Intro to Simulink
advertisement

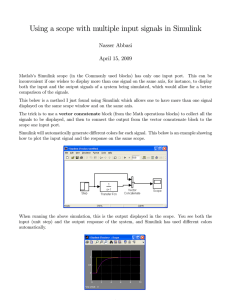
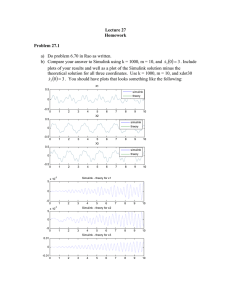
Introduction to Simulink Prof. Dr. Y. Samim Ünlüsoy Prof. Dr. Y. Samim ÜNLÜSOY Mech. Eng. Dept., Middle East Technical ME 513 Vehicle Dynamics 1 University, Ankara To start Simulink, one has to first double click on the Matlab icon and wait for the Matlab window to open. SIMULINK Then, click on the “Simulink” icon Prof. Dr. Y. Samim Ünlüsoy Introduction to Simulink 2 “Simulink Library Browser” will open. Prof. Dr. Y. Samim Ünlüsoy Introduction to Simulink 3 Click on the “File” menu item. Select “New” and then click on “Model” Prof. Dr. Y. Samim Ünlüsoy Introduction to Simulink 4 A clean window is going to open. New Simulink model is to be built on this window. Prof. Dr. Y. Samim Ünlüsoy Introduction to Simulink 5 Now, let us try to understand the logic behind Simulink, using a familiar system. x Consider a one degree of freedom mass-spring-damper system. m c k z Prof. Dr. Y. Samim Ünlüsoy + cx + kx = cz + kz mx Introduction to Simulink 6 x Reorganize the equation of motion such that the highest derivative term is expressed in terms of the rest : m c k z Prof. Dr. Y. Samim Ünlüsoy x=− c k c k x − x + z + z m m m m Introduction to Simulink 7 x=− c k c k x − x + z + z m m m m x m c SIMULINK Now start with the acceleration and integrate to get velocity. x k 1 s z Simulink/ Continuous/ integrator Prof. Dr. Y. Samim Ünlüsoy x Then integrate velocity to get displacement. x 1 s x Introduction to Simulink 1 s x 8 Click on the “integrator” icon inside “continuous” selection of the “Simulink Library Browser” and drag it into the model window and leave it there. Then repeat it for the second integrator. Prof. Dr. Y. Samim Ünlüsoy Introduction to Simulink 9 Bring the cursor on the arrowhead of the first “integrator” icon and drag it to the arrowtail on the second “integrator” to create the signal line for velocity. Prof. Dr. Y. Samim Ünlüsoy Introduction to Simulink 10 x=− c k c k x − x + z + z m m m m SIMULINK x It is possible to generate the first two terms on the right hand side. m c k x z c x m 1 s c m Simulink/ Math Operations/ Gain Prof. Dr. Y. Samim Ünlüsoy Introduction to Simulink x x 1 s k x m k m 11 x=− c k c k x − x + z + z m m m m SIMULINK It is now time to generate the last two terms on the right hand side. Simulink/ Sources/ Sine wave z x k m Sine wave z du/dt Simulink/ Continuous/ differentiator Prof. Dr. Y. Samim Ünlüsoy k z m x 1 s c m c m x 1 s k m c z m Introduction to Simulink 12 x=− c k c k x − x + z + z m m m m SIMULINK Finally sum all the terms and form the acceleration signal. x Simulink/ Math Operations/ sum z Sine wave + +- z du/dt Prof. Dr. Y. Samim Ünlüsoy 1 s - k m x 1 s x c m k m c m Introduction to Simulink 13 x=− c k c k x − x + z + z m m m m SIMULINK Simulink/ Sources/ constant A It is possible to provide different inputs using a switch. Simulink/ Signal Routing/ Manual Switch x 1 s Constant z - k m Manual Switch + +- z du/dt x 1 s x c m k m c m Sine wave Prof. Dr. Y. Samim Ünlüsoy Introduction to Simulink 14 The resulting Simulink model looks like this ! Prof. Dr. Y. Samim Ünlüsoy Introduction to Simulink 15 You can enter parameter values by clicking on each element. x A 1 s Constant z - k m Manual Switch + +- z du/dt x 1 s x c m k m c m Sine wave Prof. Dr. Y. Samim Ünlüsoy Introduction to Simulink 16 A better choice is to write the symbol instead of the value. The values can be written in an m-script file. When the m-script file is run, data values will be saved in the workspace. x A 1 s Constant z - k m Manual Switch + +- z du/dt x 1 s x c m k m c m Sine wave Prof. Dr. Y. Samim Ünlüsoy Introduction to Simulink 17 % Data file for sdof.mdl m=310; % [kg] C=980; % [N/m/s] K=15000; % [N/m] A=0.005; % [m] f=2; % [Hz] This is the m-script file to load data to workspace. x A 1 s Constant z - k m Manual Switch + +- z du/dt x 1 s x c m k m c m Sine wave Prof. Dr. Y. Samim Ünlüsoy Introduction to Simulink 18 Now, you would like to observe the variation of some variable, say x, with time. So add an oscilloscope ! Simulink/ Sinks/ scope Scope x A 1 s Constant z - k m Manual Switch + +- z du/dt x 1 s x c m k m c m Sine wave Prof. Dr. Y. Samim Ünlüsoy Introduction to Simulink 19 So, the final form of the Simulink diagram is : Prof. Dr. Y. Samim Ünlüsoy Introduction to Simulink 20 First run the m-file for data by writing its name on the Matlab “Command Window” and pressing enter. Check that the correct data has been stored in workspace. Prof. Dr. Y. Samim Ünlüsoy Introduction to Simulink 21 Now to run Simulink for 10 seconds, click on the arrow head. Prof. Dr. Y. Samim Ünlüsoy Introduction to Simulink 22 To see the variation of x with time, double click on the scope. Prof. Dr. Y. Samim Ünlüsoy Introduction to Simulink 23 The scope window will appear with the plot of x versus time. Prof. Dr. Y. Samim Ünlüsoy Introduction to Simulink 24 Click on the binoculars icon to fit graph to frame Prof. Dr. Y. Samim Ünlüsoy Introduction to Simulink 25