POWER ELECTRONICS
advertisement
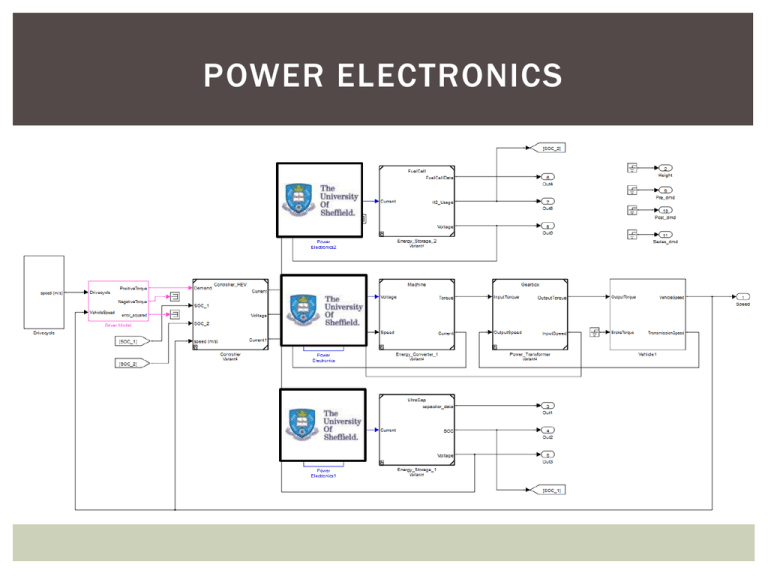
POWER ELECTRONICS Reliability Assessment of Power Converters with Partial Redundancy and Variable Power Distribution Challenges (1) Reliability indicators · Mean time to failure (MTTF) is not enough fo r r eliability ass essment when s ystem s power distribution varies. Three-step assessment method Step 1:Compare failure rates of all components at all states and select necessary ones · List components in the system · List the working conditions of components · Calculate and compare failure rates l (t) of components at all states Footstone (2) Reliability models 2.1 Component-level reliability model · Should we consider all the failure rates or not? 2.2 System-level reliability model · Part-count and combinatorial models are simple but cannot evaluate the r eliability of f aulttolerant system. · Markov model can evaluate the fault-tolerant system s reliability but complex. Step 2:Build Hybrid reliability model · Distinguish the non-redundant subsystems and redundant subsystems · Build part-count model for non-redundant subsystems · Build Markov model for redundant subsystms Core Step 3: Calculate MTTF and MTTFr · Calculate MTTF Proposed · Calculate MTTFr Results metric Application of the Proposed Reliability Assessment Method V'R Cap1 TRA 0.02 SC SB SA VA VB TRB M ~ VC TRC MTTF(10-6 / hour) S'R Case I Case II 0.01 S'Rr SBb SAa V'r Cap2 SCc Ldc3 Va TRa Ldc2 Vb TRb Case III 0 50 40 30 20 Ldc1 o T A( Vc TRc C) Sa Sb Sc Vdc1 Vdc3 Vdc2 (Bat) (FC) (U-cap) 4 2 3 1 0 Po(kW) 100 98 94 MTTFr (%) S'r 90 86 Case I Case II 82 Case III 78 50 TA ( 40 o 30 C) 20 4 3 2 Po(kW) 1 0 Most Vulnerable Components and Major Causes of Reliability Issues Power semiconductor devices High temperature Oscillation — High voltage or current stress Electrolytic capacitors Used to reduce voltage ripples Capacitance drops with time Electrolyte can dry up Electrolyte leaks when temperature increases Ripple currents cause temperature to increase How to Improve the Reliability of Power Converters? Propose compact power converters to reduce the power semiconductor devices Propose impedance-based stabilisation methods to eliminate the system oscillation and avoid the high voltage or current stress Propose active ripple eliminator to remove Electrolytic capacitors Compact Power Electronics Interface Six possible power flow modes Bidirectional with reduced power switch Higher reliability but lower cost Flexible control of power/current/voltage Possible applications in B-UC HEV, FC-B-UC HEV and hybrid energy storage systems Compact Power Electronics Interface Inverter + S4 S6 S8 IAC M S3 L2 VDC I1 + V2 Battery 1 + V1 L1 S5 VAC S7 S2 I2 S 1 DC/DC Battery 2 The inverter and the DC-DC converter are integrated