistance, ammeter, ohms, voltmeter, volts A flow of electricity is called an electric _________________. We use an _____________________ to measure electric current and we measure current in _____________. Voltage is measured using a ______________ and has units of ______ _________________ is the opposition to current flow in a circuit. It is measured in __________________. 1. Copy out the equation for resistance ‘Ohm’s Law’ from your notes indicating the units to be used. 2. A 45 ohm resistor is connected to a power supply and 3 amps of current flow from the battery? Show all working to calculate the voltage of the power supply. 3. A 12 volt car battery is connected to a headlamp bulb of resistance 30 ohms, what current flows through the bulb? 4. An electrical engineer has lost the packet which an unmarked resistor came out of and she can’t tell what resistance it is. The engineer connects the resistor to a 16 volt power supply and she measures a current of 0.0025 amps flowing through the resistor. Show with full working how she could calculate the value of the resistance. 5. Research superconductors - metals with no resistance. a What materials can act as superconductors? b Why is it so difficult to achieve superconduction? c Give the full website addresses of your sources Millburn Academy S3 Physics page 4 Electricity and Electronics Homeworks Due in S3 Electricity Homework 3 / / Current, energy and power in circuits 1. This circuit was set up C B + 24 volts DC - 2.7 Amps A a. What kind of circuit is this? b. Describe the flow of electrons from the negative terminal of the supply as it goes round the circuit c. If the switch at A opened, would you expect the lamp to still be on? d. What current would you expect at points A, B and C? e. If the variable resistor was decreased what would you expect to see at the lamp? 2. This circuit was set up C 2.4 Amps 0.8 Amps B + 2.4 volts DC A 3.6 Amps a. What kind of circuit is this? b. Describe the flow of electrons from the negative terminal of the supply as it goes round the circuit. c. What current would you expect at points A, B and C? Millburn Academy S3 Physics page 5 Electricity and Electronics Homeworks Homework 4 Power in Circuits Due in / / 1. Complete the following passage filling in the blank spaces with words from the word bank. Word bank: converted current energy number Joules Power An electrical _____________transfers energy round a circuit. Energy has units of ___________. The rate at which this energy is __________is power. ________has units of Watts. The higher the __________of watts the more quickly the _________is converted by the circuit. 2. Copy out the two formulae for energy and power from your notes, indicating the correct units for each quantity. 3. A lamp has a power rating of 10 watts and is left switched on for 5 minutes. Calculate the energy converted by the lamp in this time. 4. List the following appliances in order of power rating with most powerful first: iPod, TV, torch, radio, washing machine, kettle, toaster, hair drier. You may need to do some research by looking at actual appliances or using the internet. 5. An electric shower is rated at 9 kW. A person takes a shower lasting 13 minutes. (a) Calculate how many joules of energy are used. (b) Another person uses an 8 kW shower and stays under the shower for only 11 minutes. Calculate the difference in energy used by the second person compared to the first. 6. Research the power consumption of an appliance labelled as “low power” or “energy efficient” Find out the actual power rating of the appliance and the savings in costs or energy anticipated. Millburn Academy S3 Physics page 6 Electricity and Electronics Homeworks S3 Electricity Homework 5 Input and output devices Due in / / 1. Draw circuit diagram symbols for the following components: Thermistor Light dependent resistor Solar Cell Loudspeaker Microphone Relay Light emitting diode (LED) 2. What are the energy changes for the following components: Loudspeaker Motor Light emitting diode (LED) Microphone Solar Cell? 3. For an electronic device of your choice use the internet to find a diagram of what is inside the device. Use the search terms ‘teardown’ and the name of the device you want to find out about. Copy the diagram or print it out and and label it to include At least two input devices, at least two output devices Some of the circuits which carry out the processes. Include the web address for the main website you used to get the information. Millburn Academy S3 Physics page 7 Electricity and Electronics Homeworks Revision questions 1. Draw a circuit diagram of a battery, switch, resistor ammeter and LED in series. Add a voltmeter connected in parallel to measure the voltage of the LED. 2. Write down the four rules for a current in a circuit b voltage in a series circuit c current in a parallel circuit d voltage in a parallel circuit 3. A 960 ohm resistor is connected to a power supply and 0.048 amps of current flow from the power supply. Show all working to calculate the voltage of the power supply. 4. A 12 volt car battery is connected to a headlamp bulb of resistance 30 ohms, what current flows through the bulb? 5. An engineer connects a resistor to a 16 volt power supply and she measures a current of 0.04 amps flowing through the resistor. Calculate the value of the resistance. 6. A lamp has a power rating of 200 watts and is left switched on for 10 minutes. Calculate the energy converted by the lamp in this time. 7. Draw logic diagrams and truth tables for the following logic gates: AND OR NOT Millburn Academy S3 Physics page 8 Electricity and Electronics Homeworks