The DC-DC converter can interface two sources with only two additional power switches. More compact with higher power density, cost effective and less degradation for components Stabilisation of Cascaded DC/DC Converters via Adaptive Series-Virtual-Impedance Control of the Load Converter + Vin _ vbus iin + _ Source Converter io ZSVI + Load v¢bus _ Converter Z¢iL ZoS ZiL Logic of S1 & S2 Out D ibus Input > 0 0 Out 1 Tv ( s)] Po + - 2 bus Gid ( s )GPWM ( s )V 4 f RC vbus HPF A |abs| + B PI E 4 Kr f RC 1/S 1 2 3 - vˆbus 1 Tv ( s)] Po vir GASVI(s) 2 Gid ( s )GPWM ( s )Vbus + 2 Memory 1 2 3 Relay S1 fCS S2 C vˆor + _ Gv(s) 1 ZinOL(s) iˆo GiiOL(s) ZASVI(s) GvgOL(s) vˆir + + vˆe ZoOL(s) GPWM(s) + + + iˆbus Gid(s) Memory 0 0 Basic idea Realization Input £ 0 1 1/S Δvbus |Δvbus| _ ZASVI(s) Logic of Relay Input2 < 0.5 Input2 ³ 0.5 Input3 Input1 + Vo _ d̂ Hs(s) Gvd(s) _ + + vˆo Experiment Verification of the ASVI Control Strategy Lf vin1 iL QL Cf LC input filter + vin - Lf Cf Case I 6 mH 150 mF Case II 6 mH 60 mF Lf1(400mH) iL1 DL PWM module Cf1(150mF) + vo - Io RLd (5.76) vbus, vo and iin ADC module Digital control system DC/DC converter Case I Start ASVI Case II iL: [5 A/div] 20.08 ms Start ASVI iL: [5 A/div] 8.79 ms vbus: [20 V/div] vbus: [20 V/div] iL1: [5 A/div] iL1: [5 A/div] vo: [5 V/div] vo: [5 V/div] Active Ripple Eliminators Adding a ripple eliminator to the current ripples so that ripples on the DC bus are small without using large capacitors. compensate the voltage maintained electrolytic WITH THE S T R AT E G Y Outcomes Journal papers: 1.X. Zh ang , Q.-C. Zho ng an d W.-L. Ming , Stab ilization of Cascad ed DC/DC Converters via Ad ap tiv e Series -Virtu al -Imp ed an ce Con tro l of th e Lo ad Conv erter , IEEE Trans . o n Pow er Electro nics , 2016. 2.X. Zh ang , Q.-C. Zh ong and W.-L. Ming , Stab ilization of a Cascad ed DC Conv erter Syste m via Adding a Virtual Ad ap tiv e Par allel I mp ed an ce to the Input o f the Load Converter, IEEE Trans. on Pow er Electronics , 2015. 3.Xin . Zh ang , Xin bo Ru an , Qin g -Ch ang Zhong, “Virtu al -I mp ed an ce -Based Co n tro l Strateg y of Regu lating th e In pu t I mp ed an ce of Lo ad Converter fo r Imp rov ing th e Stability of Cascaded Systems ,” IEEE Trans. Industria l Electronics , 2015. 4.Wen -Long Min g, Qin g -Ch ang Zhong , and Xin . Zh ang , “A sing le -ph ase f ou r-switch rectif ier with signif icantly r edu ced cap acitan ce,” IEEE Trans . Pow er Electronics , 2015. 5.Xin Cao , Qing -Chang Zhong , Wen -Long Min g, “Ripp le Elimin ato r to S mo oth DC-Bus Voltag e and Redu ce th e Total Cap acitan ce Requ ired ”, IEEE Trans . Industria l Electronics , 2015. 6.X. Zh ang , Q.-C. Zhong and W.-L. Min g, A Virtu al RLC Da mp er to Stabilize DC/DC Converters Having an LC I nput Filter while I mp rov in g th e Filter Perfo r man ce , Submit ted , 2016. Outcomes Conference papers: 1.Xin . Zh an g, Qing -Ch ang Zhon g, Wen -Lon g Ming , “ Fast Scale Instab ility Proble m and Phase-Sh if ted -Car rier Solution of Buck Derived Cascaded System ,” IEEE ECCE 2015. 2.Xin . Zh ang , Qing -Ch ang Zho ng, Wen -Long Min g, Xinbo Ruan , “Stab ilization of a Cascad ed DC Syste m v ia Add ing a Virtual I mp ed an ce in Series with th e Lo ad Converter,” IEEE PEDG 2015. 3.Xin . Zh ang , Qing -Ch ang Zho ng, Wen -Long Min g, Xinbo Ruan , “Stab ilization of a Cascad ed DC Syste m v ia Addin g a Virtu al I mp ed an ce in Parallel with th e Lo ad Converter,” IEEE PEDG 2015. 4.Xin . Zh ang , Qing -Ch ang Zhon g, Wen -Long Min g, “ I mp ed ance -Based Lo cal Stab ility Criterion for Standalon e PV-battery Hybrid System,” IEEE PEDG 2015. 5.Jun Cai, Qing -Chang Zhong , Dav id Sto ne, “ A n ew po wer converter f o r h y brid en erg y storage systems,” IEEE IECON 2014. 6.Jun Cai, Qing -Chang Zhong , “An Asy mme trical Ga mma Z -source Hybrid Power Converter with Space Vector Pulse-wid th Modulation ,” IEEE ECCE 2014. 7.Jun Cai, Qing - Chang Zhong , “ A co mp act b id irectio nal DC-DC co nv erter with two sources,” IEEE PEDG 2014. 8.Jun Cai, Qing -Ch ang Zh ong , Dav id Ston e, “A ΓZ-sou rce conv erter b ased h yb rid power converter for battery FCHEVs,” UKACC 2014. Outcomes Conference papers: 9.Xin C ao , Qin g-C h ang Zho n g, Wen -Long Min g, “An alysis and Con tro l of R ip p le Eliminato rs in DC Systems”, IEEE Green Tech 2014. 10.Q.-C. Zhon g, W.-L. Ming , an d M. Krstic, “ Imp rov ing th e p ower qu ality o f tractio n power syste ms with a sing le-f eed ing wire,” in Pro c. IEEE Green Techno log ies Conference , 2013. 11.Q.-C. Zho ng , W.-L. Min g, X. C ao , and M. Krstic, “R edu ction o f DC-b us vo ltag e rip p les and capacito rs fo r single-ph ase PW M-con tro lled rectif iers,” in Pro c. IEEE IECON 2012. 12.Xin . Zh ang , Qing -Ch ang Zho ng, Wen -Long Ming , “A Virtu al R LC Da mp er to Stab ilize a DC /DC Conv erter Hav ing an LC Inpu t Filter wh ile I mp rov ing the Filter Performan ce ,” Submitted 2016. 13.Xin. Zhang , Qin g -Ch ang Zhong, Wen -Lo ng Ming , “ So urce-sid e Series -v irtu al i mp ed an ce Co ntro l Strateg y to Stab ilize th e C ascad ed Syste m with I mp rov ed Performan ce ,” Submitted 2016. 14.Xin . Zh ang , Qin g -Ch ang Zhong, Wen -Lo ng Ming , “Stab ilization o f C ascad ed DC/DC Con ver ters v ia Sh ap in g th e Lo ad Inp ut I mp ed an ce b y Ad ap tiv e Series -Virtual Imp ed an ce Control,” Submitted 2016. 15.Xin. Zh an g, Qing -Ch ang Zhon g, Wen -Lon g Min g, “ Reliab ility Assess men t o f Po wer Converters with Partial R ed u ndan cy and Variab le Power Distribu tio n,” Sub mitted 2 015 .